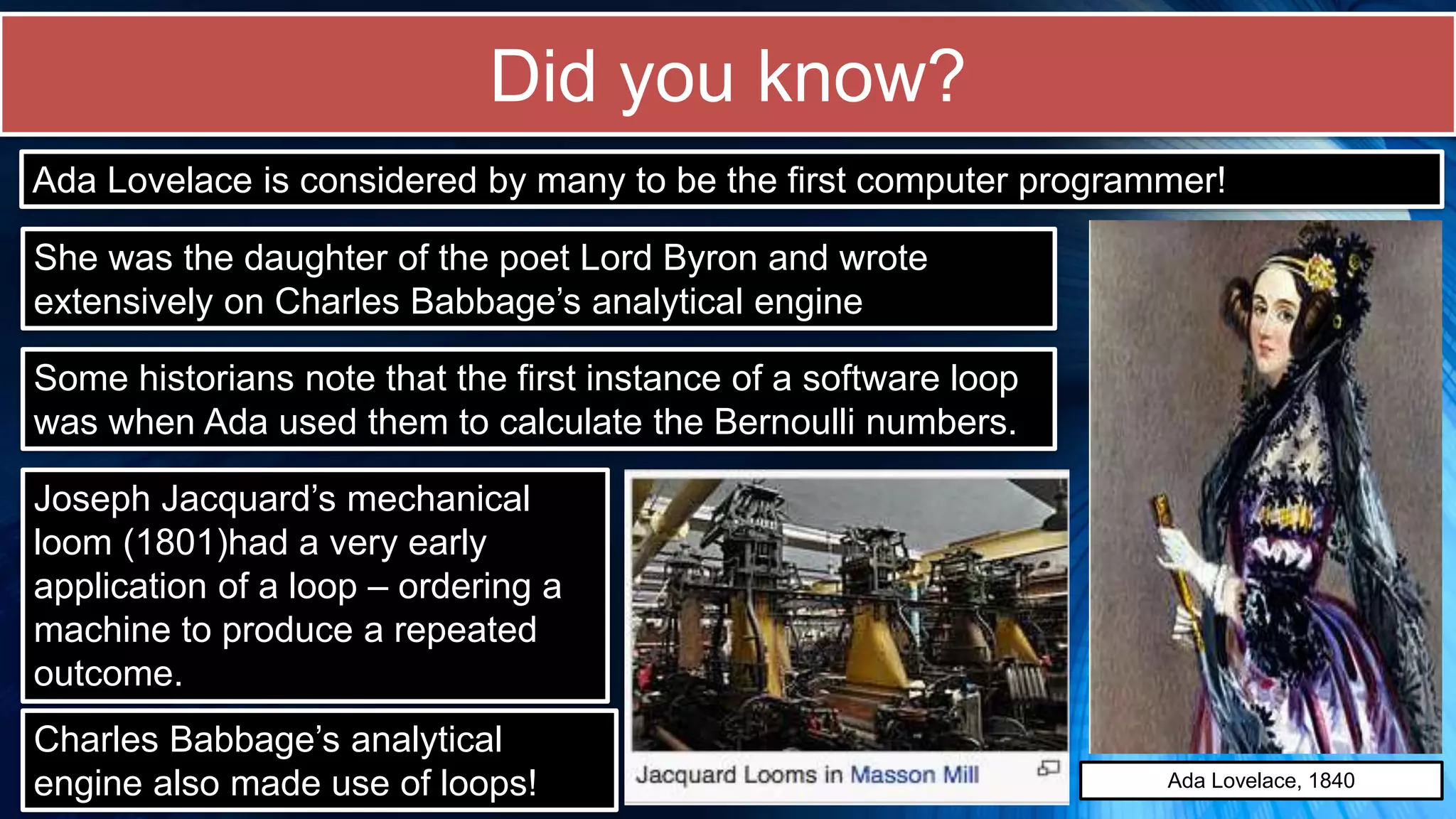
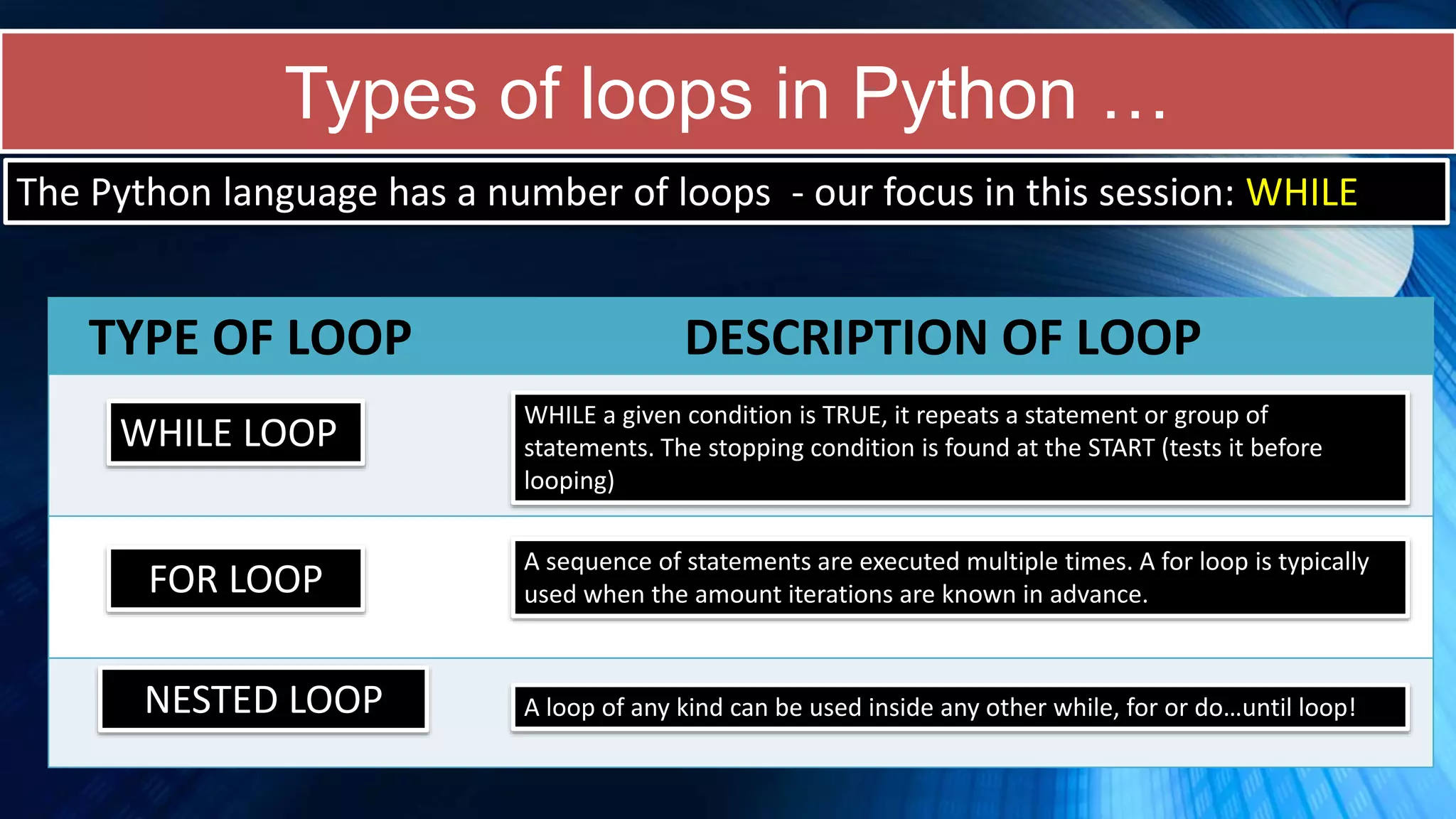
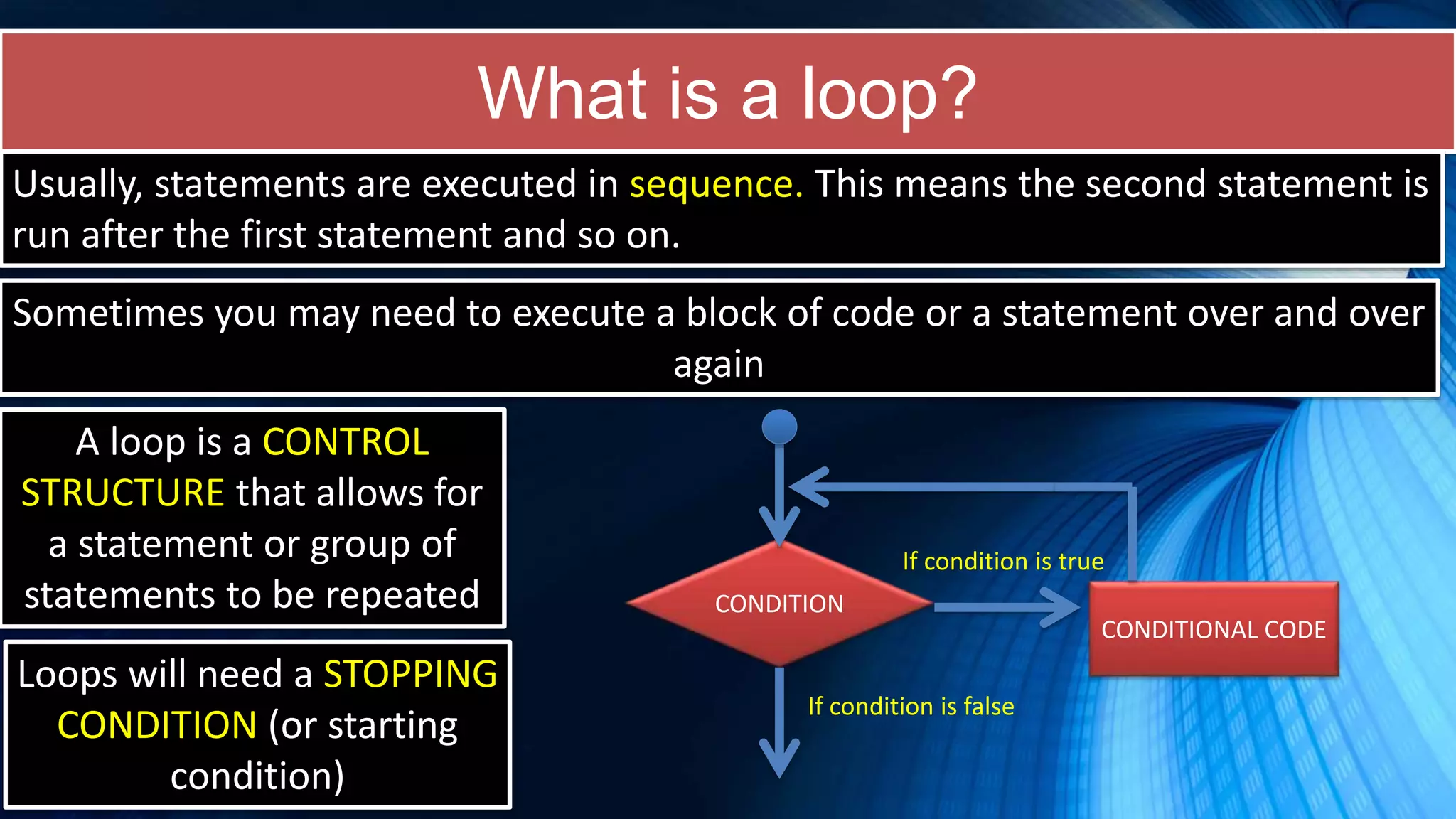
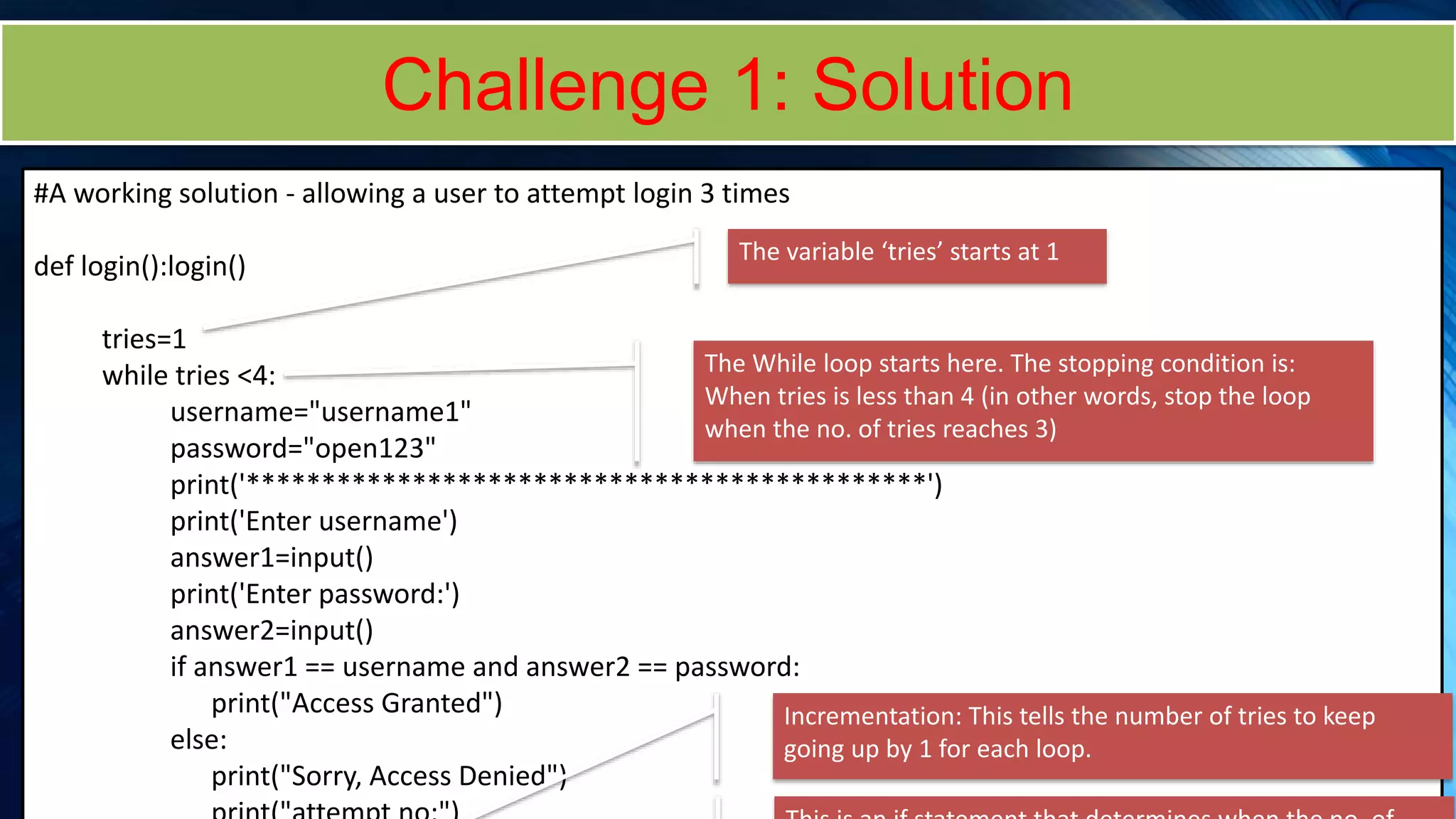
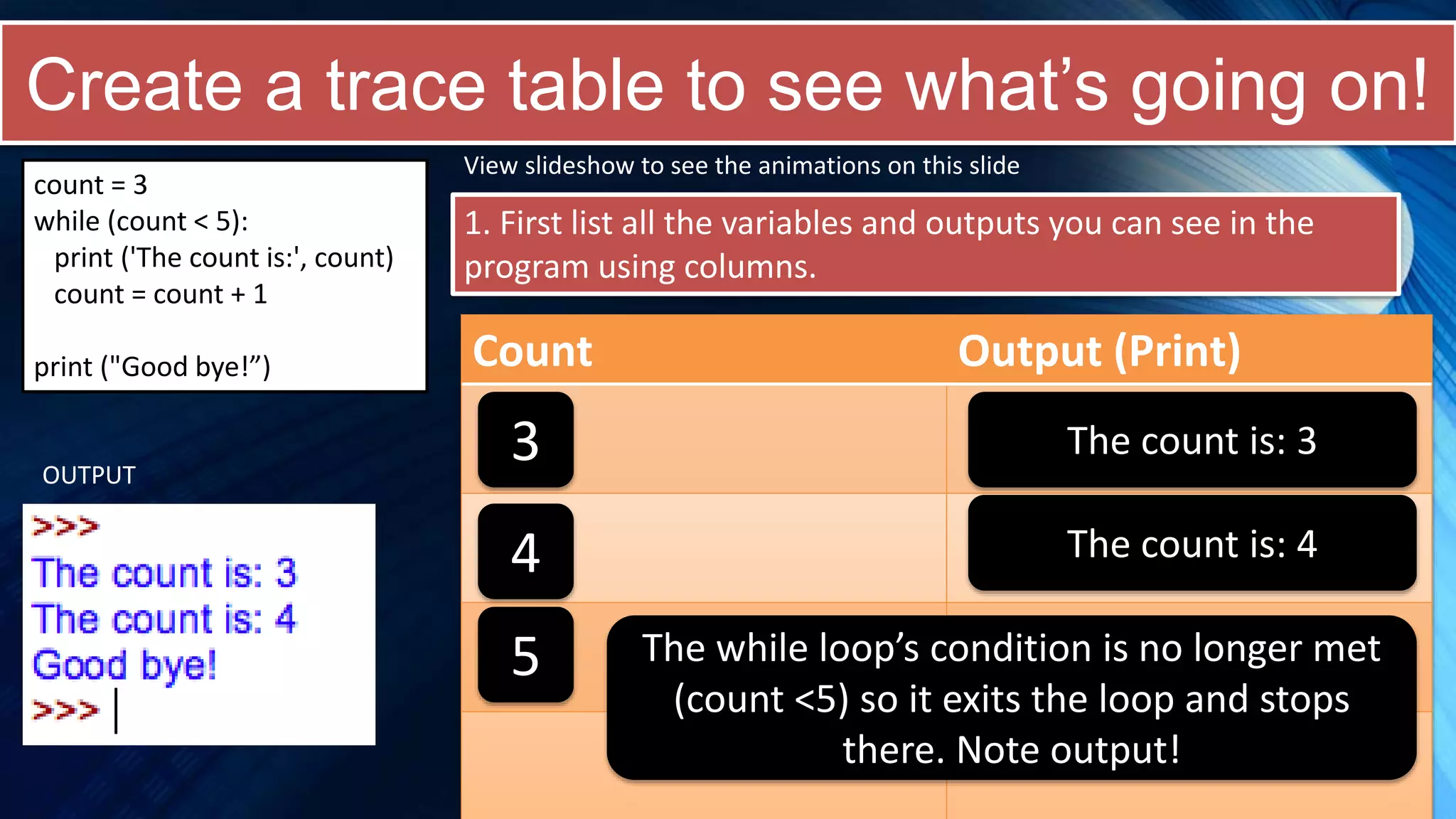
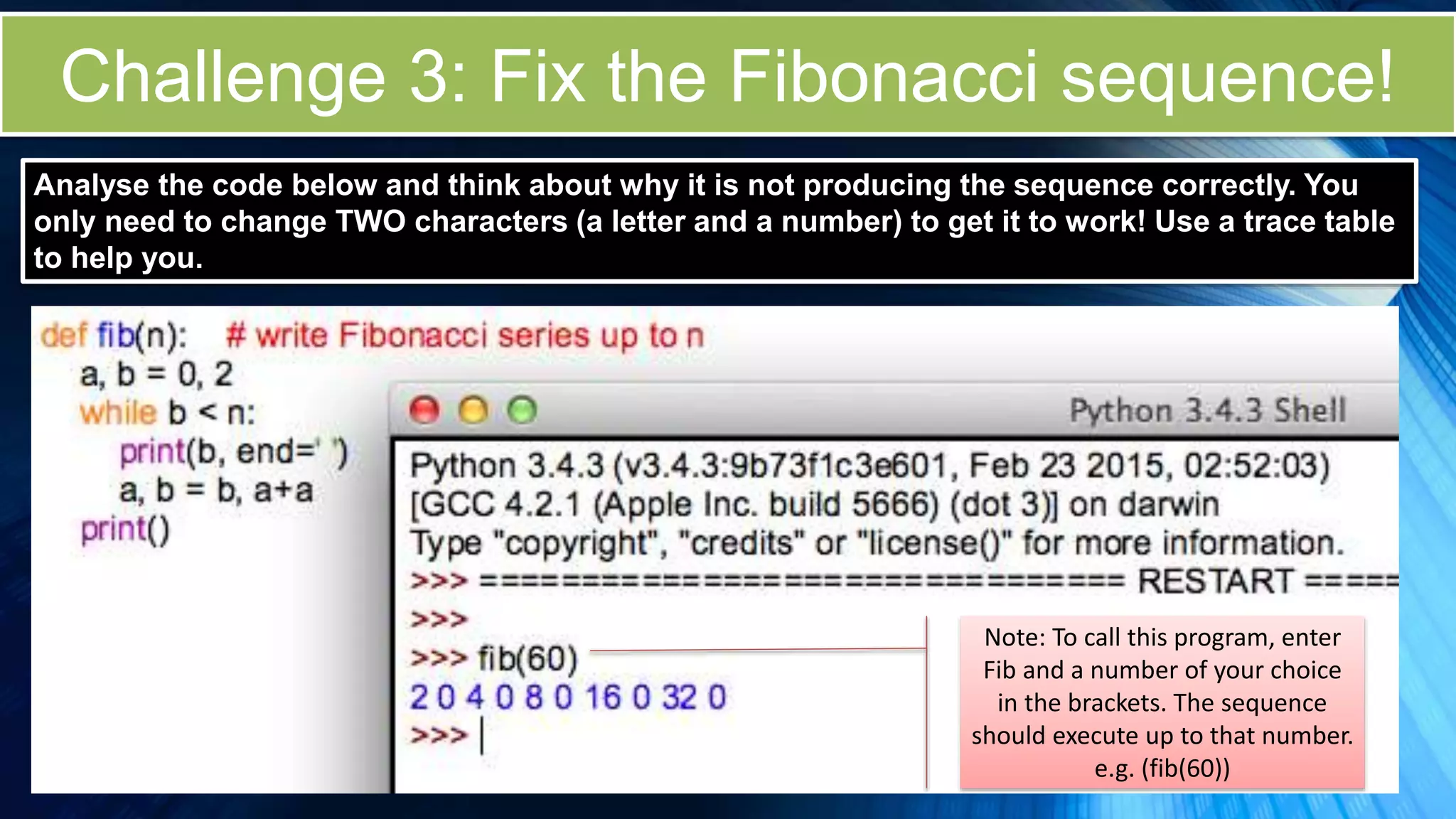
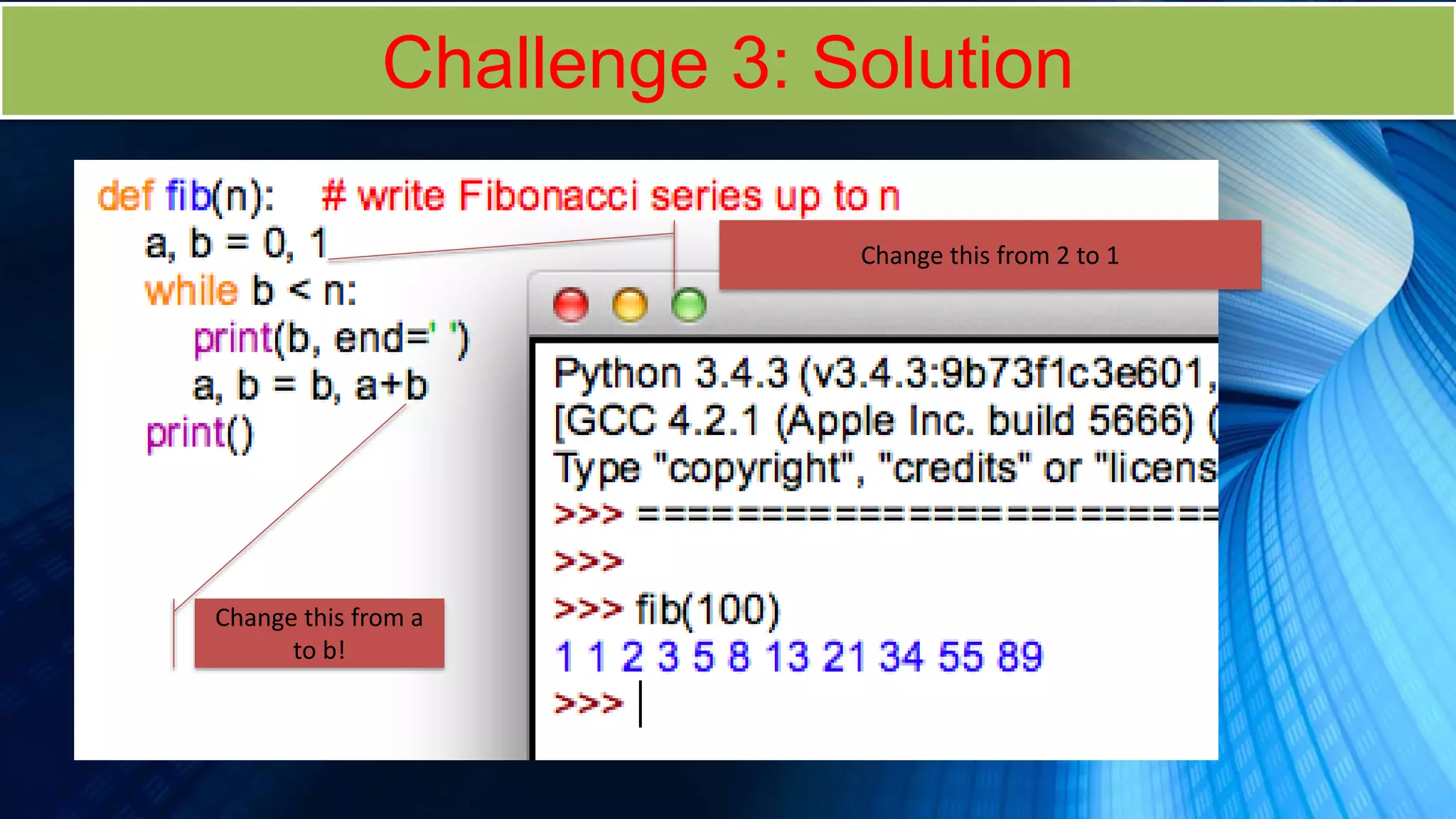
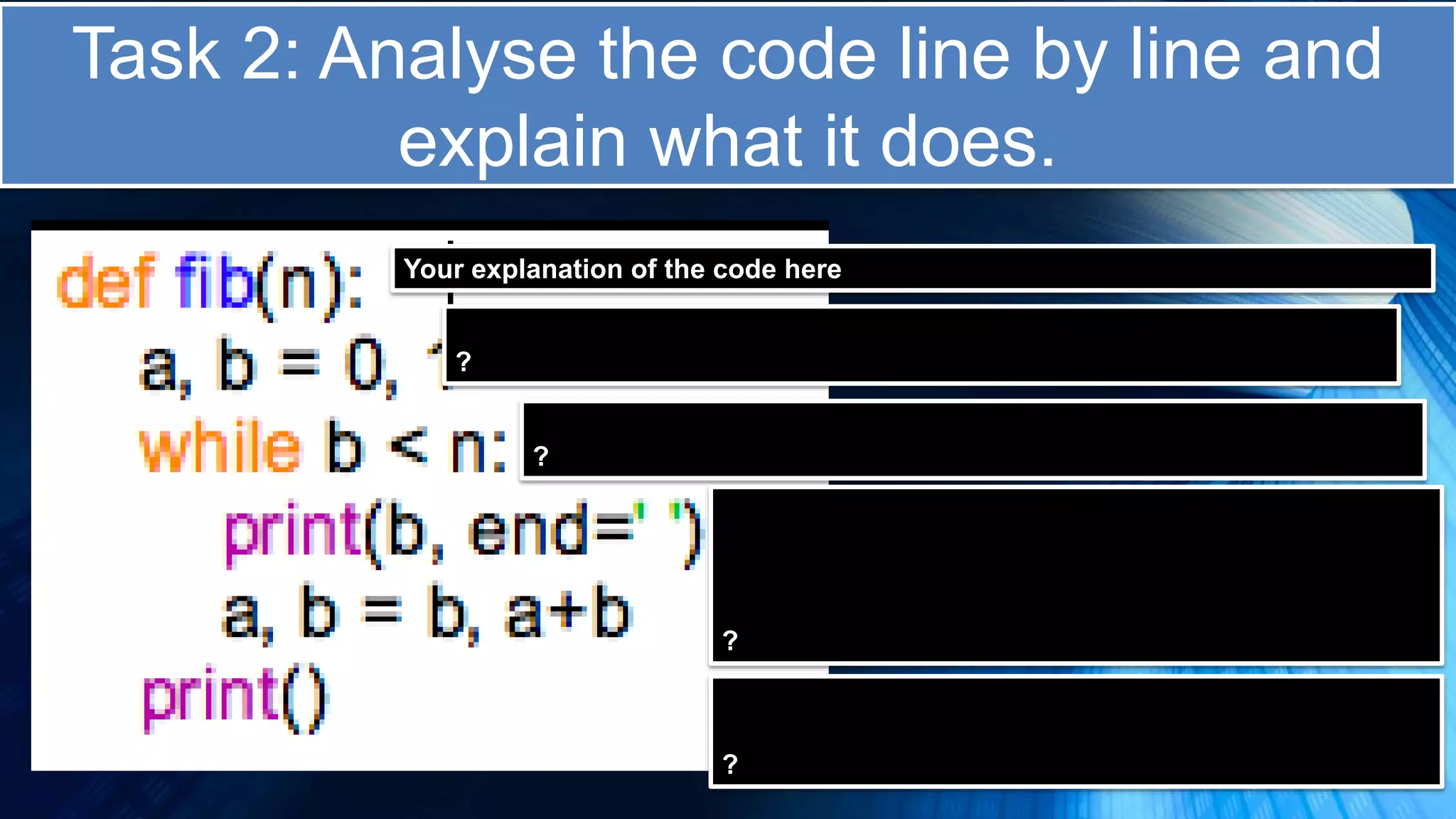
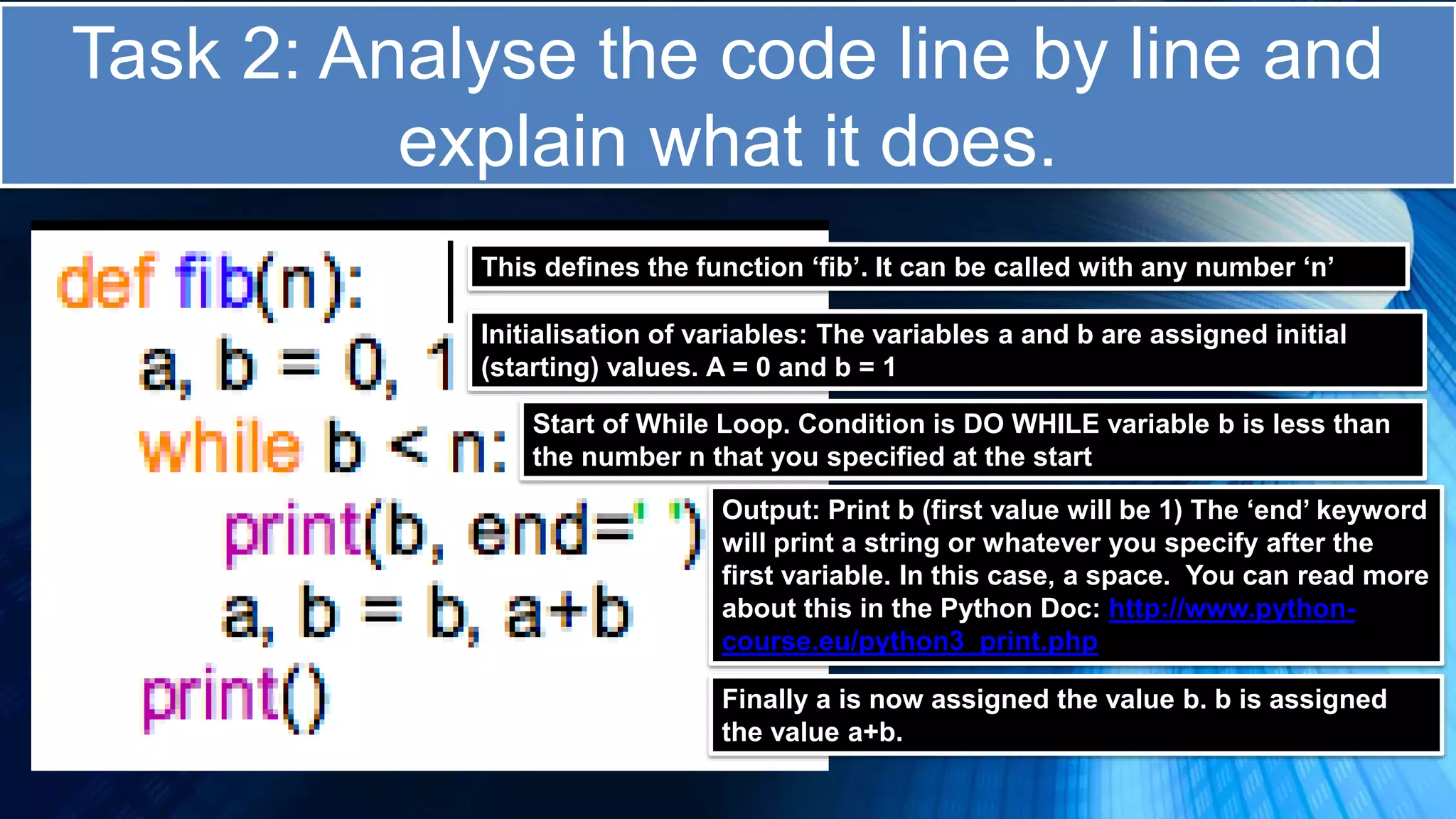
The document covers a comprehensive introduction to programming in Python, focusing on key concepts such as iteration using loops (while and for), functions, lists, and string manipulation. It includes coding tasks, theory about the Fibonacci sequence, historical context on computing, and practical challenges for learners. Various resources and suggested projects for further exploration in computer science are provided, as well as a comparison between different types of loops.