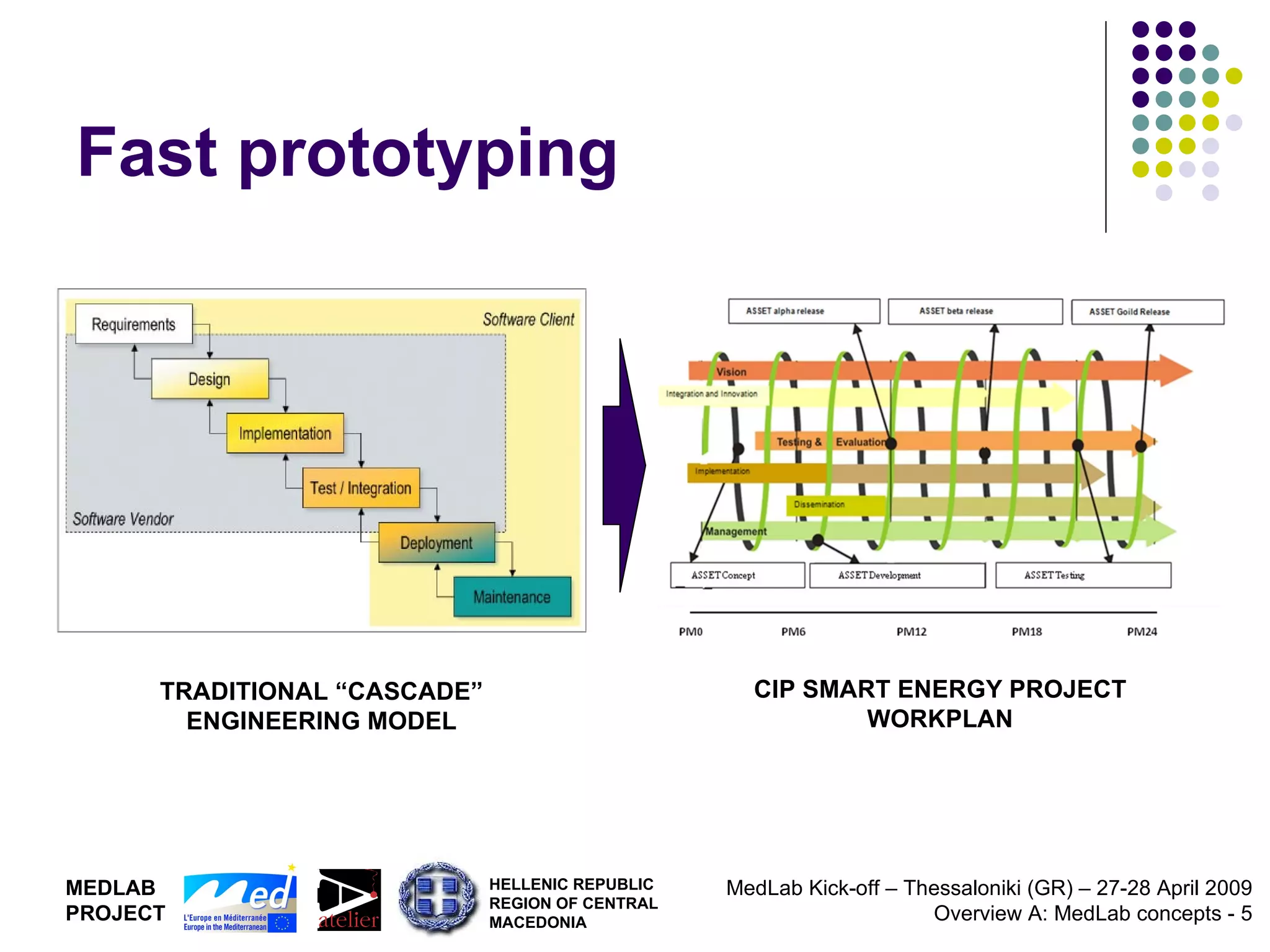
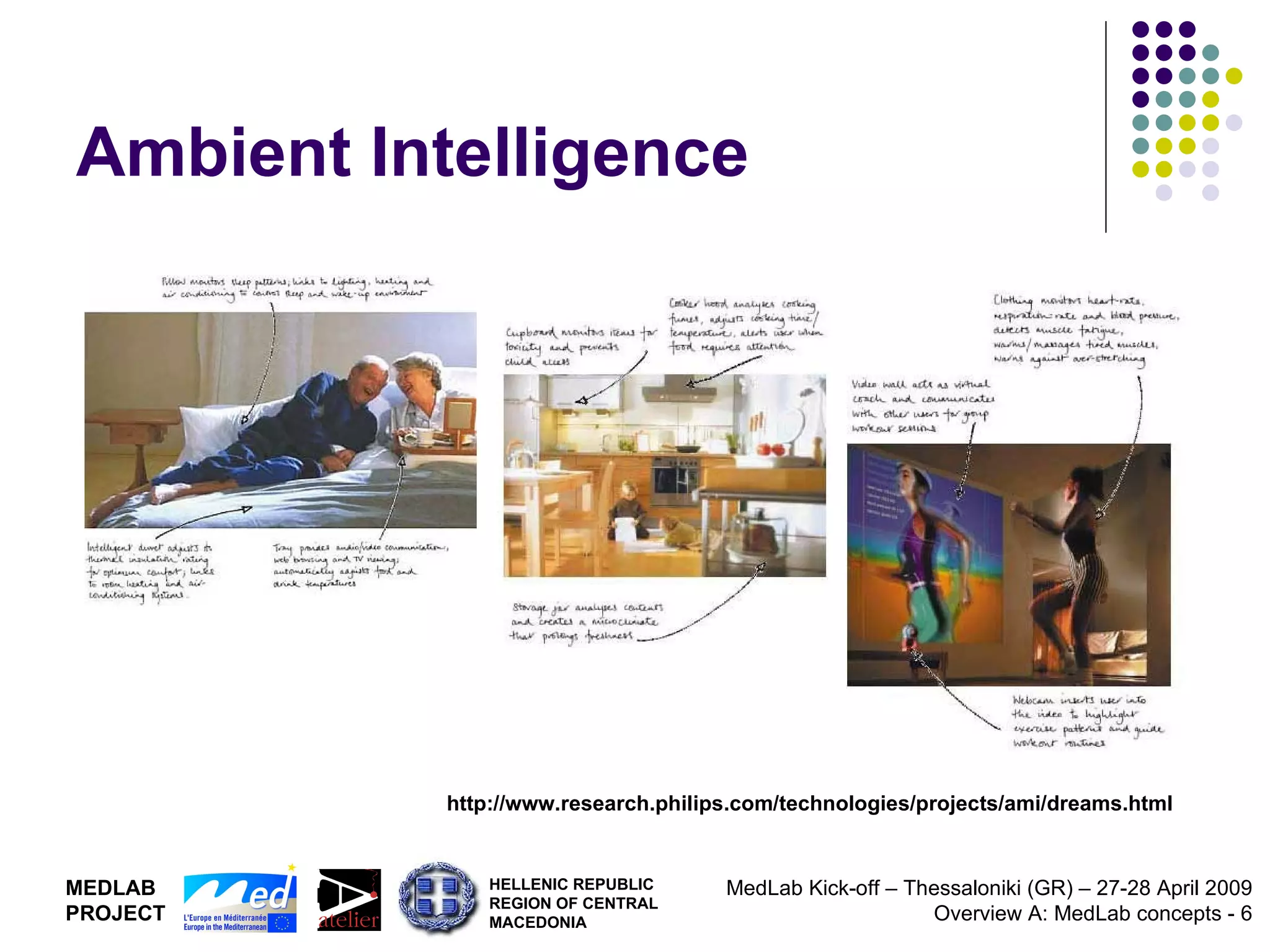
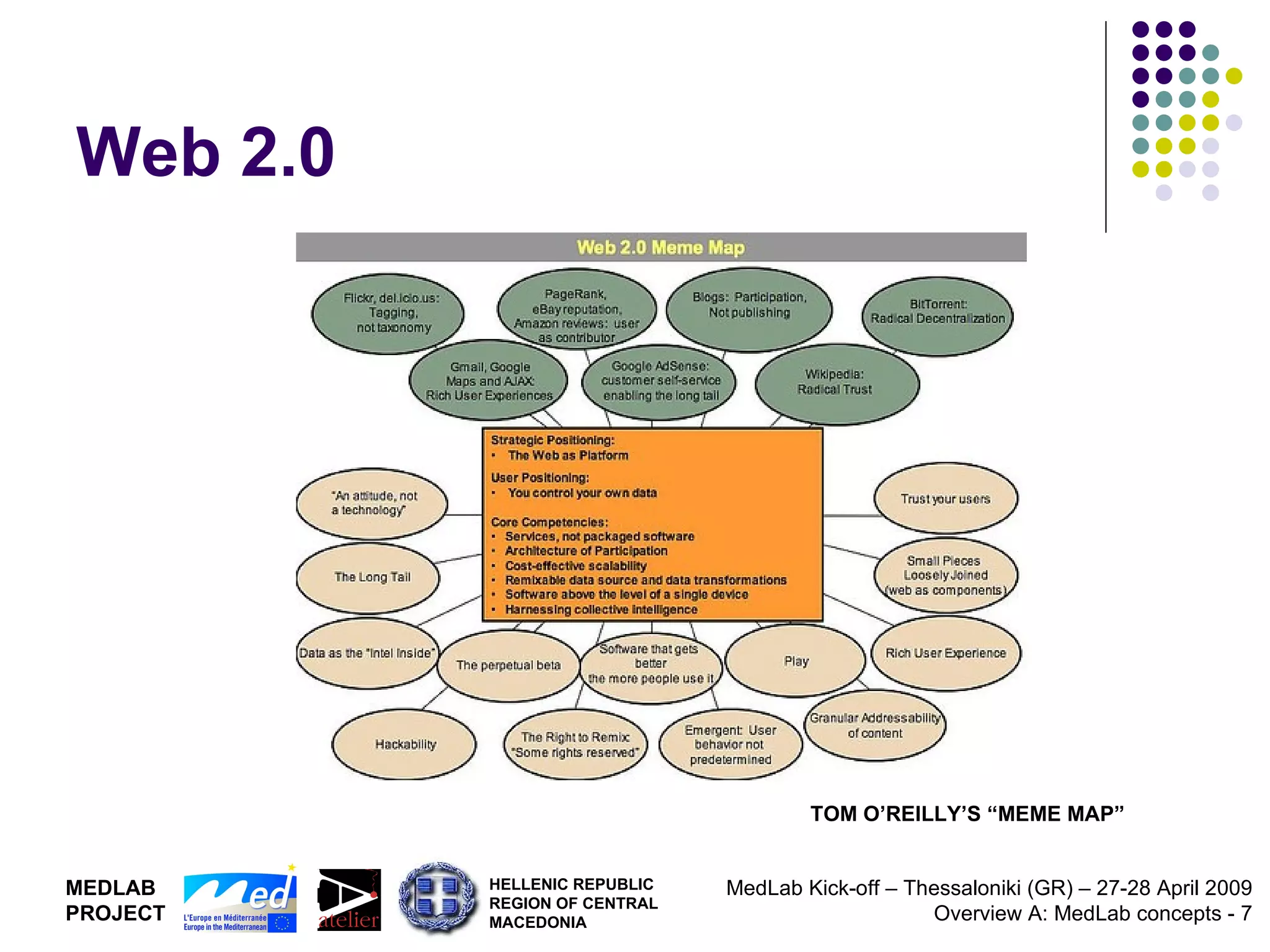
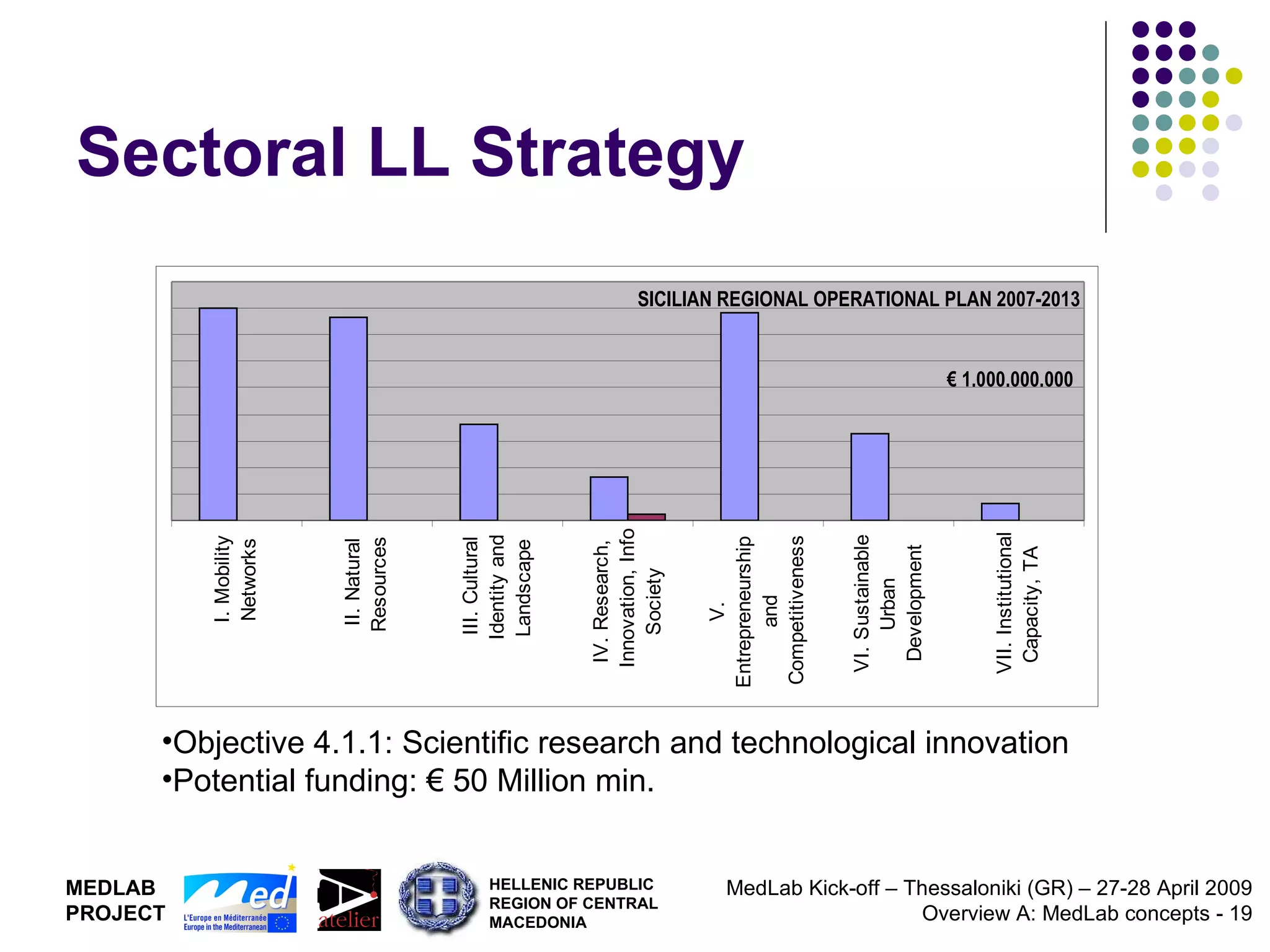
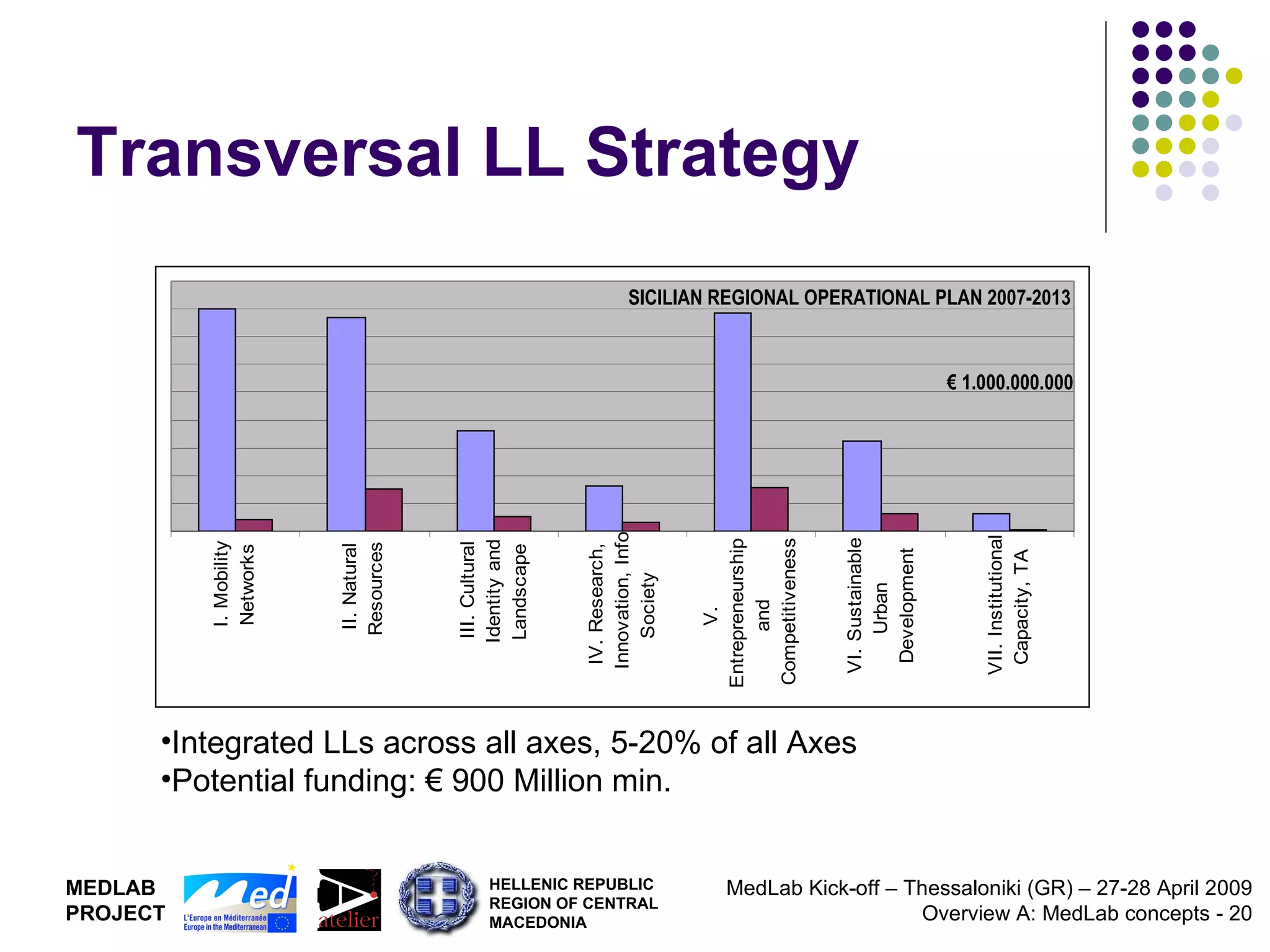
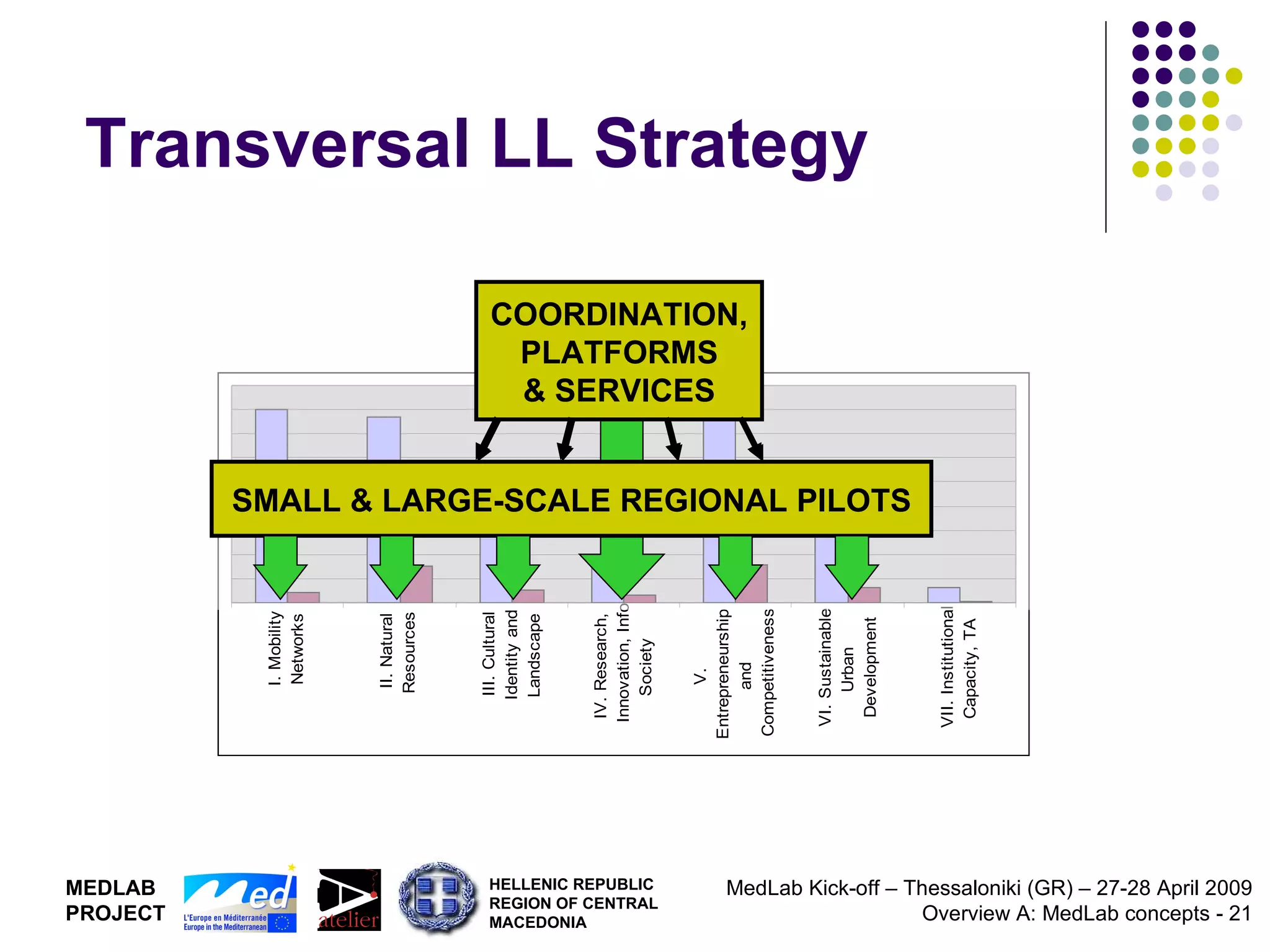
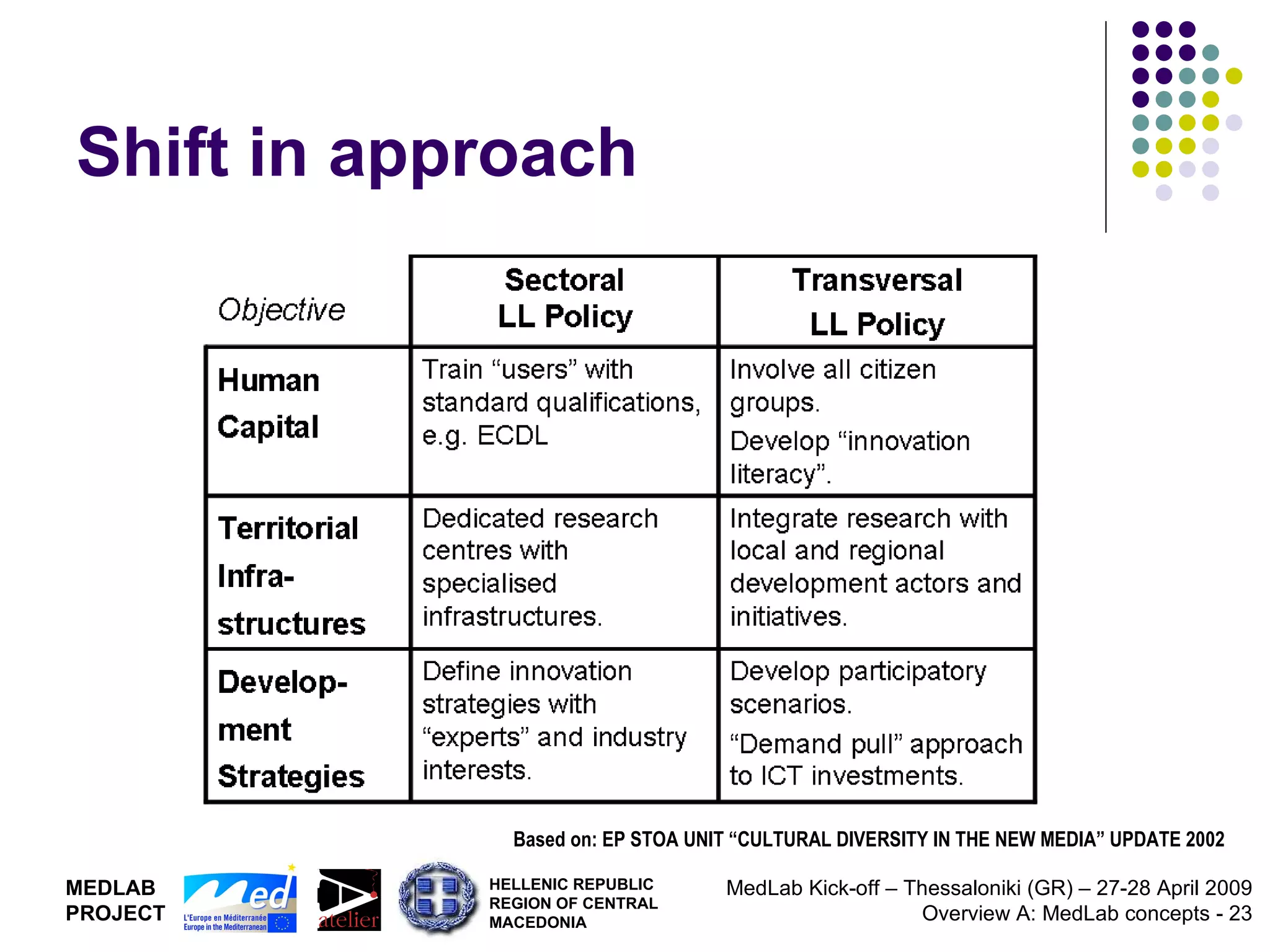
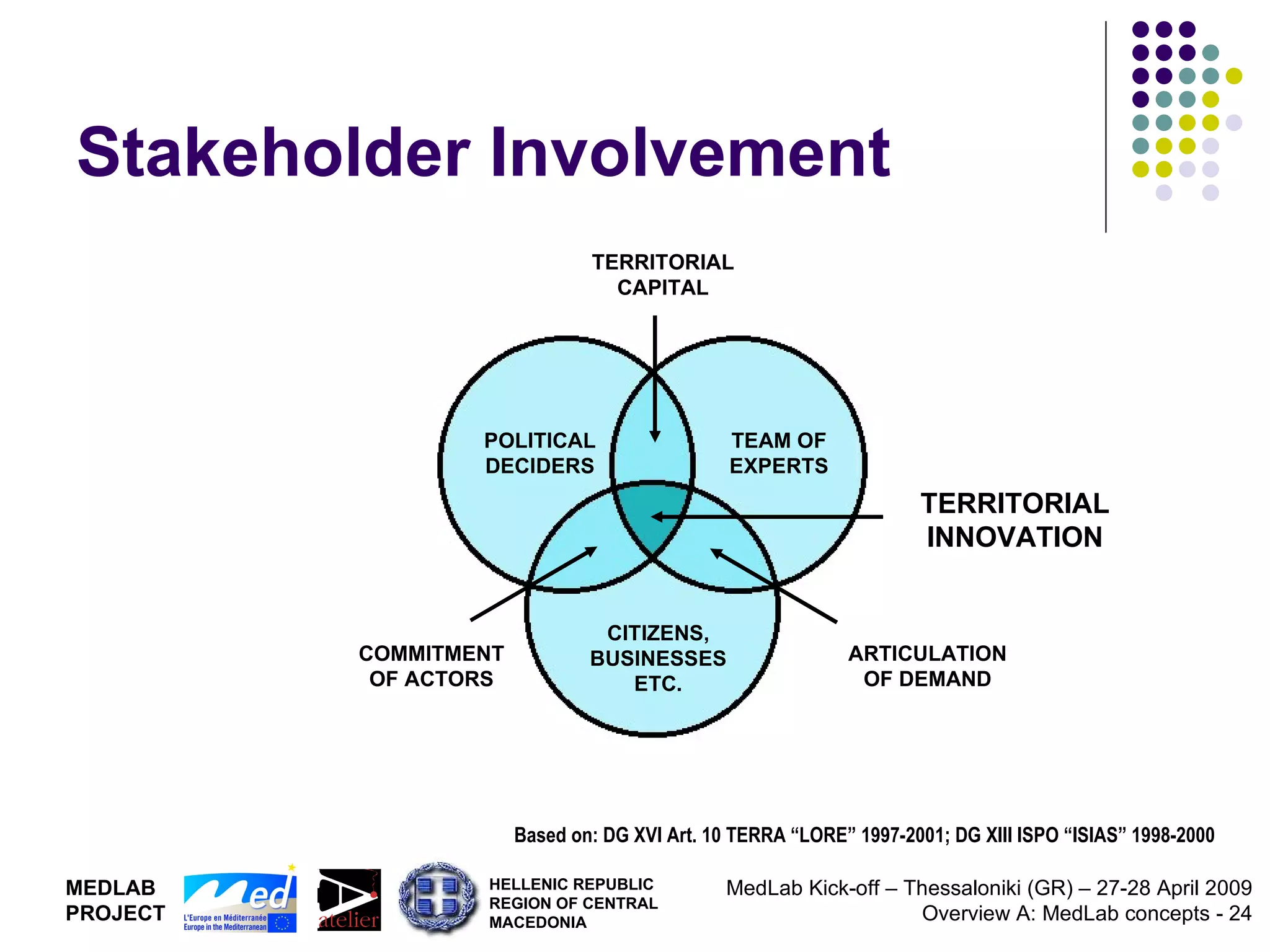
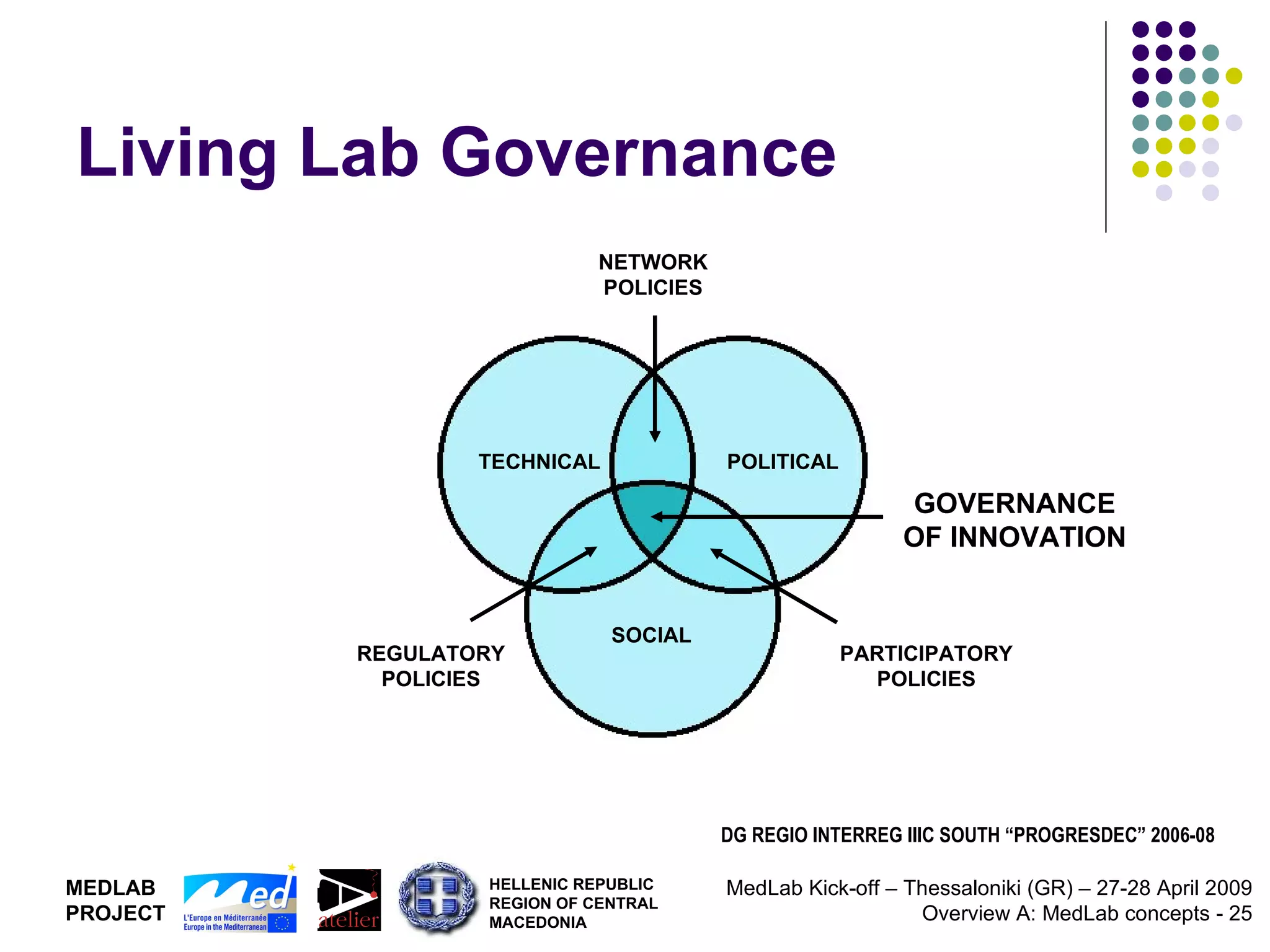
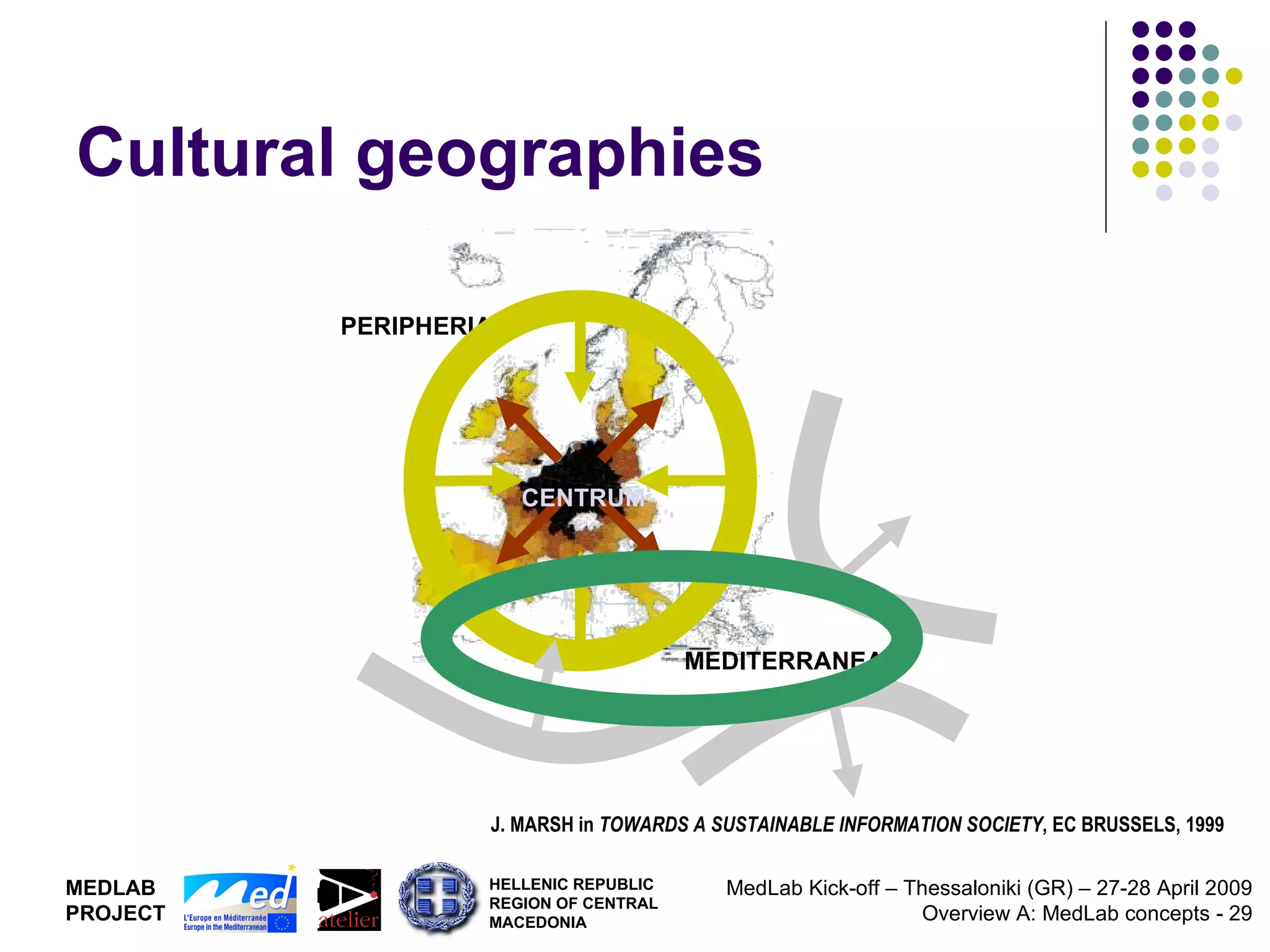
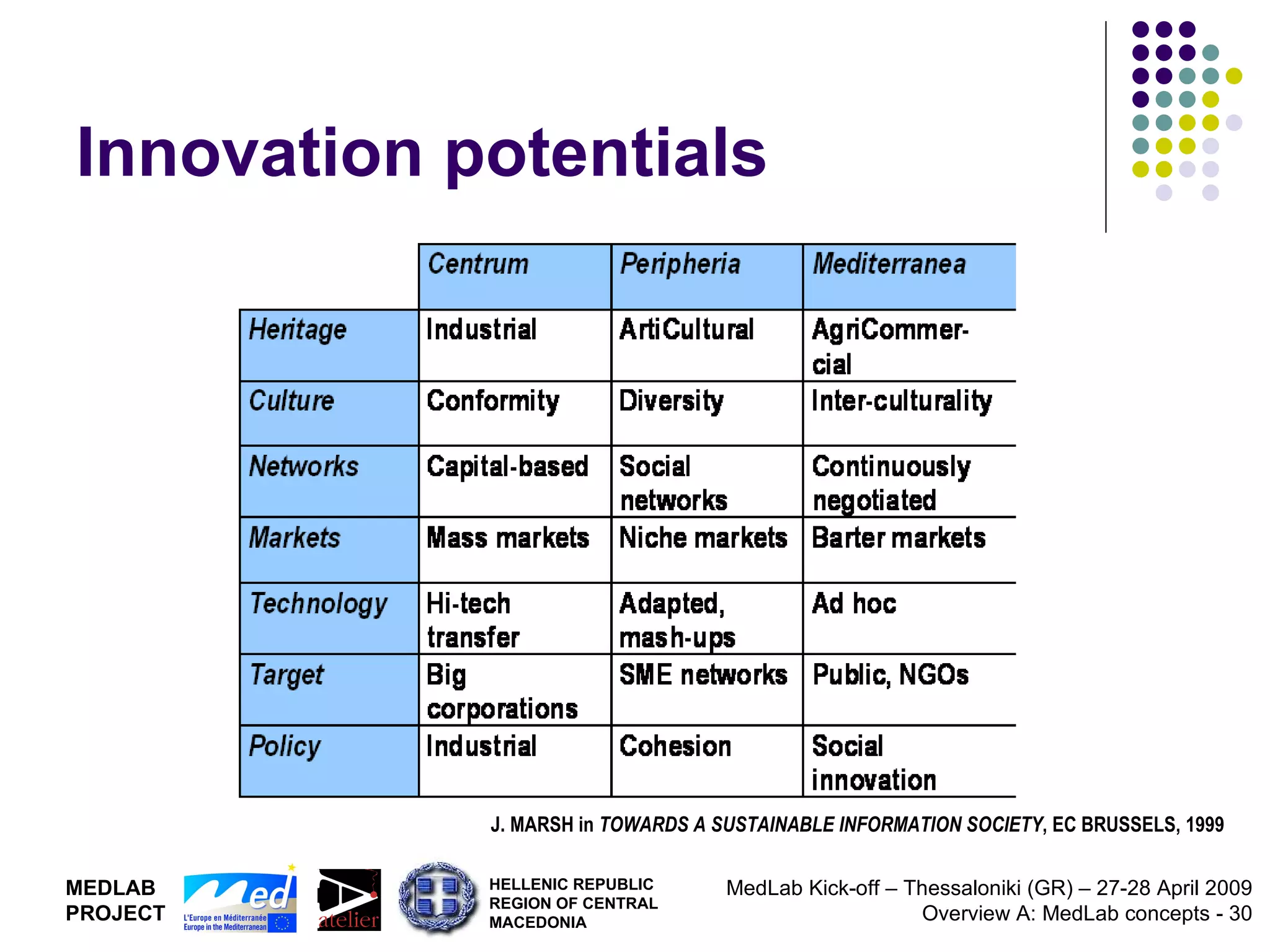
1. The document discusses Living Labs, which are user-driven open innovation ecosystems that involve citizens, businesses, and government working together on research and development.
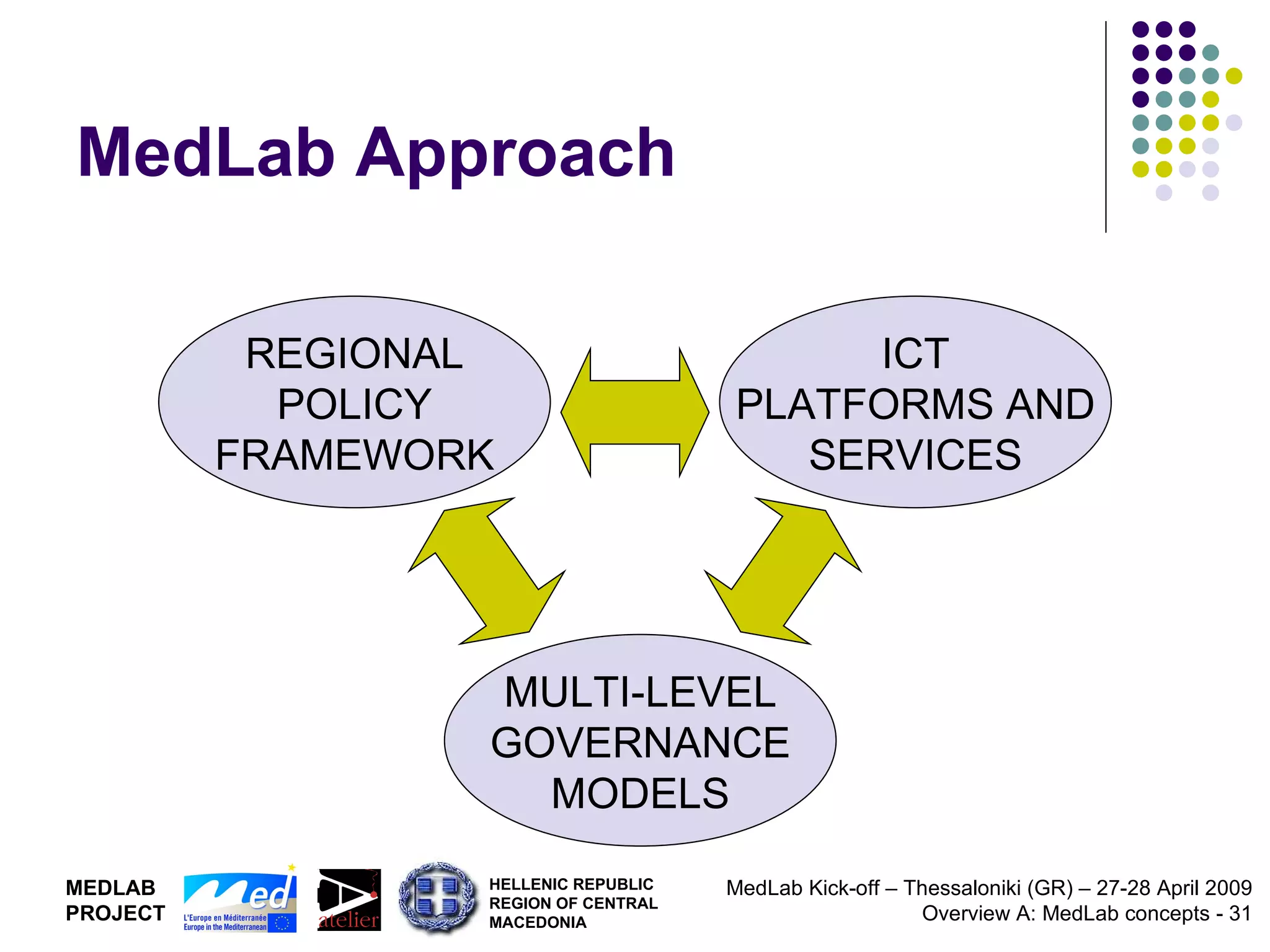
2. It proposes developing a trans-national Mediterranean Living Lab that would integrate Living Lab approaches into regional policy to support territorial innovation and co-design of new ICT services through multi-level governance models.
3. The goal is to generate new models of development based on technological, social, organizational, and institutional innovation.
![MedLab concepts Project overview session A Jesse Marsh Atelier/RCM [email_address]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/overviewa-090612021349-phpapp01/75/MedLab-concepts-Living-Labs-Regional-Development-and-the-Mediterranean-1-2048.jpg)