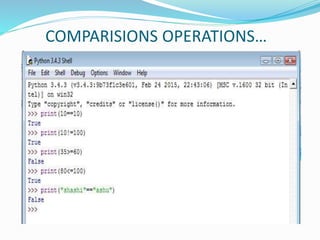
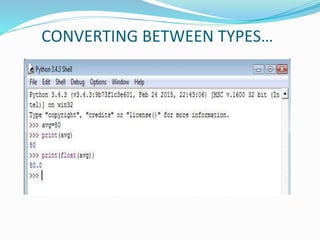
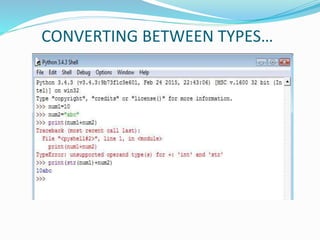
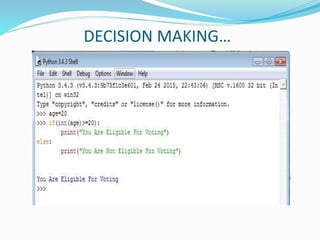
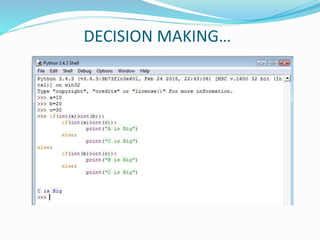
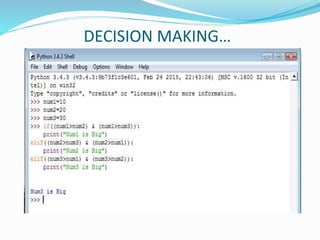
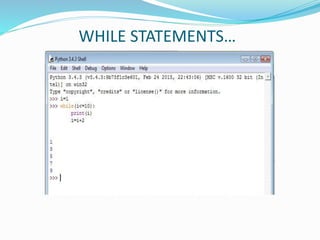
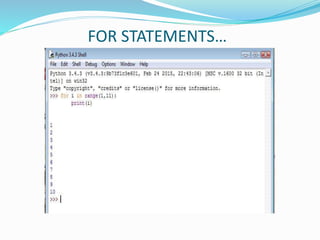
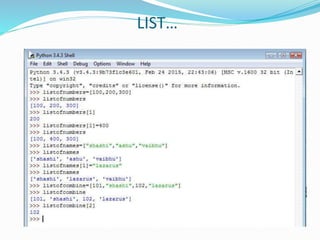
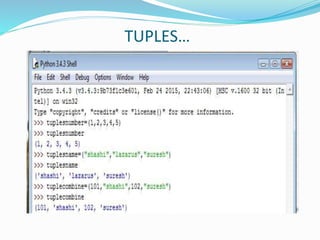
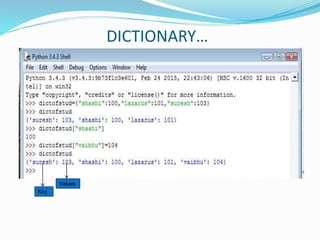
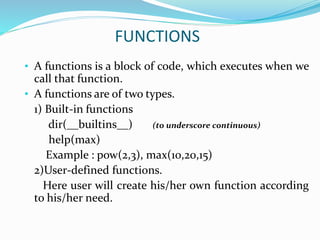
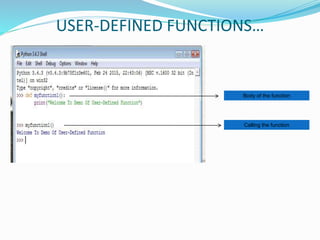
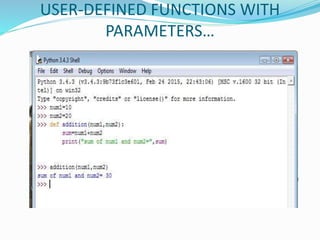
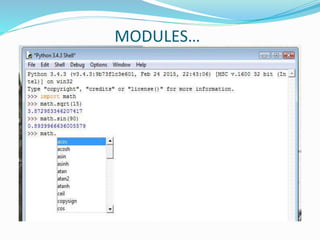
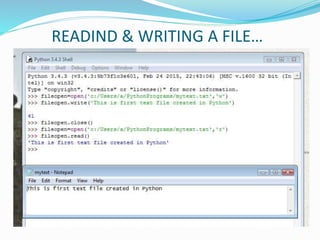
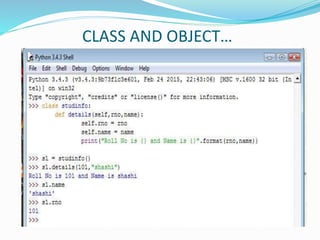
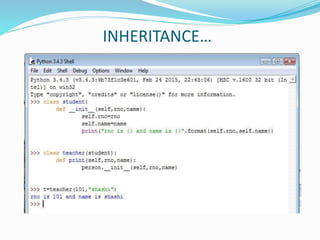
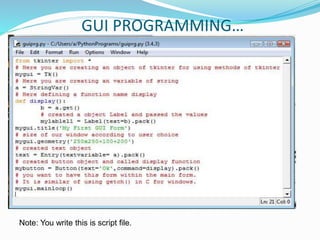
The document provides an overview of Python, including its history, applications, and characteristics as a programming language. It covers fundamental concepts such as syntax, variables, data types, decision making, loops, functions, and file handling, as well as object-oriented programming features like classes and inheritance. Additionally, it mentions resources for learning Python and the basics of GUI programming.