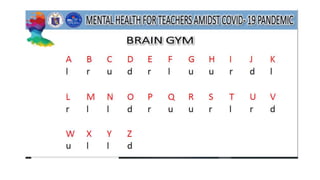
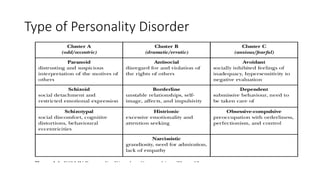
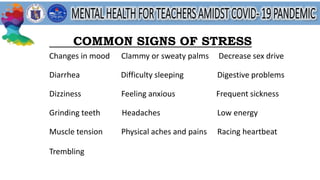
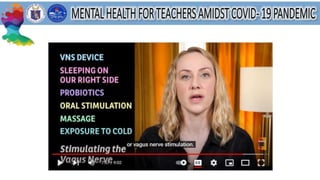
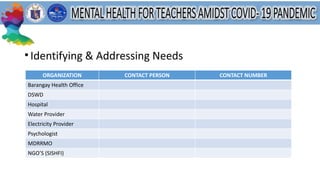
This document discusses mental health and provides resources for support. It defines several mental health conditions like anxiety, depression, bipolar disorder, and personality disorders. It also shares statistics on mental health in the Philippines and guidelines from DepEd on providing mental health and psychosocial support. Additionally, it offers tips for managing stress, validating feelings, and identifying support systems. Overall, the document aims to raise awareness of mental health issues and provide guidance for addressing related challenges.