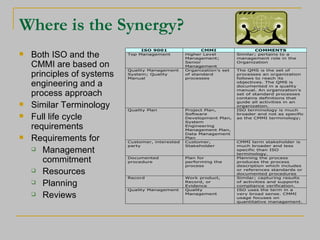
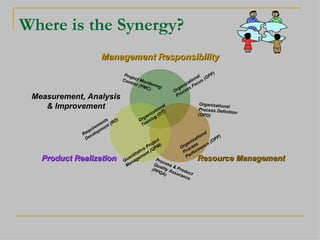
The document compares and contrasts the CMMI (Capability Maturity Model Integration) and ISO 9001 quality standards. While CMMI focuses more on software/systems development processes and provides detailed engineering practices, ISO 9001 establishes a general quality management system for organizations. Both aim to improve processes but through different approaches - CMMI through progressive maturity levels and ISO 9001 through annual audits. The document argues that CMMI and ISO 9001 complement each other and organizations can benefit from using both standards together.