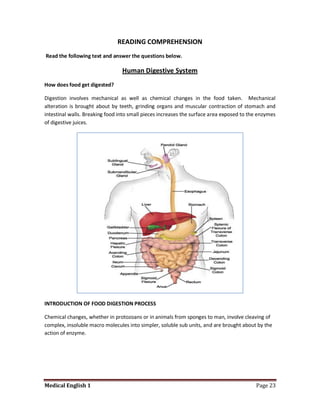
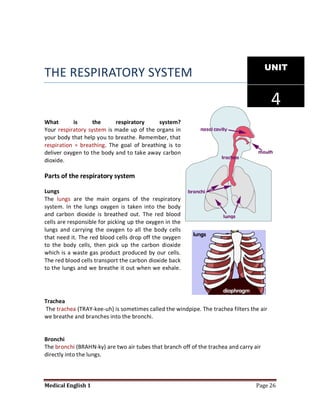
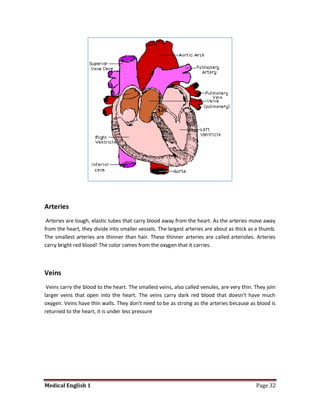
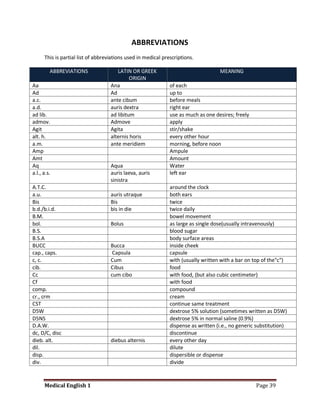
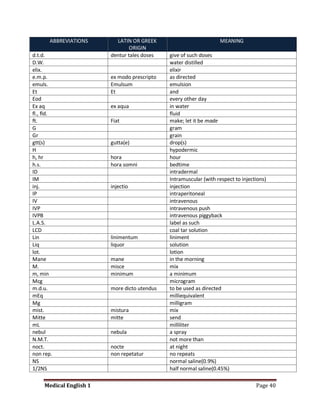
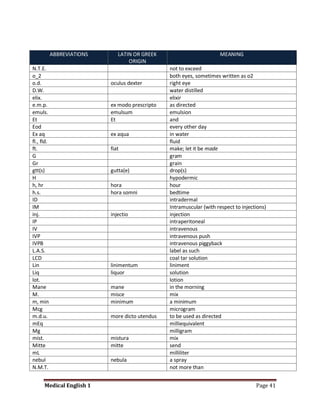
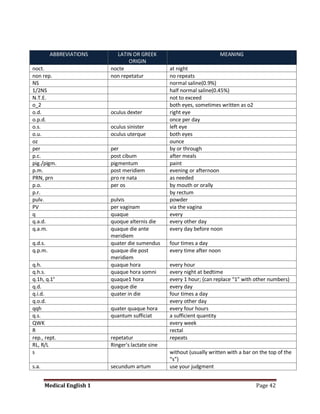
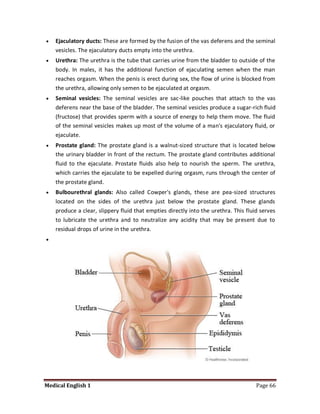
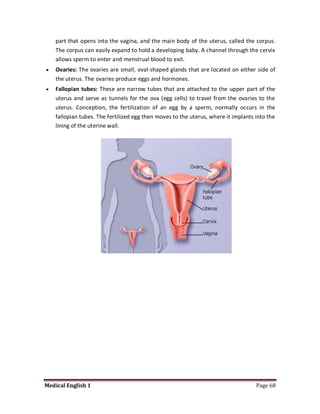
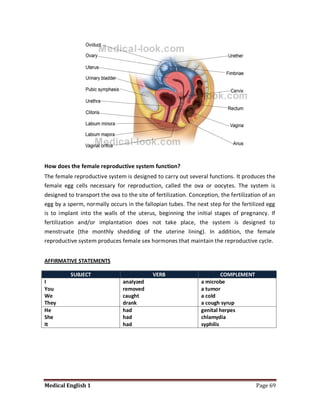
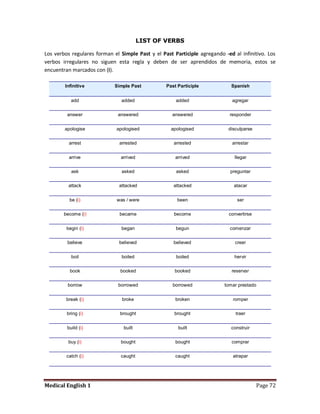
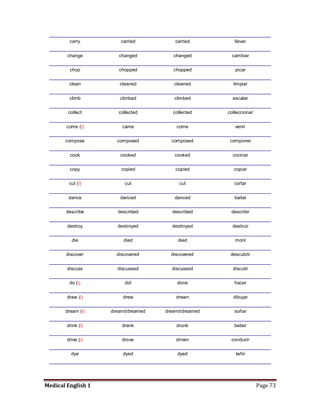
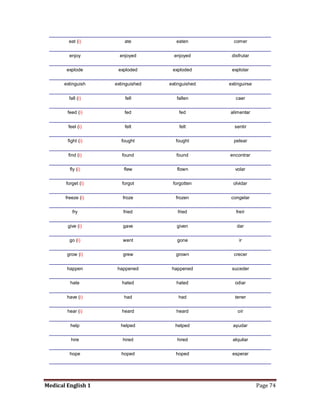
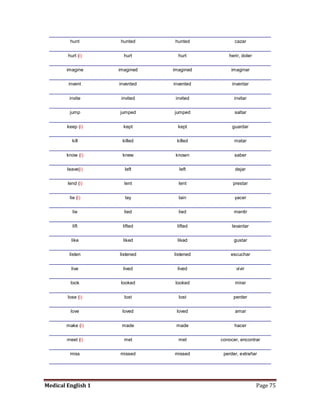
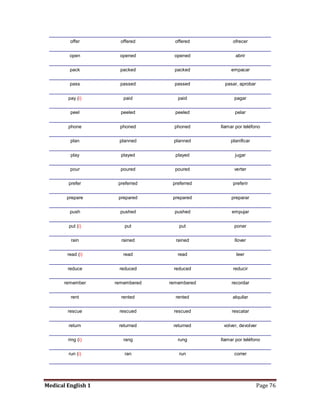
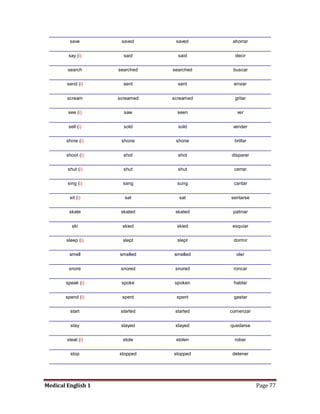
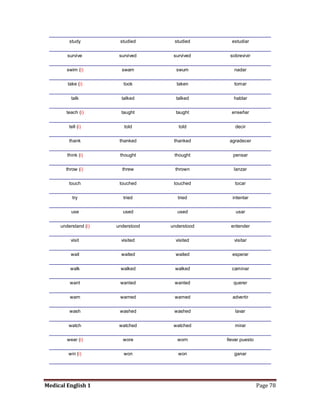
Medical specialists are experts in specific fields of medicine or diseases. They treat particular parts of the body or focus on certain illnesses. Family doctors maintain lists of local specialists and can refer patients to the appropriate one for each medical issue. Many specialists require a referral from a primary care physician before seeing a patient. Common types of specialists include those focused on the stomach, heart, and diseases like AIDS.