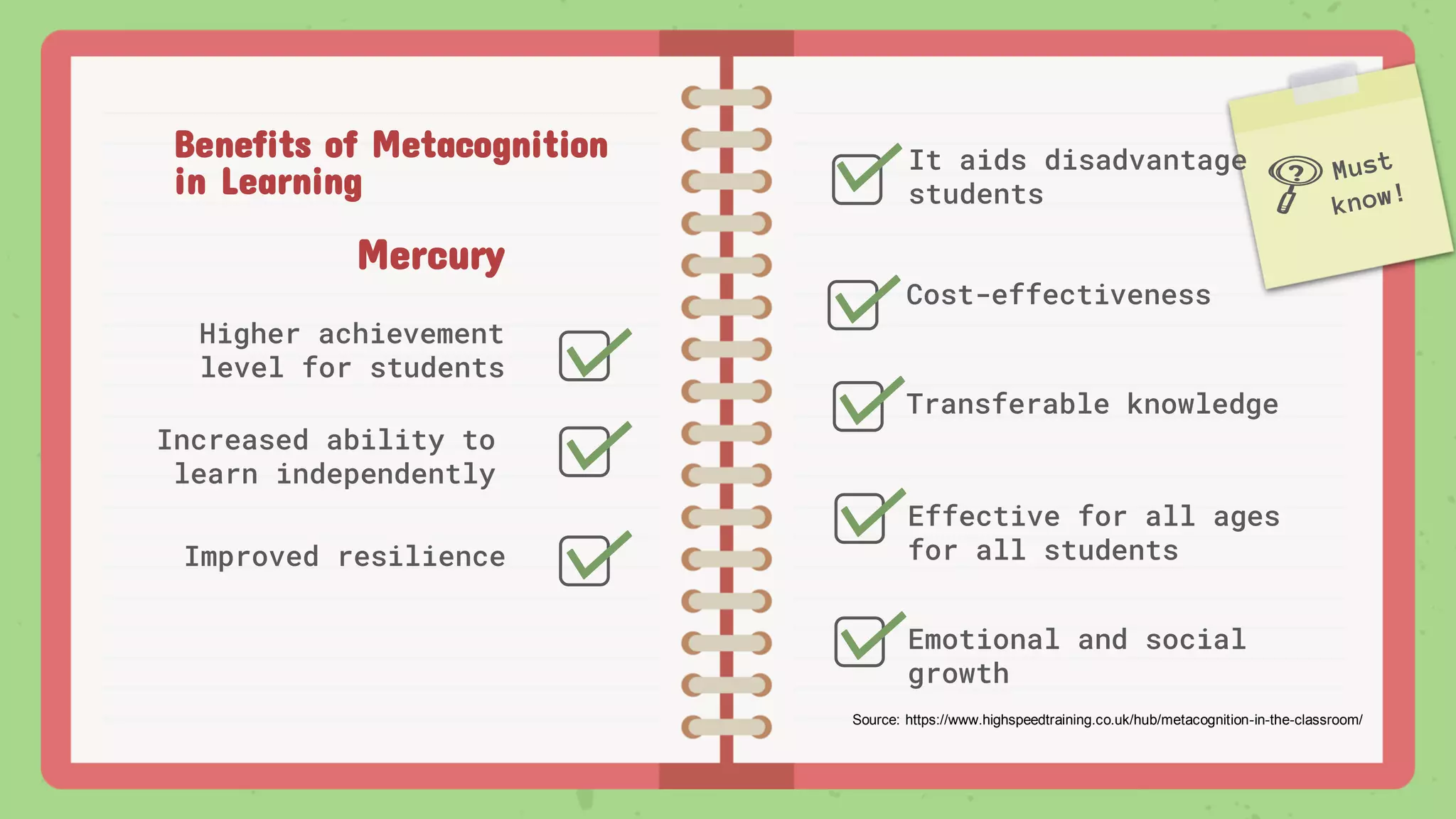
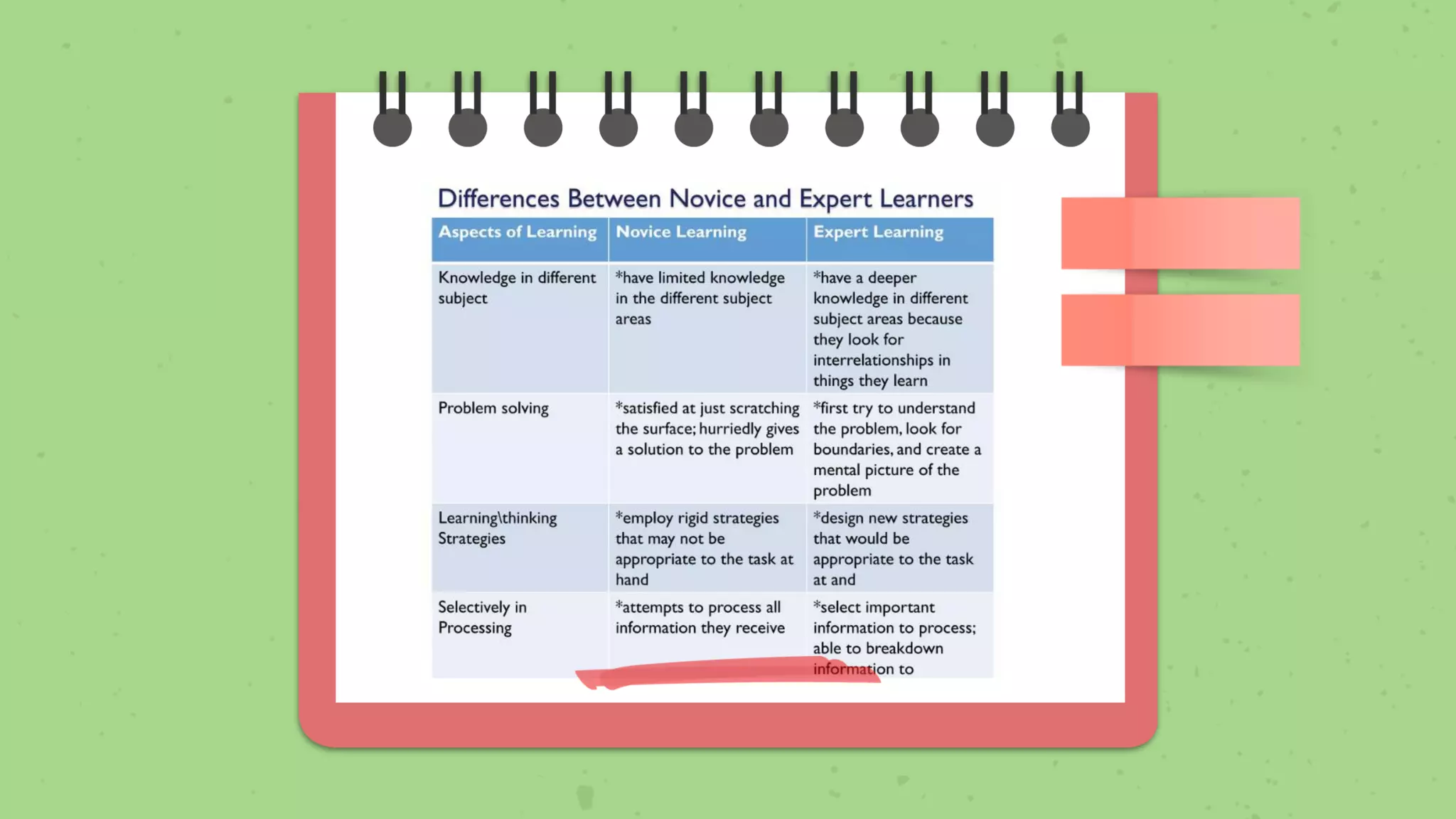
The document discusses left-brained and right-brained dominance and provides descriptions of their characteristics. It then introduces the concept of metacognition as thinking about one's own thinking and lists strategies to facilitate learning, such as making predictions, developing questions, and relating ideas to prior knowledge. Finally, it outlines benefits of metacognition such as higher achievement, independence, and transferable knowledge.