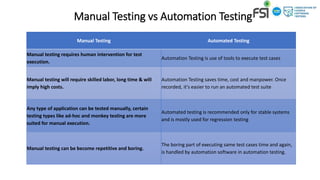
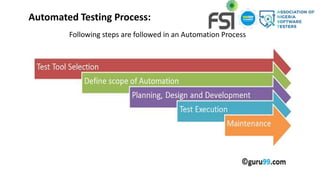
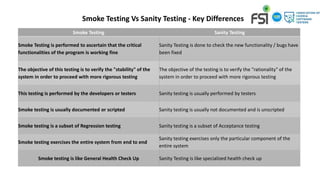
Manual testing involves manually executing test cases without automation tools. It is necessary to check automation feasibility before automating tests. There are two main categories of testing: functional testing which tests features/functionality, and non-functional testing which verifies attributes like performance. Automation testing uses tools to execute test cases and saves time/costs compared to manual testing. Common types of testing include unit, integration, system, smoke, sanity, and regression testing which help ensure quality.