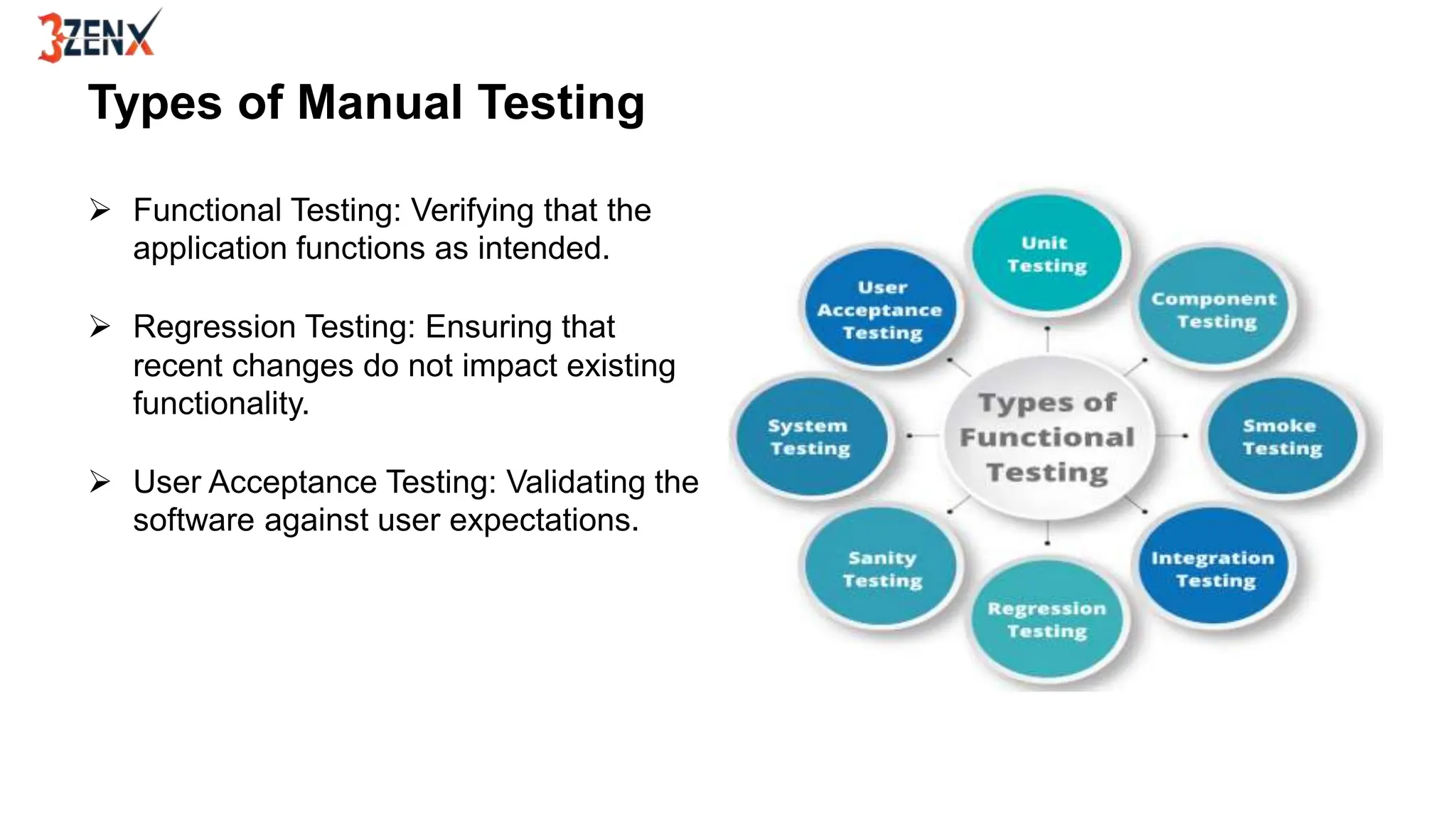
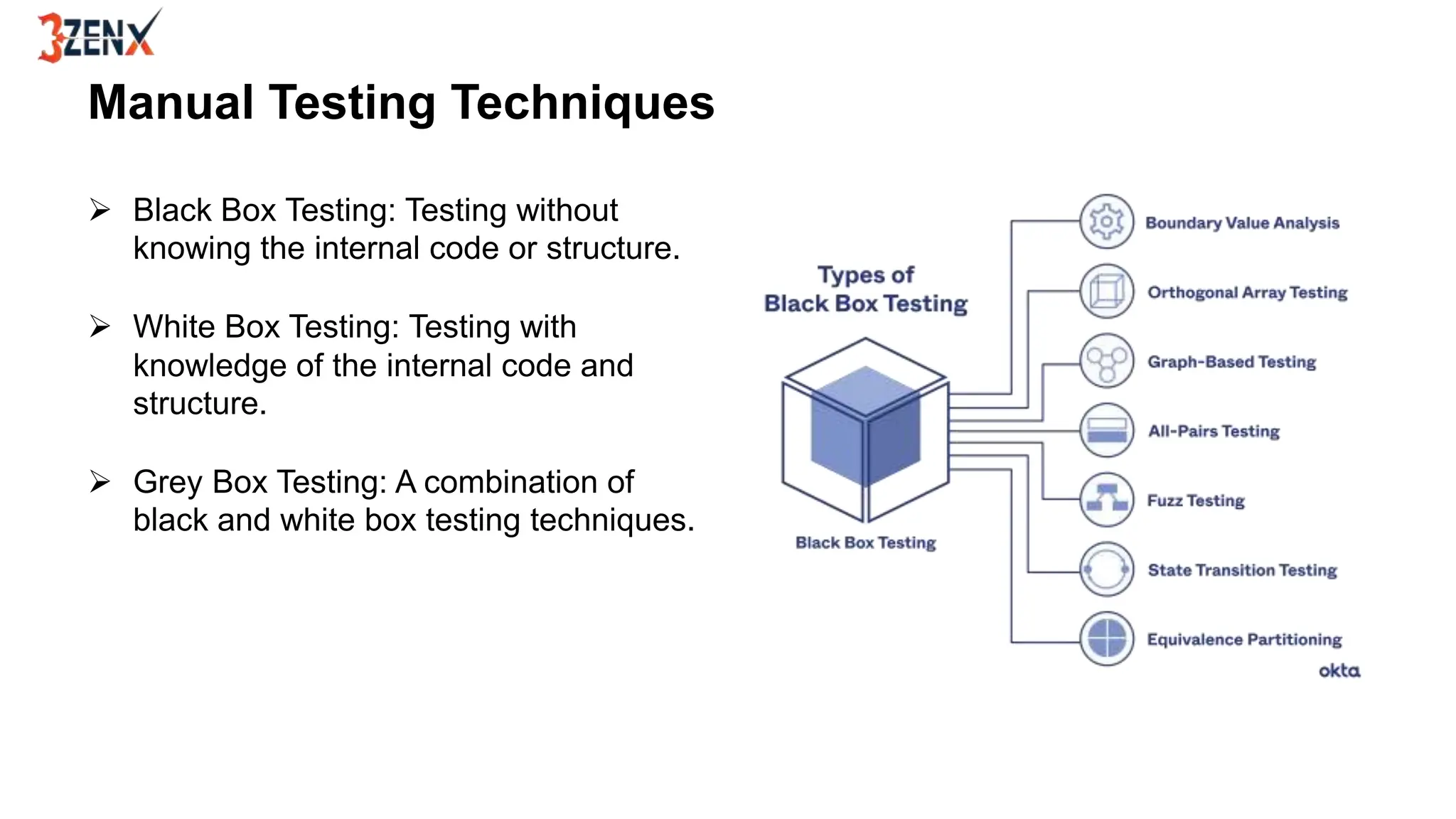
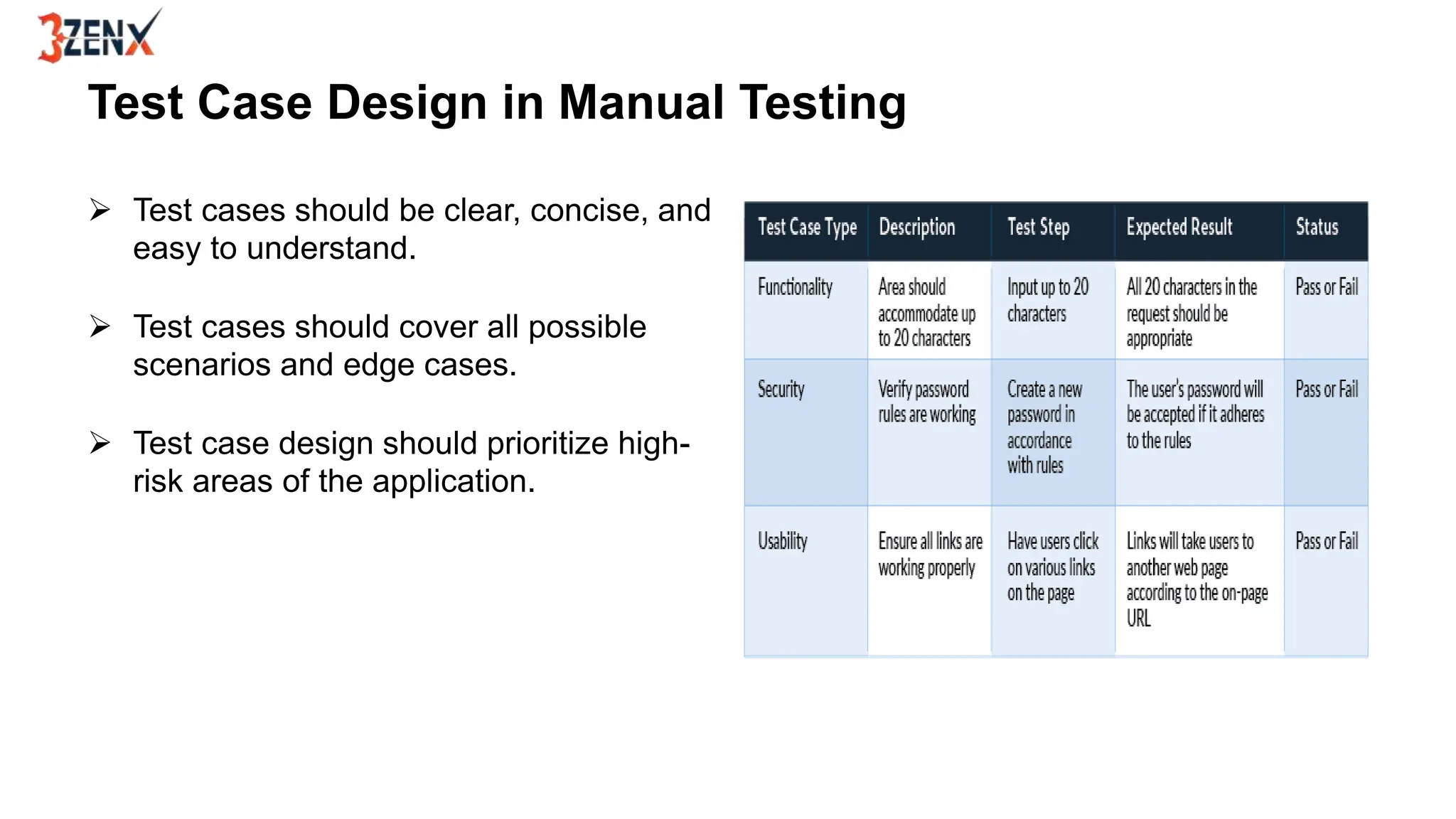
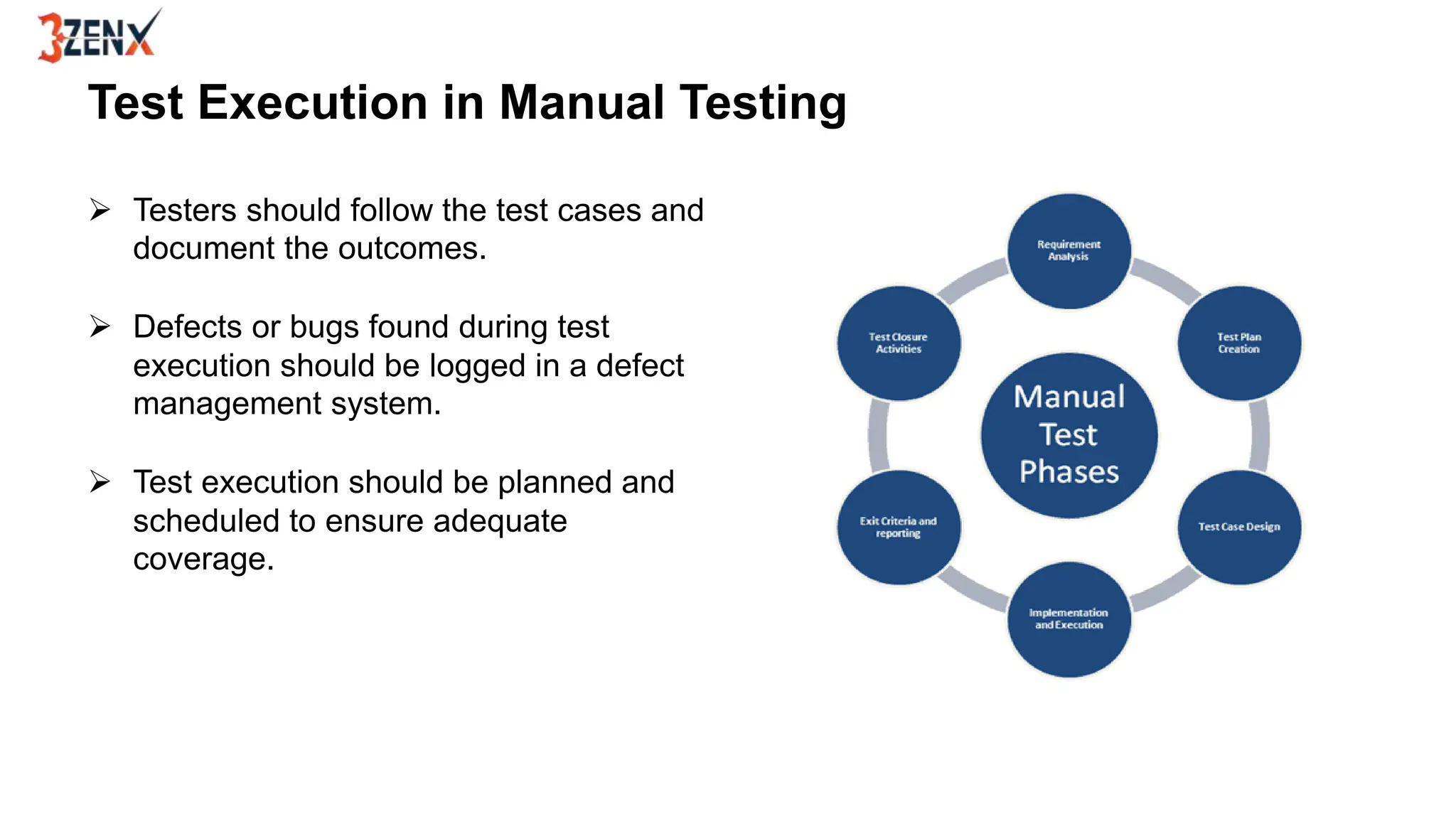
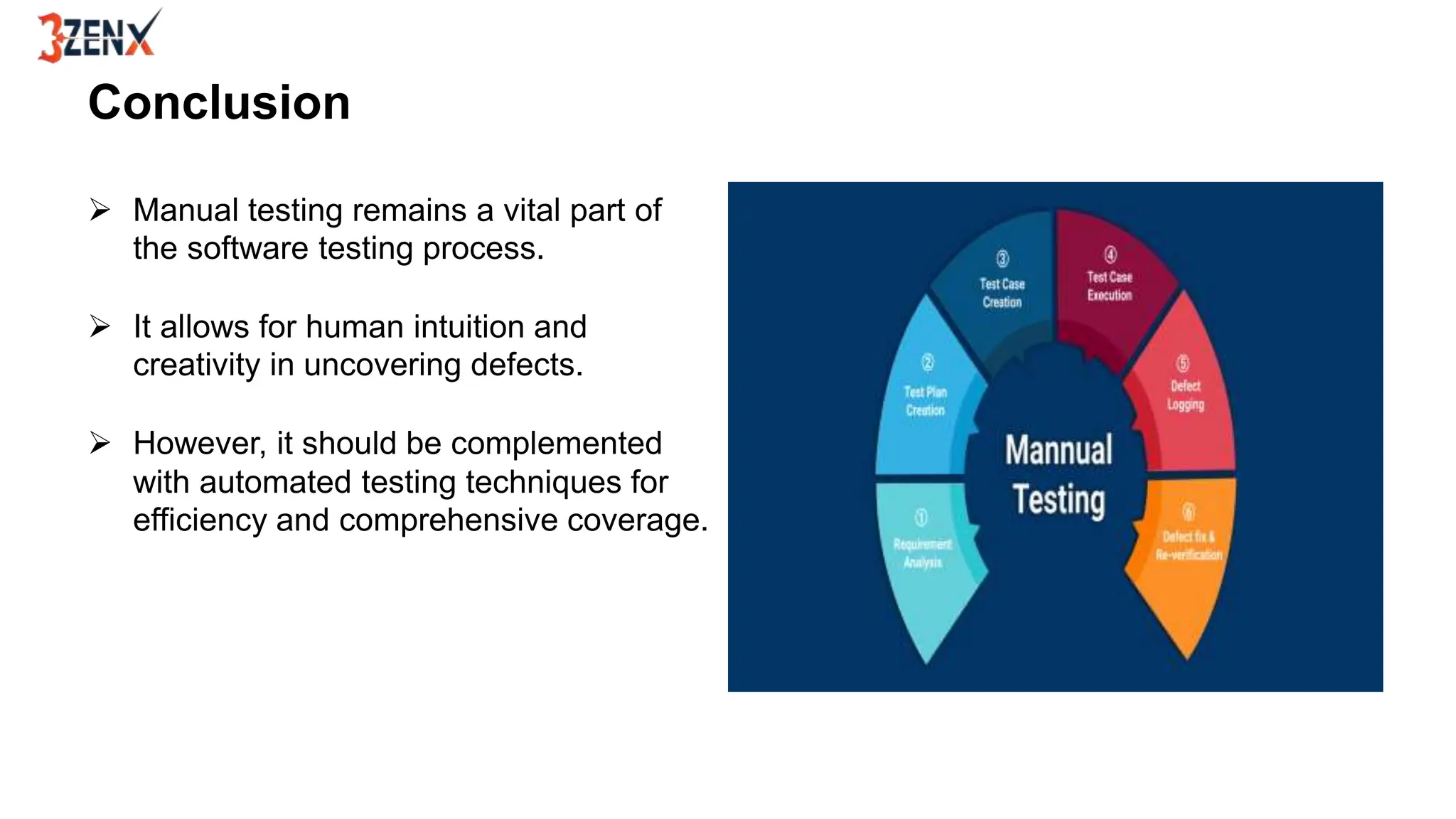
Manual testing is a technique where human testers execute test cases to find defects in software applications, ensuring quality and functionality. It includes various types such as functional, regression, and user acceptance testing, and employs techniques like black box, white box, and grey box testing. While manual testing provides valuable insights through human intuition and flexibility, it should be complemented by automated testing for efficiency.