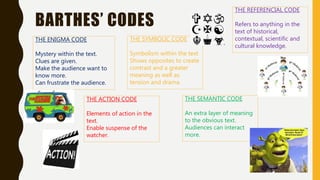
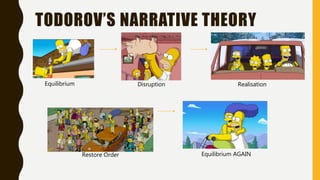
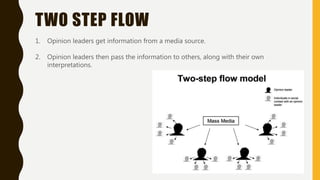
The document outlines several media theories including Propp's character theory, Barthes' codes (enigma, semantic, action, referential, symbolic), Todorov's narrative theory of equilibrium, disruption, and realization, Levi-Strauss' concept of binary oppositions, audience classifications of ABC1 and C2DE, the hypodermic syringe theory of media influence, uses and gratifications theory, reception theory of preferred, negotiated, and oppositional readings, the two step flow model of opinion leaders influencing others, and Mulvey's concept of the male gaze in film.