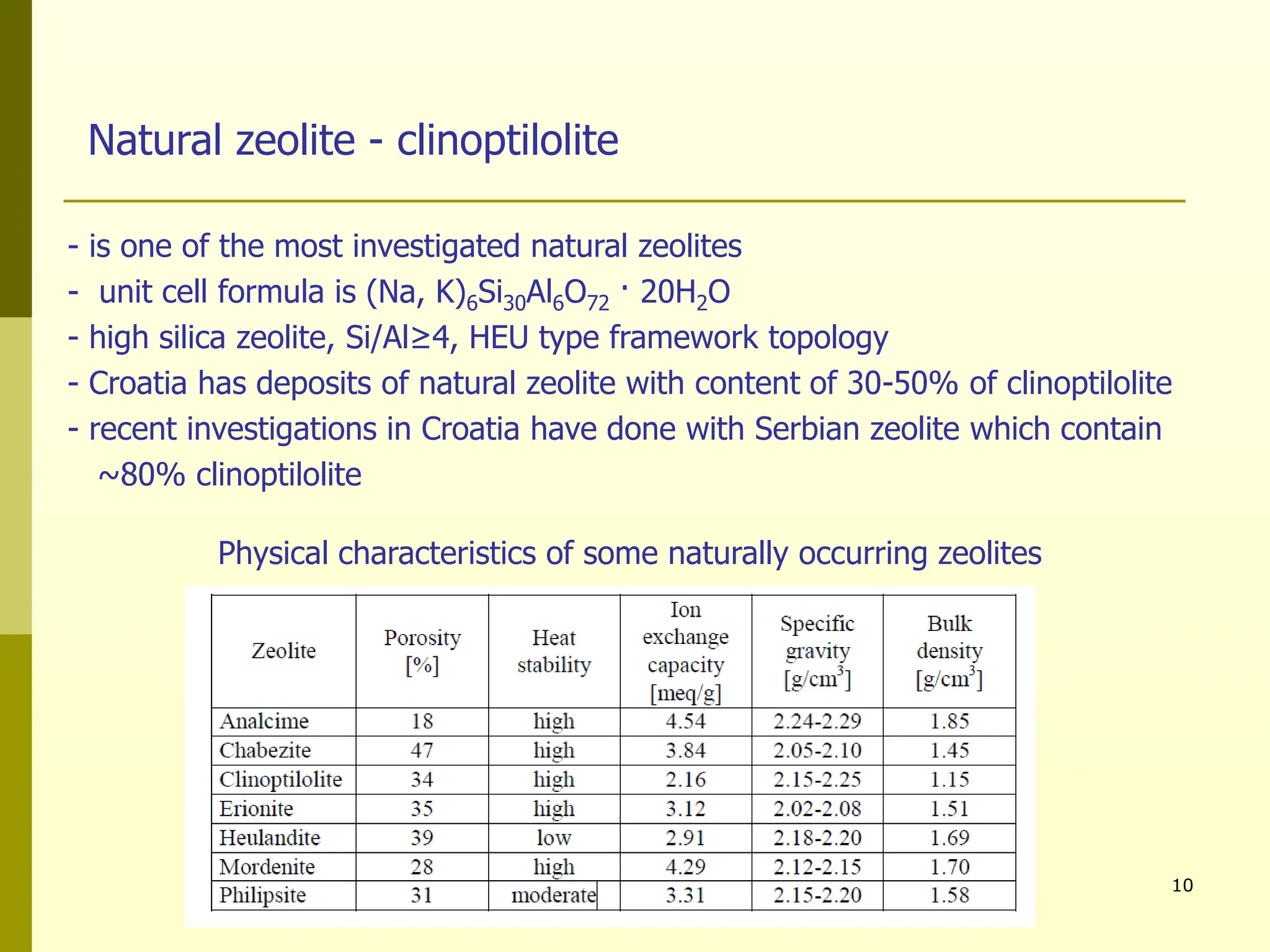
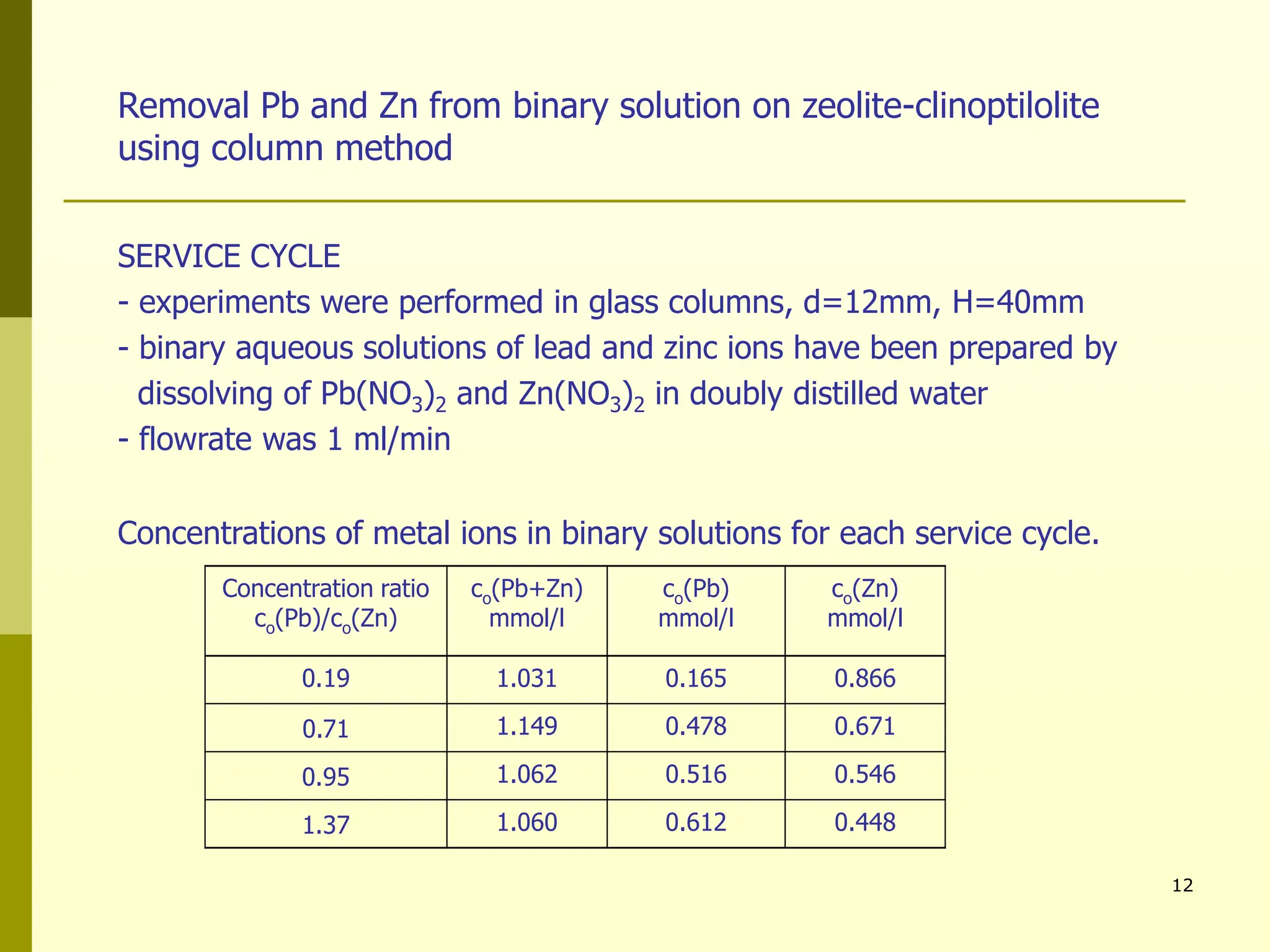
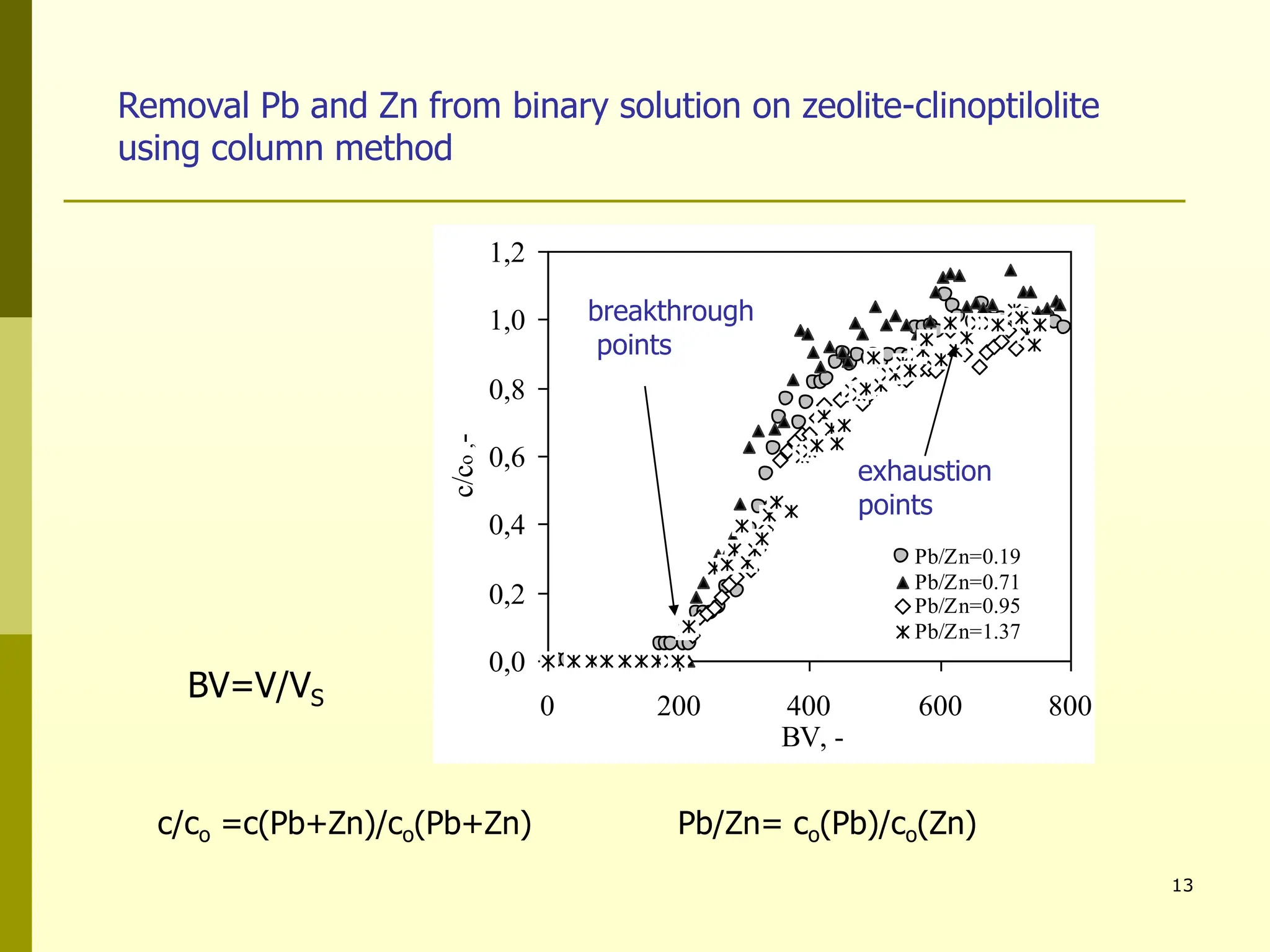
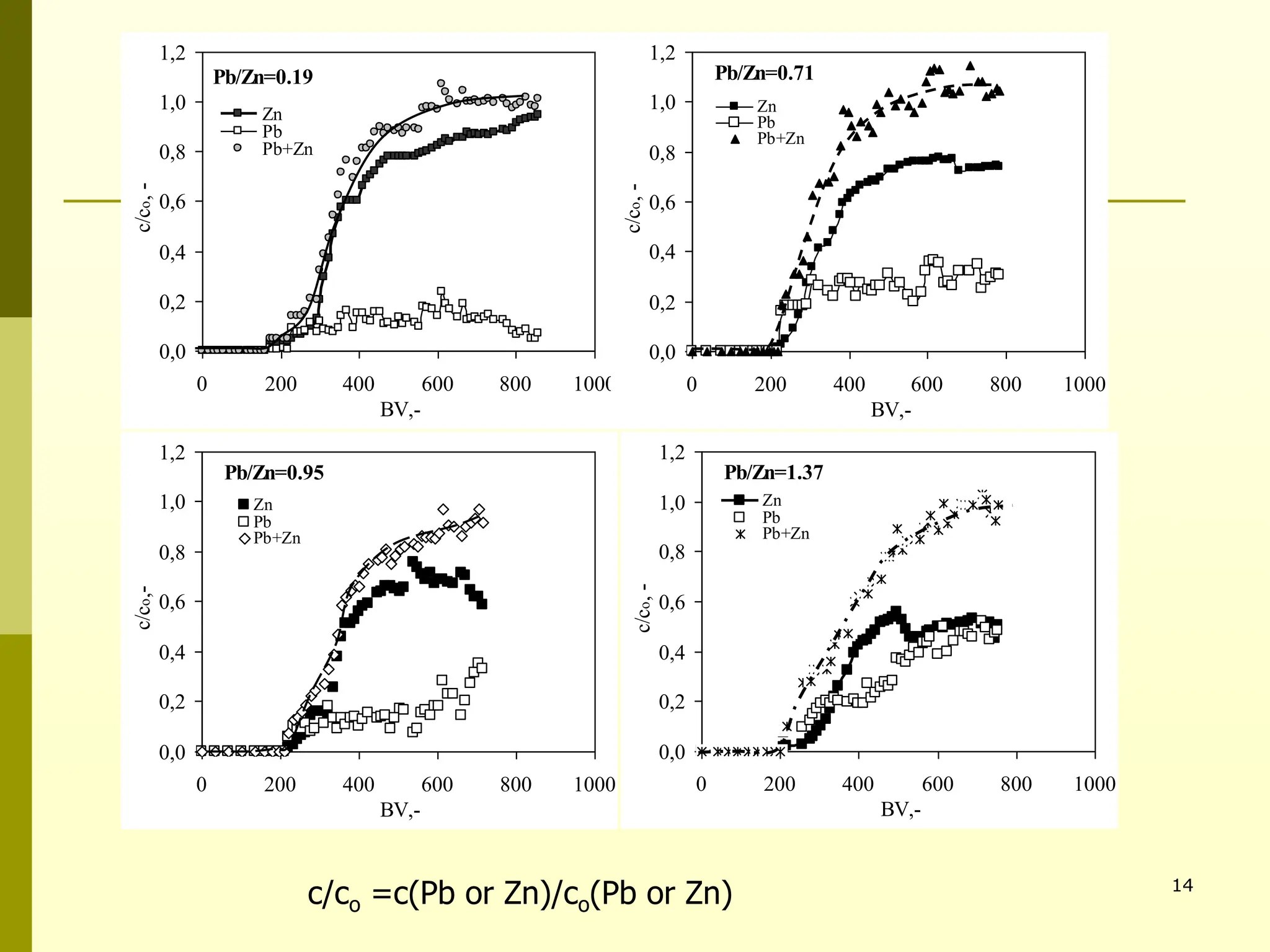
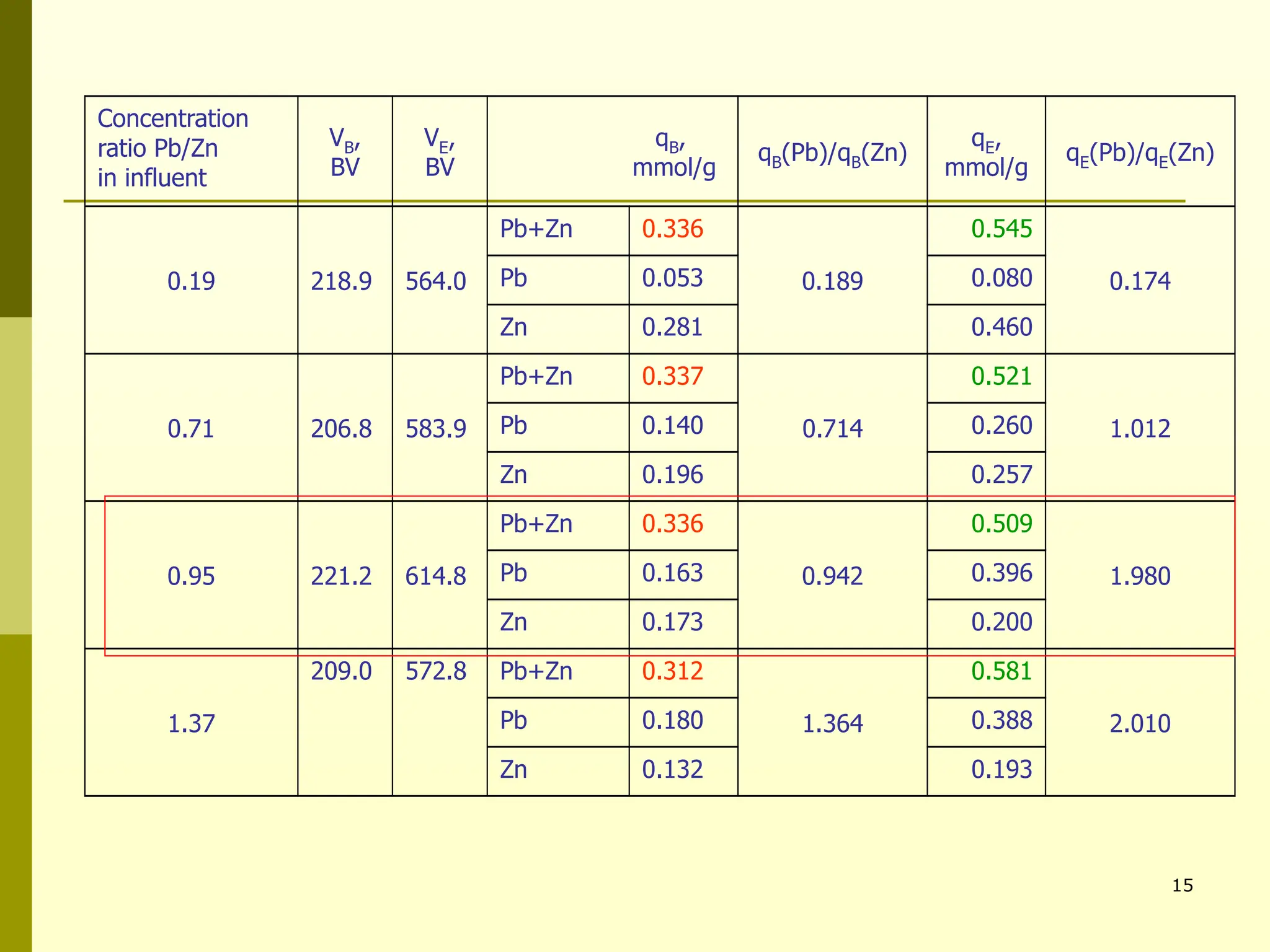
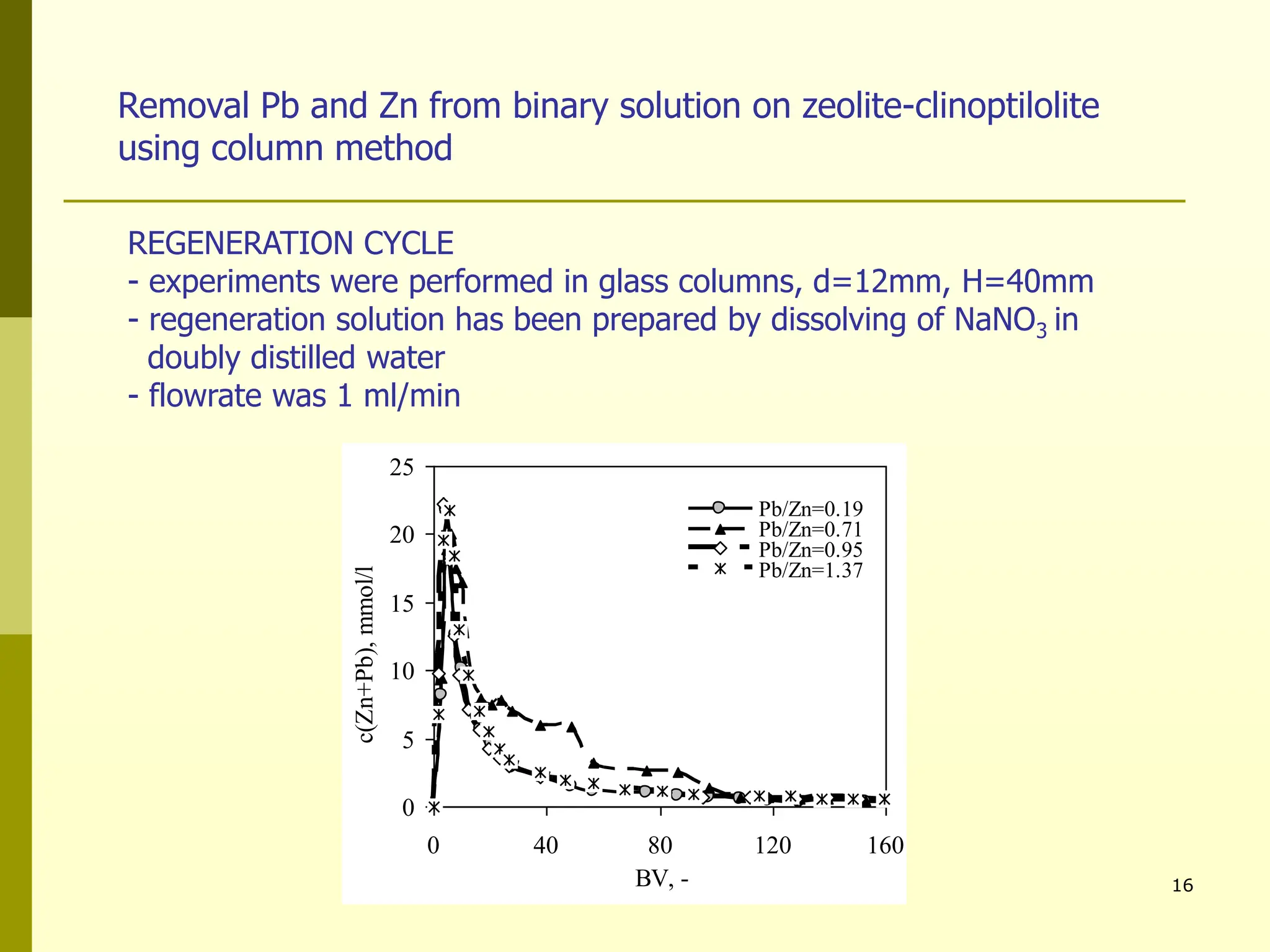
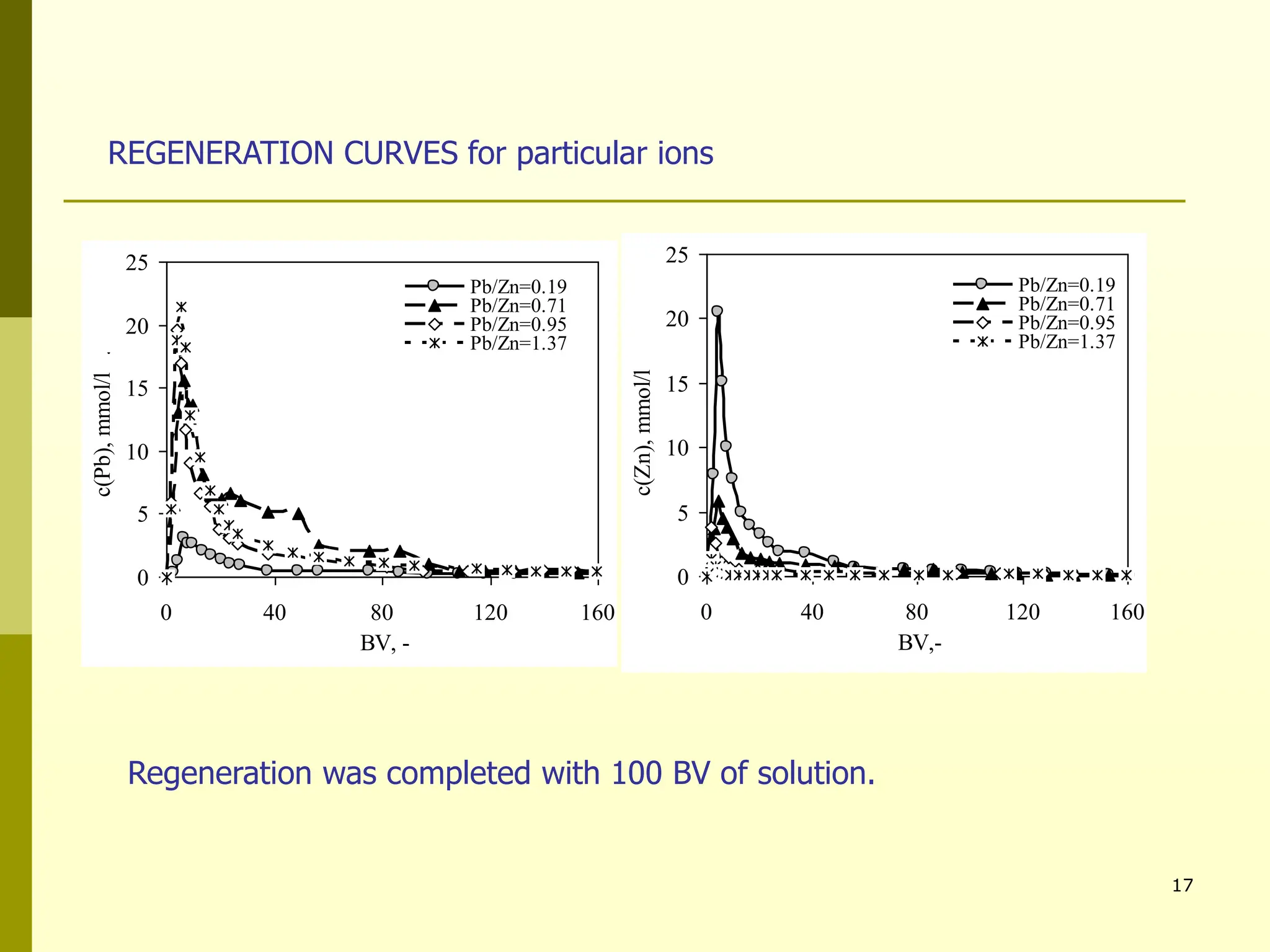
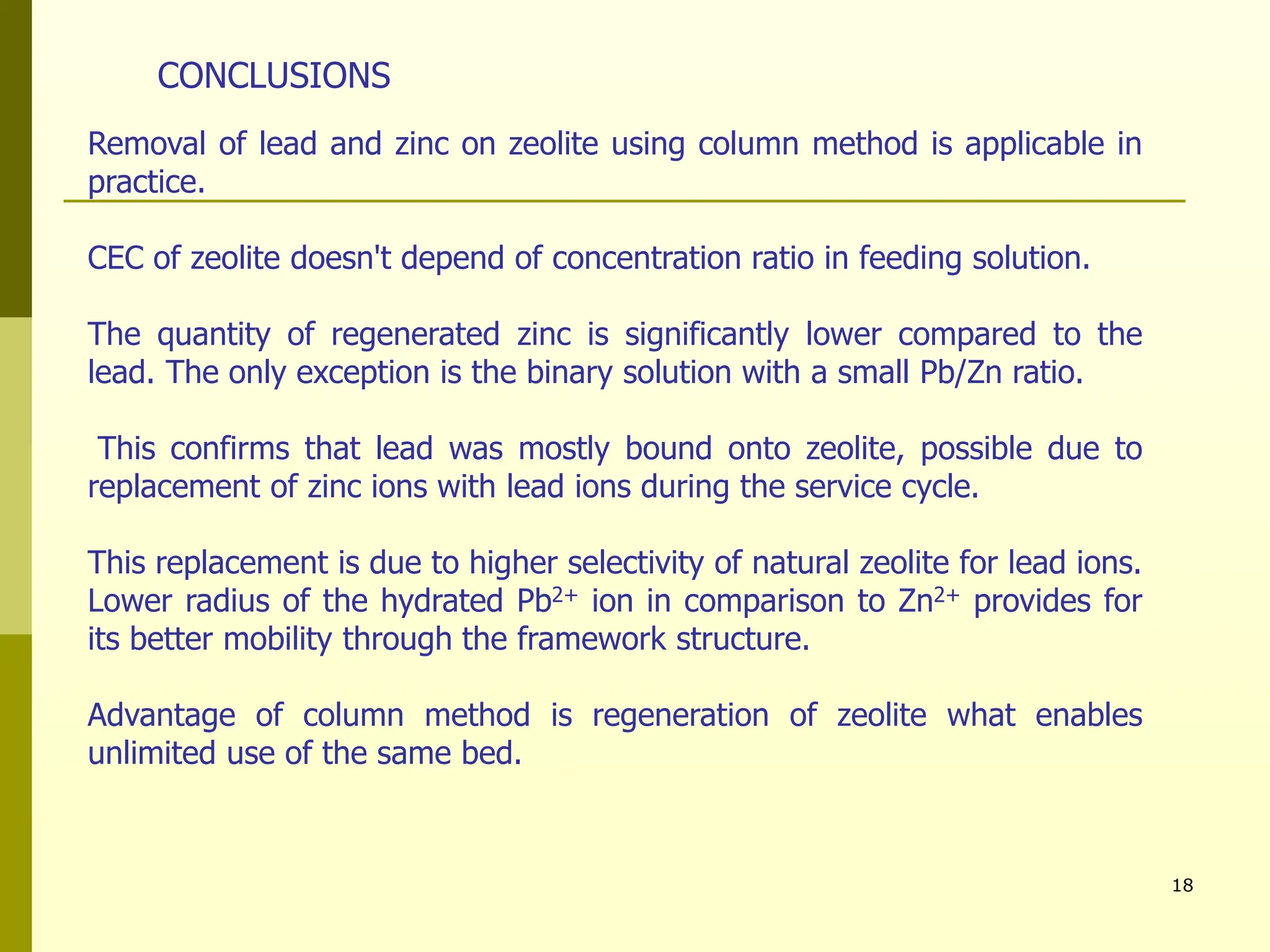
The document summarizes research on using natural zeolites for removing lead and zinc from binary solutions. Column tests were conducted with clinoptilolite zeolite to treat solutions with varying concentration ratios of lead to zinc. The zeolite effectively removed both metals, with lead being preferentially bound and more readily regenerated. The column method proved applicable in practice and allowed unlimited reuse of the zeolite bed through regeneration. The research aims to explore natural zeolites for water protection applications.