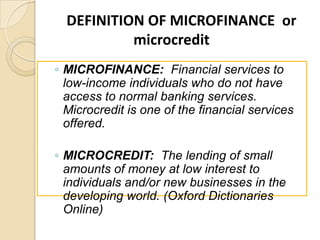
Microfinance began in the 1970s when Muhammad Yunus provided small loans to poor villagers in Bangladesh that allowed them to start businesses. He founded the Grameen Bank in 1983 to provide financial services to the poor who lacked access to traditional banking. Microfinance provides loans, savings, insurance and other services to low-income individuals and groups to help them become self-sufficient entrepreneurs. It aims to give the poor opportunities to earn sustainable incomes and improve their standards of living through small business ownership and access to capital. Studies show microfinance can encourage economic development by stimulating entrepreneurship and empowering the poor.