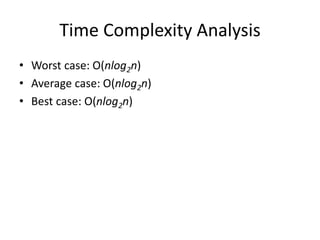
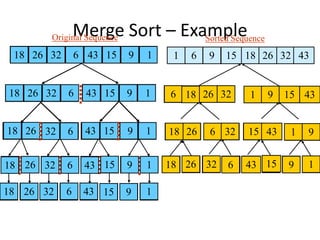
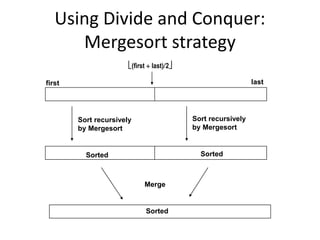
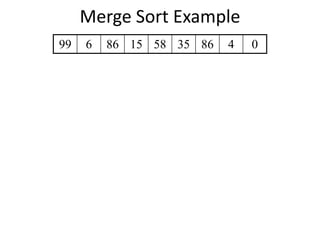
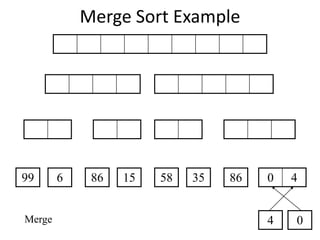
The document explains the merge sort algorithm, which is a divide and conquer sorting technique that recursively splits an unsorted list into two halves, sorts each half, and then merges them back together. It includes examples and a C++ program demonstrating how the algorithm works and its performance analysis with a time complexity of O(n log n) for worst, average, and best cases.












![Program
#include<iostream.h>
#include<conio.h>
class MS
{
private:
int A[10];
public:
int n;
int low, high;
void get_data();
void Mergesort(int low, int high);
void Combine(int low, int mid, int high);
void Display();
};
void MS::get_data()
{
cout<<"n Enter the length of the list";
cin>>n;
cout<<"n Enter the list elements: n";
for(int i = 0; i<n; i++)
{
cin>>A[i];
}
}
void MS::Mergesort(int low, int high)
{
int mid;
if(low<high)
{
mid = (low+high)/2; //split the list at mid
Mergesort(low, mid); //first sublist
Mergesort(mid+1, high); //second sublist
Combine(low, mid, high); //merging two sublists
}
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/15748164-240425134957-fe8c3a57/85/merge-sort-help-in-language-C-with-algorithms-18-320.jpg)
![Program
void MS::Combine(int low, int mid, int high)
{
int i,j,k;
int temp[10];
i = low;
j = mid+1;
k = low;
while(i <= mid && j <= high)
{
if(A[i] <= A[j])
{
temp[k] = A[i];
i++;
k++;
}
else
{
temp[k] = A[j];
j++;
k++;
}
}
while(i<=mid)
{
temp[k] = A[i];
i++;
k++;
}
while(j<=high)
{
temp[k] = A[j];
j++;
k++;
}
for(k = low; k <= high; k++)
{
A[k] = temp[k];
}
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/15748164-240425134957-fe8c3a57/85/merge-sort-help-in-language-C-with-algorithms-19-320.jpg)
![Program
void MS::Display()
{
cout<<"n The sorted array is:n";
for(int i = 0; i<n; i++)
{
cout<<" "<<A[i];
}
}
int main()
{
MS obj;
obj.get_data();
obj.low=0;
obj.high=(obj.n)-1;
obj.Mergesort(obj.low, obj.high);
obj.Display();
getch();
return 0;
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/15748164-240425134957-fe8c3a57/85/merge-sort-help-in-language-C-with-algorithms-20-320.jpg)