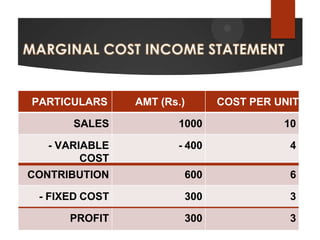
Marginal costing is a technique used to determine the cost of producing one additional unit of a product. It involves classifying costs as either fixed or variable. Fixed costs remain constant regardless of production levels, while variable costs change directly with the production volume. Marginal costing only considers variable costs in the cost per unit calculation to determine contribution. Contribution is the amount of sales revenue left over after deducting variable costs and represents the funds available to cover fixed costs and profit. This technique helps businesses with decisions like production levels, bulk order pricing, and break-even analysis.