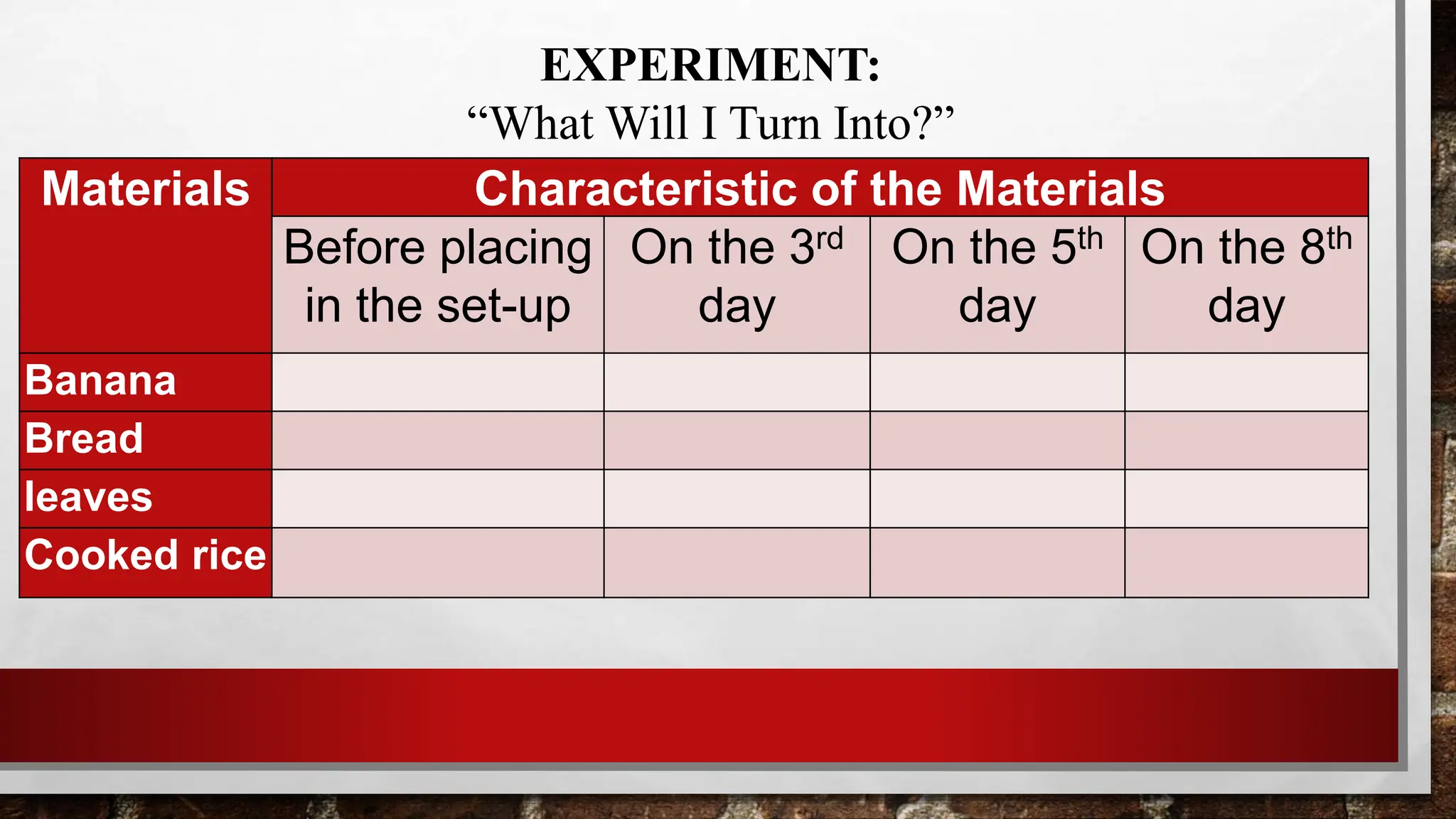
Decay refers to the slow destruction of materials in the presence of water, air, and soil. Many factors contribute to decay, including temperature, light, moisture, and the type of material. Examples of materials that undergo decay include dead plants and animals, leftover foods, fruits and vegetable peels, and leaves. Materials that do not decay include rubber, glass, metal, and plastic. The document instructs students to identify decaying and non-decaying materials and observe how samples like banana and bread decompose over a period of days in an experiment.