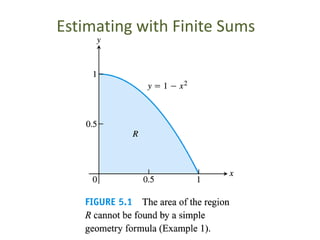
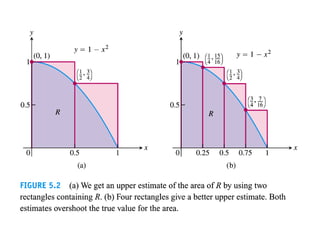
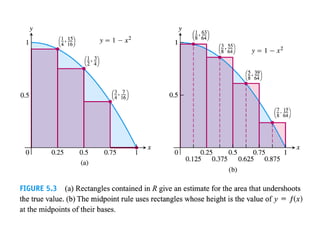
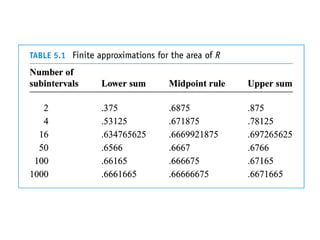
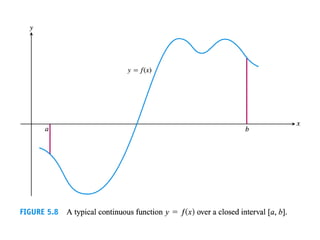
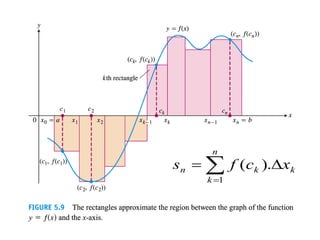
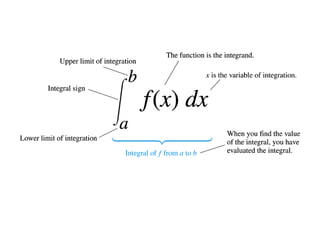
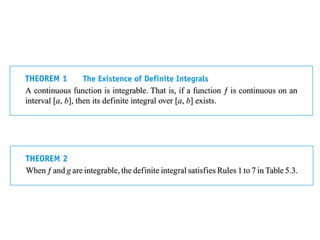
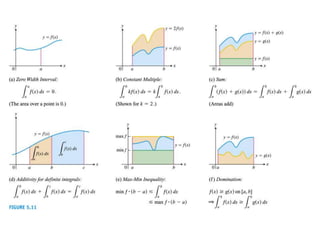
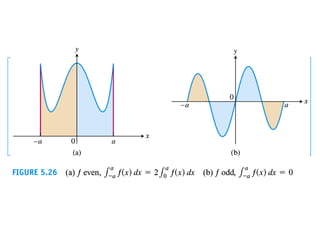
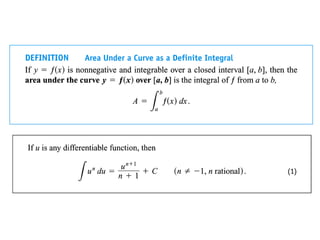
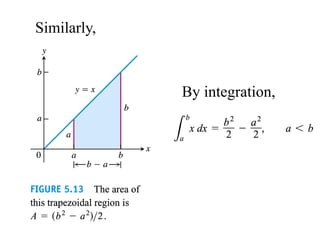
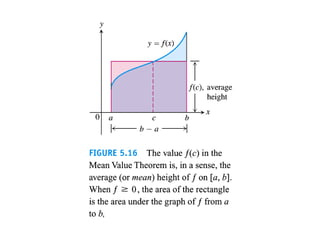
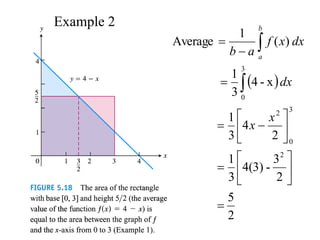
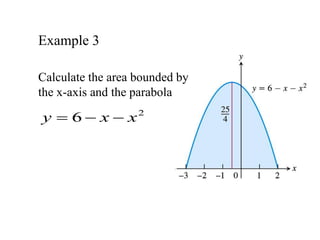
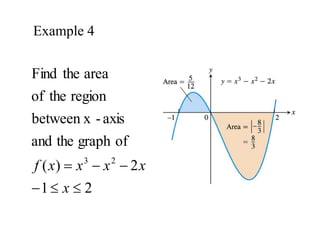
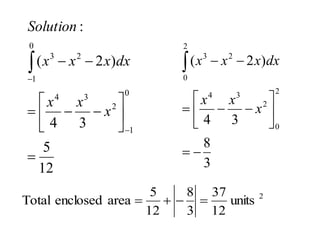
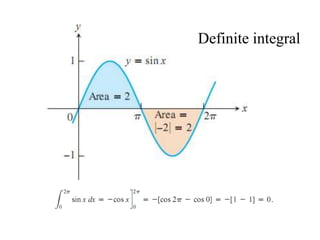
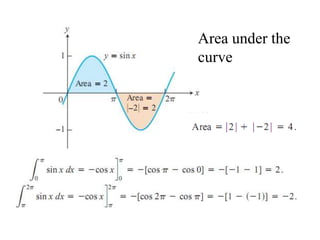
The document discusses the process of estimating areas under curves using definite integrals, featuring multiple examples of calculating such areas using different functions. It highlights key steps, including sketching the curves, determining integration limits, and applying integration techniques. Additionally, it presents various scenarios involving intersections and areas bounded by curves.




![Example 1
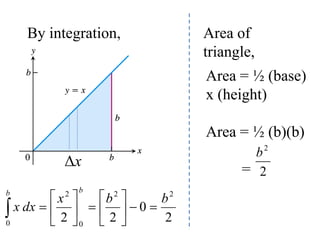
Find the area A under
y = x over the interval
[0,b], b > 0](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/ee101l1integarea-240626032612-24c7f137/85/mathmathmathmathmathmathmathmathmathmath-16-320.jpg)

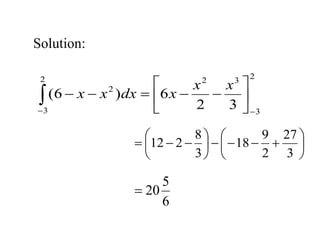

![
b
a
dx
x
g
x
f
Area )]
(
)
(
[](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/ee101l1integarea-240626032612-24c7f137/85/mathmathmathmathmathmathmathmathmathmath-29-320.jpg)


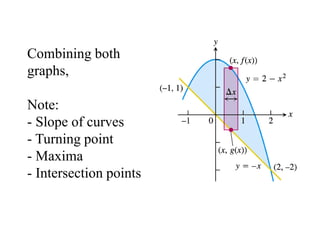
![2
2
1
3
2
2
1
2
2
1
2
unit
2
9
3
1
2
1
2
3
8
2
4
4
3
2
2
)
2
(
)]
(
)
2
[(
)]
(
)
(
[
x
x
x
dx
x
x
dx
x
x
dx
x
g
x
f
A
b
a
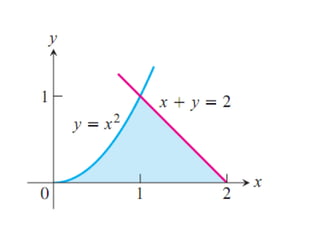
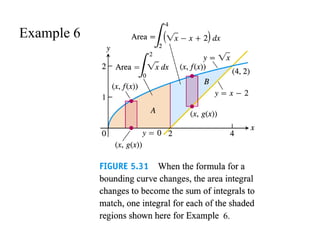
Solution for
area between
2 curves:](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/ee101l1integarea-240626032612-24c7f137/85/mathmathmathmathmathmathmathmathmathmath-36-320.jpg)


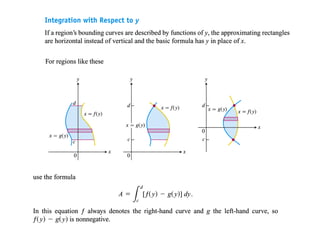
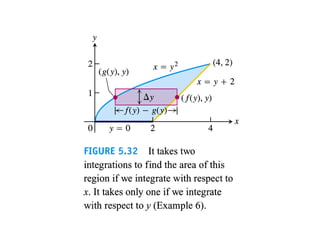
![Solution:
Solving simultaneous equation of
gives roots y=-1, y=2.
Limits a=0,b=2.
2
and
2
y
x
y
x
3
10
)
2
(
)]
(
)
(
[
2
0
2
dy
y
y
dy
y
g
y
f
A
b
a](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/ee101l1integarea-240626032612-24c7f137/85/mathmathmathmathmathmathmathmathmathmath-42-320.jpg)