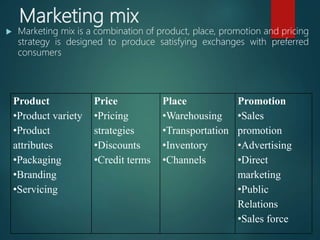
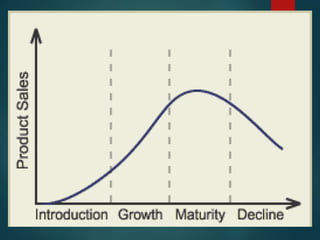
The document focuses on the marketing mix, which comprises product, price, place, and promotion strategies aimed at satisfying consumer needs. It discusses product management, planning, development, and the product life cycle stages—introduction, growth, maturity, and decline. Additionally, it covers various pricing strategies, distribution channels, and promotional methods that businesses can utilize to successfully market their products.























![ Odd-even pricing:
(eg: fixing Rs 499 for Rs 500 ranged products)
Dual pricing:
(different price in different market)
Psychological pricing:
[higher price indicates a higher level of quality & vice versa]
Prestige pricing:
also known as premium pricing.
Price lining:
(eg- car seller come up with 3 verities of pricing for same model,
Movie tickets)
Based on customer](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/marketingmix-200414100142/85/Marketing-mix-26-320.jpg)








