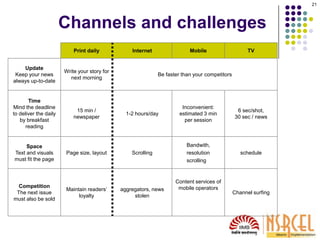
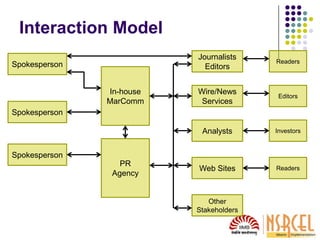
This document provides guidance on media relations strategies for startups. It discusses the media landscape, how news is produced, and types of media interactions. The key points are:
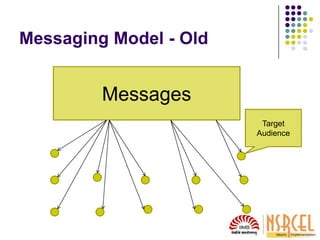
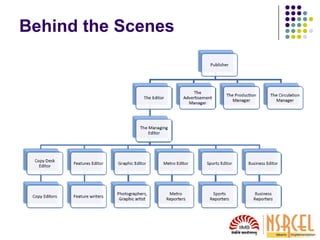
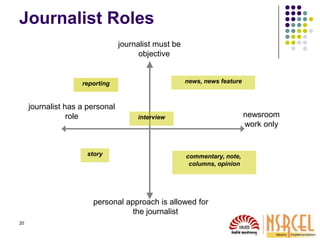
1) Understanding how media works is important for startups seeking publicity. News is a product that media sells and they prioritize stories their readers want.
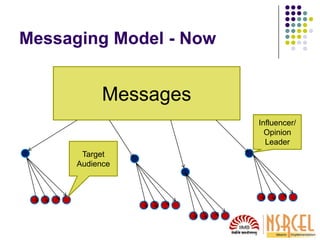
2) Building relationships with journalists, opinion leaders, and influencers who cover your industry is important. Attend events, write comments online, and develop your brand as an expert in your field.
3) Have a clear media pitch highlighting how your startup benefits readers. Create a media kit and pitch your story to relevant publications and journalists. Media relations takes sustained effort but can help start