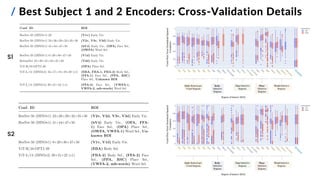
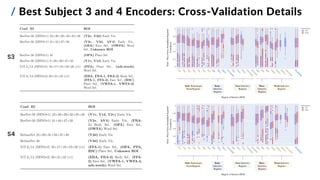
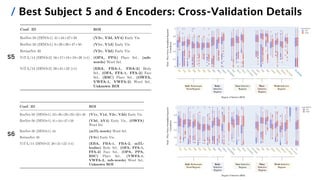
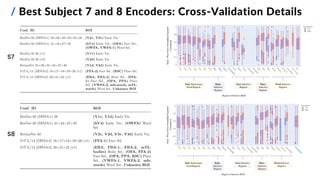
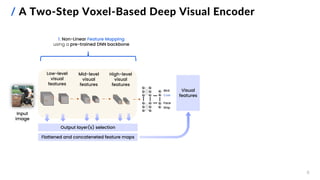
This document presents a study on developing deep neural encoding models to predict fMRI responses in the human visual cortex to natural visual scenes. The study uses a large dataset of fMRI responses from 8 subjects viewing 73,000 natural images. Various pre-trained deep neural networks are evaluated as feature extractors to map images to visual features. A two-step voxel-based encoding approach is proposed, applying dimensionality reduction before training linear regression models for each voxel. The best models achieve high prediction accuracy across visual cortical regions of interest, demonstrating the effectiveness of transfer learning from computer vision models for the image-fMRI encoding task.

![[ INTRODUCTION ]
2](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/carbonegiorgiopresentazionelmds20marzo2024-240322201621-22700d72/85/Master-s-Thesis-Data-Science-Presentation-2-320.jpg)
![/ Visual Encoding in Neuroscience
Visual Neural Encoding
▪ humans understand complex visual stimuli
▪ visual information is represented as neural
activations in the visual cortex
▪ neural activations (or responses) ➨ patterns of
measurable electrical activity
Visual Encoding Models [1]
▪ mimic the human visual system
▪ explain natural visual stimulus ⬌ neural activations
relationship
▪ structured system to test biological hypotheses about
the visual pathways Visual
Encoding
model
Neural
responses
Stimulus Brain
scan
Visual
cortex
3
[1] Naselaris et al. (2011). Encoding and decoding in fMRI. NeuroImage 56.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/carbonegiorgiopresentazionelmds20marzo2024-240322201621-22700d72/85/Master-s-Thesis-Data-Science-Presentation-3-320.jpg)
![/ The Algonauts Project 2023: Challenge and Dataset
Algonauts 2023 Challenge goals:
▪ promote artificial intelligence and computational
neuroscience interdisciplinary research
▪ develop cutting-edge image-fMRI encoding models of
the visual brain
Natural Scene Dataset [2] :
▪ fMRI responses to ~73,000 images from MS COCO
▪ each of the eight subjects was shown: ~9000-10000
training images and ~150-400 test images
▪ measured the fMRI activity in the 39,548 voxels of the
visual cortex
▪ betas ➨ single value response estimates
▪ functional Region of Interest (ROI) label for each voxel
4
[2] Allen et al. (2021). A massive 7T fMRI dataset to bridge cognitive neuroscience and artificial intelligence. Nature Neuroscience 25.
2
-2 0
fMRI betas for the
39,548 voxels
Stimulus
images
LH RH
Early
retinotopic
ROIs
Body
selective
ROIs
Face
selective
ROIs
Place
selective
ROIs
Word
selective
ROIs
Functional classes of regions of interest (ROIs)
LH RH](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/carbonegiorgiopresentazionelmds20marzo2024-240322201621-22700d72/85/Master-s-Thesis-Data-Science-Presentation-4-320.jpg)

![[ METHODS ]
7](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/carbonegiorgiopresentazionelmds20marzo2024-240322201621-22700d72/85/Master-s-Thesis-Data-Science-Presentation-7-320.jpg)
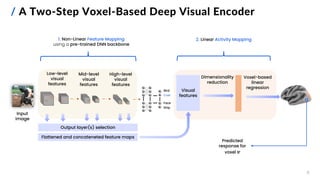

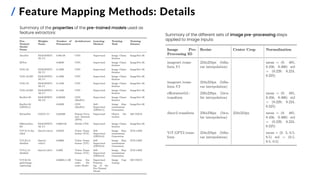
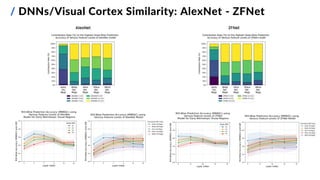
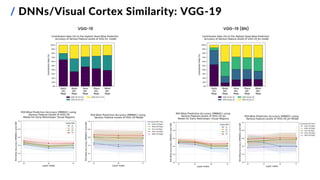
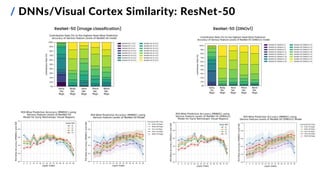
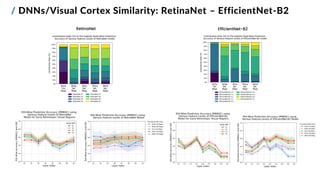
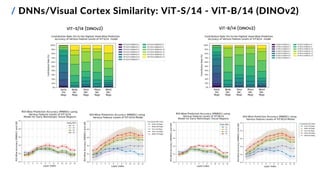
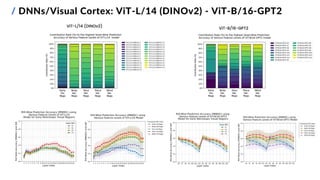
![/ Feature Mapping Methods
10
Goals:
1. find the overall and ROI-wise best-performing
feature mapping methods on Subject 1
2. compare pre-trained DNNs with:
▪ different architectures and depths
▪ different training parameters (learning tasks,
learning methods and datasets)
▪ output layer(s) at varying depths
3. test a fused features approach
Architecture Learning task/method Dataset
AlexNet Image classification ImageNet-1K
ZFNet Image classification ImageNet-1K
VGG-16/19 Image classification ImageNet-1K
EfficientNet-B2 Image classification ImageNet-1K
ResNet-50 Image classification ImageNet-1K
ResNet-50
(DINOv1) [3]
Self-supervised ImageNet-1K
RetinaNet Object detection MS COCO
Architecture Learning task/method Dataset
ViT-S/14 (DINOv2) Self-supervised LVD-142M
ViT-B/14 (DINOv2) Self-supervised LVD-142M
ViT-L/14 (DINOv2) Self-supervised LVD-142M
ViT-B/16-GPT2 Image captioning MS COCO
Pre-trained Convolutional Neural Networks (CNNs)
Pre-trained Vision Transformers (ViTs)
[3] M. Caron et al. (2021). Emerging Properties in Self-Supervised Vision Transformers. IEEE/CVF ICCV.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/carbonegiorgiopresentazionelmds20marzo2024-240322201621-22700d72/85/Master-s-Thesis-Data-Science-Presentation-11-320.jpg)
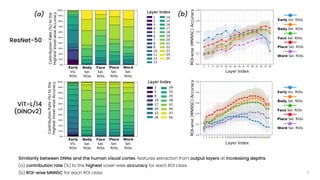
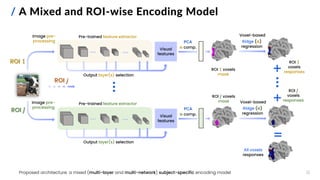
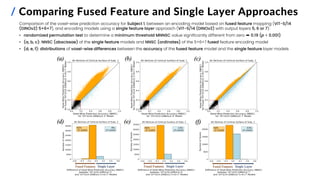
![[ RESULTS ]
13](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/carbonegiorgiopresentazionelmds20marzo2024-240322201621-22700d72/85/Master-s-Thesis-Data-Science-Presentation-14-320.jpg)
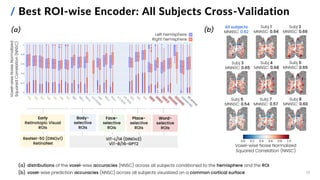
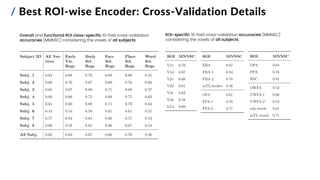
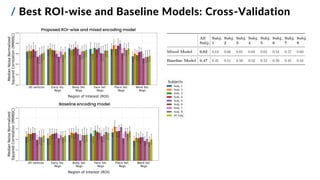
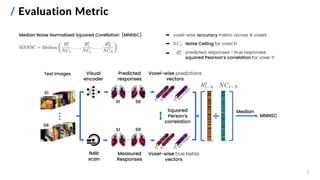
![15
/ Best ROI-wise Encoder: Test Set Performance
0
20
40
60
80
100
Median
Noise
Normalized
Squared
Correlation
(MNNSC)
Early
visual
ROIs
All
voxels
Body
sel.
ROIs
Face
sel.
ROIs
Place
sel.
ROIs
Word
sel.
ROIs
Median
Noise
Normalized
Squared
Correlation
(MNNSC)
0
20
40
60
80
100
Early
visual
ROIs
All
voxels
Body
sel.
ROIs
Face
sel.
ROIs
Place
sel.
ROIs
Word
sel.
ROIs
Subject
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
Proposed ROI-wise encoding model Baseline encoding model (AlexNet-based, not ROI-wise)
All Subjects Subj. 1 Subj. 2 Subj. 3 Subj. 4 Subj. 5 Subj. 6 Subj. 7 Subj. 8
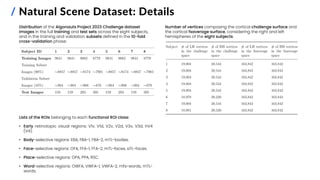
Proposed ROI-wise Encoder 0.52 0.53 0.51 0.56 0.54 0.50 0.59 0.40 0.57
Baseline Encoder 0.41 0.39 0.39 0.47 0.42 0.37 0.44 0.32 0.47
State-of-the -art Pure Neural
Encoder [4]
0.64
[4] Adeli et al. (2023). Predicting brain activity using transformers. digital preprint, bioRxiv.
Overall and subject-specific MNNSC](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/carbonegiorgiopresentazionelmds20marzo2024-240322201621-22700d72/85/Master-s-Thesis-Data-Science-Presentation-16-320.jpg)
![[ CONCLUSIONS AND FUTURE WORK ]
16](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/carbonegiorgiopresentazionelmds20marzo2024-240322201621-22700d72/85/Master-s-Thesis-Data-Science-Presentation-17-320.jpg)


![/ Bibliography
[1 ] Naselaris T, Kay KN, Nishimoto S, Gallant JL. (2011). Encoding and decoding in fMRI. NeuroImage (56).
[2] Allen, E.J., St-Yves, G., Wu, Y. et al. (2021). A massive 7T fMRI dataset to bridge cognitive neuroscience and artificial intelligence.
Nature Neuroscience.
[3] M. Caron et al. (2021). Emerging Properties in Self-Supervised Vision Transformers. IEEE/CVF ICCV.
[4] H. Adeli, S. Minni, and N. Kriegeskorte. (2023). Predicting brain activity using transformers. Preprint at bioRxiv.
[5] Gifford, A. T., Lahner, B., Saba-Sadiya, S., Vilas, M. G., Lascelles, A., Oliva, A., Kay, K., Roig, G., & Cichy, R. M. (2023).
The Algonauts Project 2023 Challenge: How the Human Brain Makes Sense of Natural Scenes. Preprint at arXiv.
[6] Yamins, D. L. K., & DiCarlo, J. J. (2016). Using goal-driven deep learning models to understand sensory cortex. Nature
Neuroscience, 19(3), Article 3.
[7] Dwivedi, K., Bonner, M. F., Cichy, R. M., & Roig, G. (2021). Unveiling functions of the visual cortex using task-specific deep neural
networks. PLOS Computational Biology, 17(8).](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/carbonegiorgiopresentazionelmds20marzo2024-240322201621-22700d72/85/Master-s-Thesis-Data-Science-Presentation-20-320.jpg)

![/ Non-Linear Activity Mapping Methods: Details
Supervised Regression Trees (RTs) learning approach, tested and
chosen parameters:
• Split criterion: Mean Squared Error (MSE)
• maximum depth of the tree [5, 10, 15] ➨ 5
• minimum number of samples required to split an internal
node [2,3] ➨ 2
• minimum number of samples needed to define a node as
a leaf node [1,2] ➨ 1
• number of features considered when searching for the
best split ➨ number of PCA components
Support Vector Regression (SVM) learning approach, chosen
parameters:
• tube width ε (maximum distance between predicted and
true values within which a penalty on the loss function is
not generated) ➨ 0.1
• regularization parameter C (high values lead to more
accurate fits on the training data but increase the
sensitivity of the model to noise) ➨ 1.0
• kernel ➨ Radial Basis Function (RBF)
• Gaussian kernel
• gamma parameter (how far the influence of
individual training examples can reach) ➨ 1 /
number of PCA components](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/carbonegiorgiopresentazionelmds20marzo2024-240322201621-22700d72/85/Master-s-Thesis-Data-Science-Presentation-23-320.jpg)