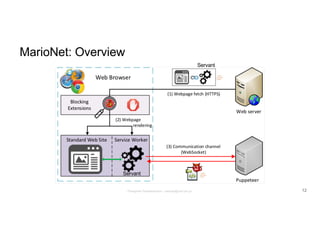
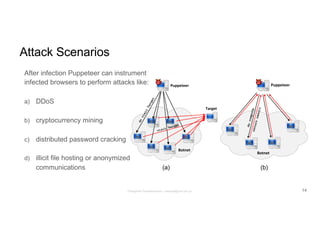
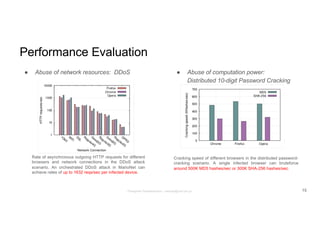
The document discusses a framework called Marionet that exploits HTML5 features to execute malicious JavaScript code persistently and stealthily through web browsers, enabling various attacks like DDoS and cryptojacking. Marionet allows attackers to maintain control over a victim's browser even after the user navigates away from the malicious site, utilizing service workers and WebSockets for covert operations. It highlights the ease of infecting users either through intentionally malicious websites or through compromised third-party content, and discusses potential countermeasures to mitigate such threats.