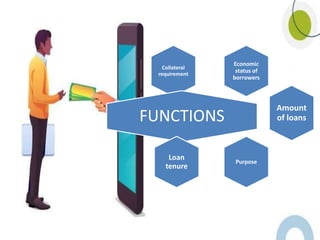
Microfinance started gaining importance in Pakistan in the late 1990s. In 2000, the government launched the Microfinance Sector Development Program to promote microfinance in the formal sector. The goal was to broaden access to financial services for the poor. The Microfinance Institutions Ordinance 2001 established a separate regulatory framework for microfinance. It allowed for three types of microfinance institutions based on their scope of operations and minimum capital requirements.