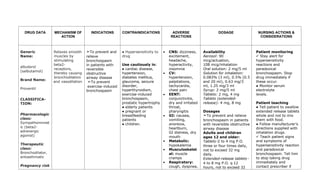
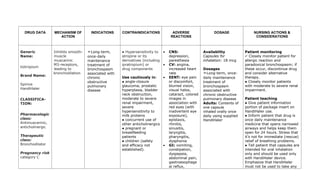
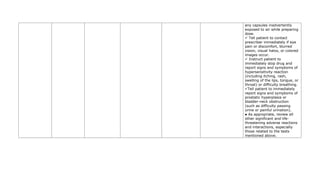
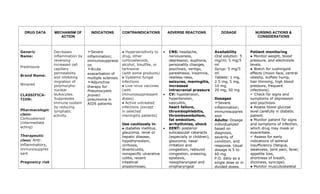
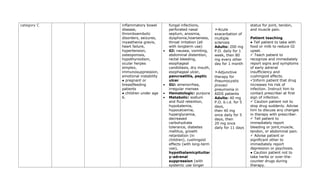
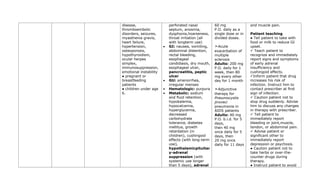
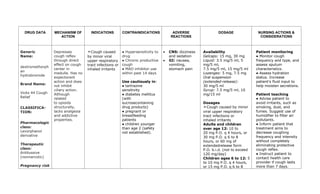
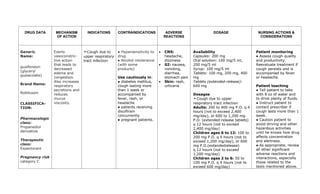
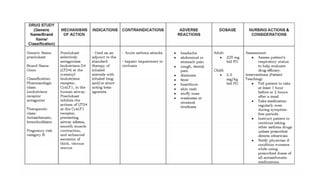
This document provides a summary of four bronchodilator drugs: albuterol, salmeterol, tiotropium, and corticosteroids. For each drug, the summary includes the generic and brand names, classification, mechanism of action, indications for use, contraindications, potential adverse reactions, dosage guidelines, and important nursing considerations. The full document provides more detailed information on the pharmacology, proper administration, and patient education for each medication.