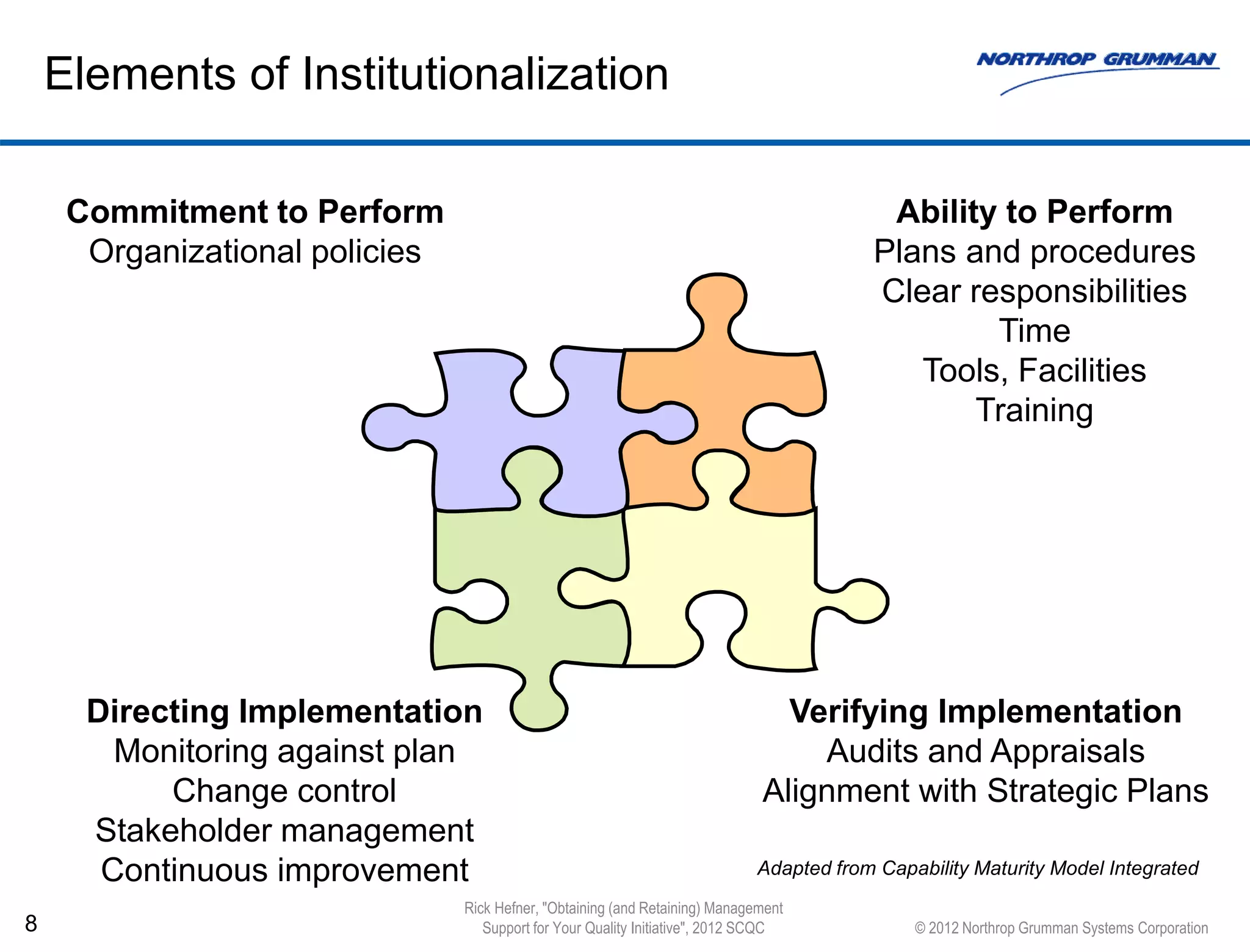
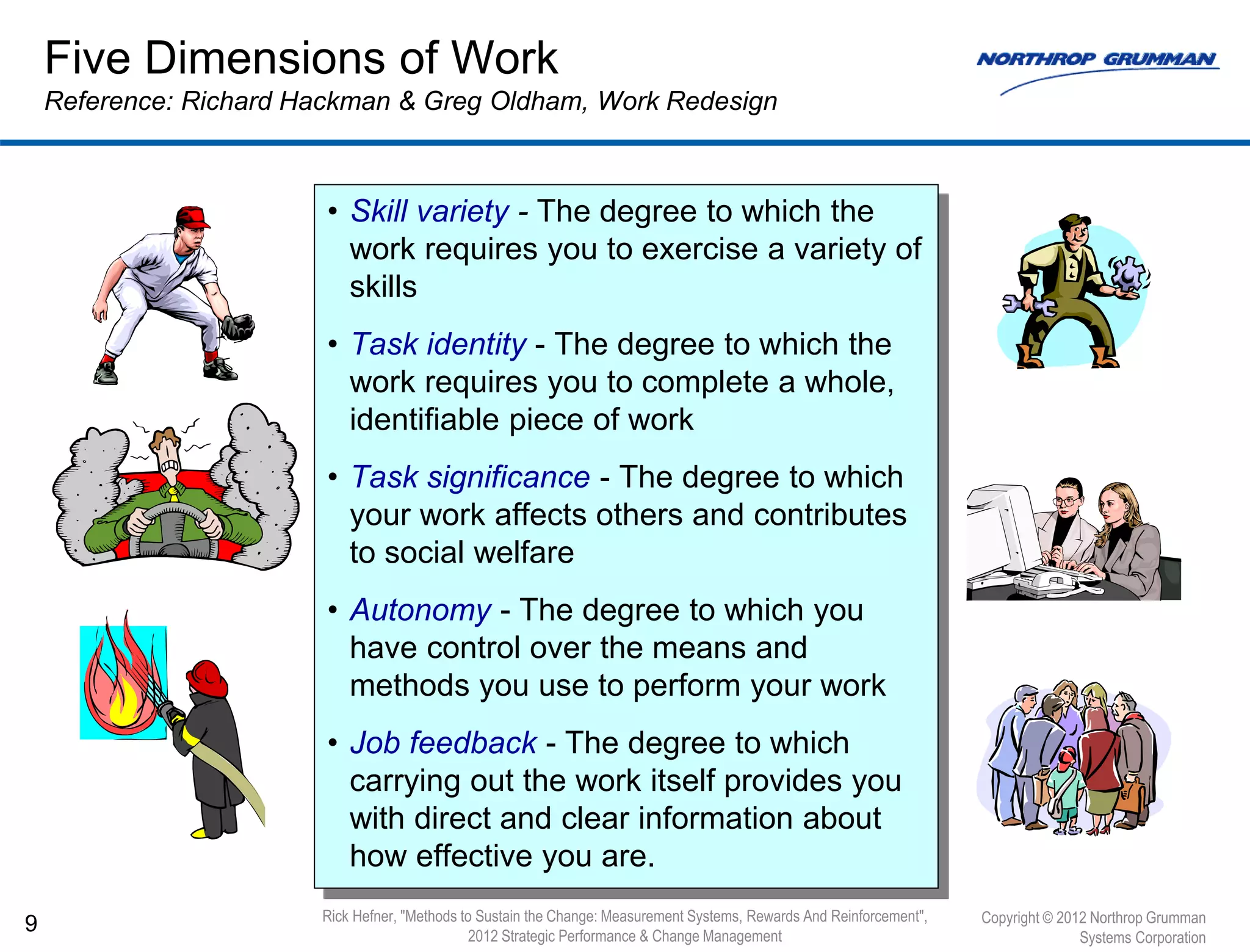
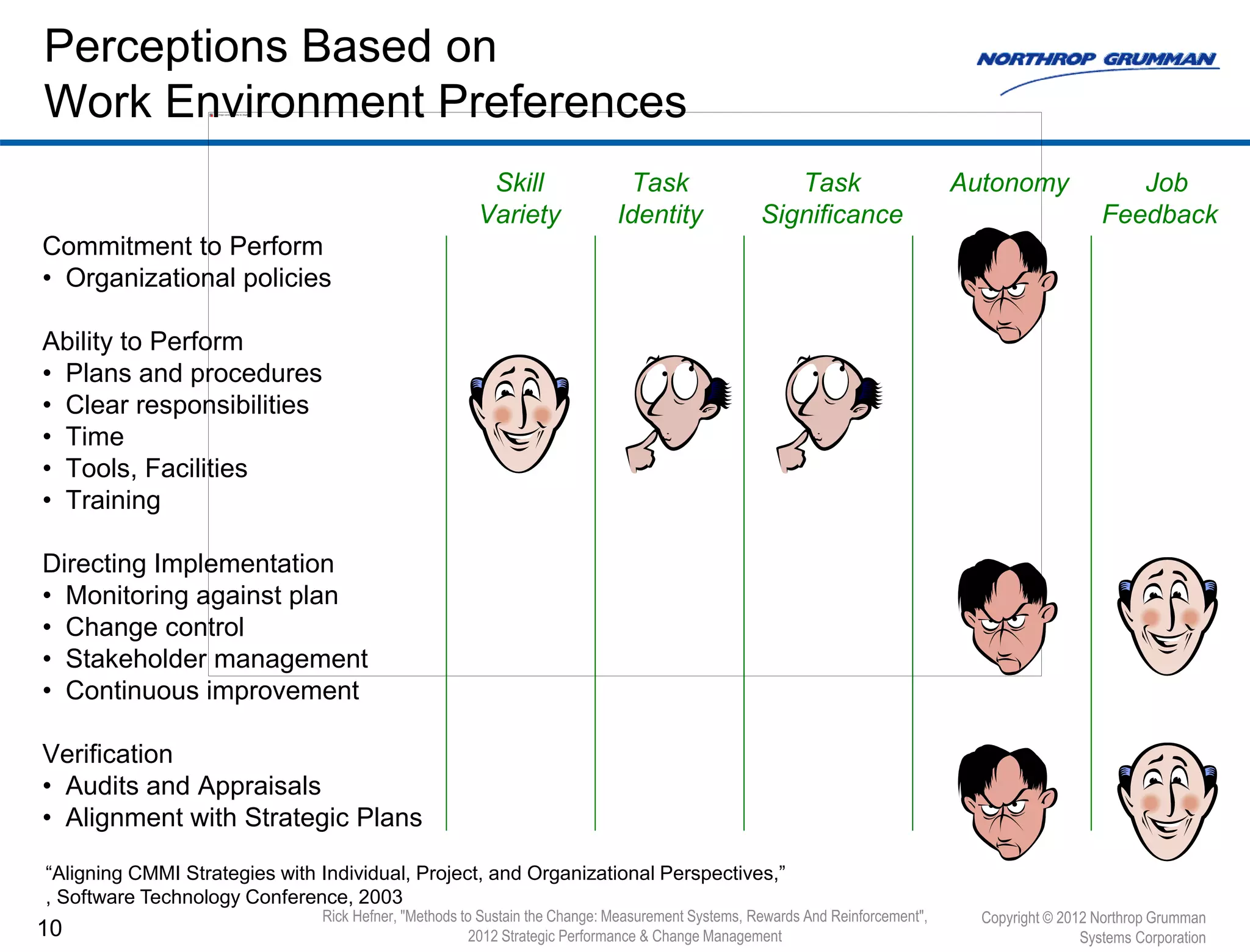
The document discusses methods to sustain change management efforts within organizations, emphasizing the importance of institutionalization, measurement systems, and reinforcement to prevent regression into old habits. It identifies key elements such as communication, accountability, and management support necessary to maintain new behaviors and achieve long-term goals. Additionally, it highlights the need for continuous improvement and the effectiveness of audits and appraisals in monitoring cultural changes.