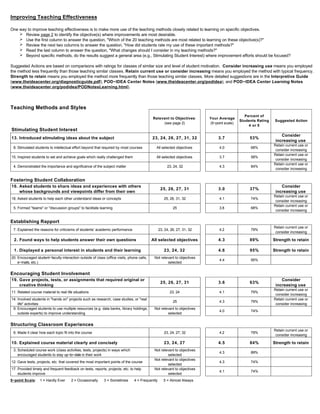
Professor Jusino teaches General Chemistry Lab II. Students provide positive feedback about Professor Jusino. They say she is always willing to help students outside of class, is very nice and good at explaining things. One student comments that the lab reports were challenging but they enjoyed the class. The diagnostic form provides statistics about student ratings of the course and professor. It shows that students reported substantial or exceptional progress on learning objectives and rated the professor and course as excellent. Areas for potential improvement include developing creative capacities and gaining a broader understanding and appreciation of intellectual/cultural activity.