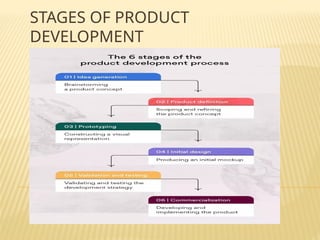
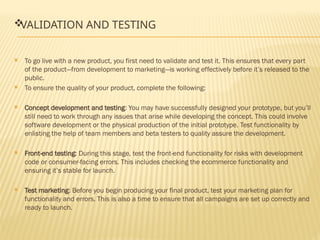
The document outlines the new product development process, emphasizing the importance of marketing activities such as idea generation, product definition, prototyping, validation, and commercialization. It details stages including defining target markets, conducting SWOT analysis, and the roles of branding, packaging, and labeling in influencing consumer perception. Effective marketing strategies are essential for attracting customers and ensuring product success in a competitive market.