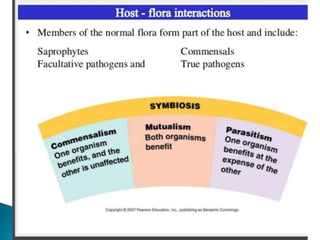
The document discusses the microbiome and microorganisms found at different body sites in humans. It notes that bacteria in the microbiome outnumber human cells 10 to 1 and play an important role in health. Common microbes found on the skin include Staphylococcus epidermidis and S. aureus in the nose. The microbiota of the mouth includes Streptococcus, Corynebacterium, and Neisseria species. The vaginal microbiota typically features Lactobacillus species which inhibit pathogens. Microbes in the gut include Lactobacillus, Bacteroides, Clostridium, and Enterococcus.