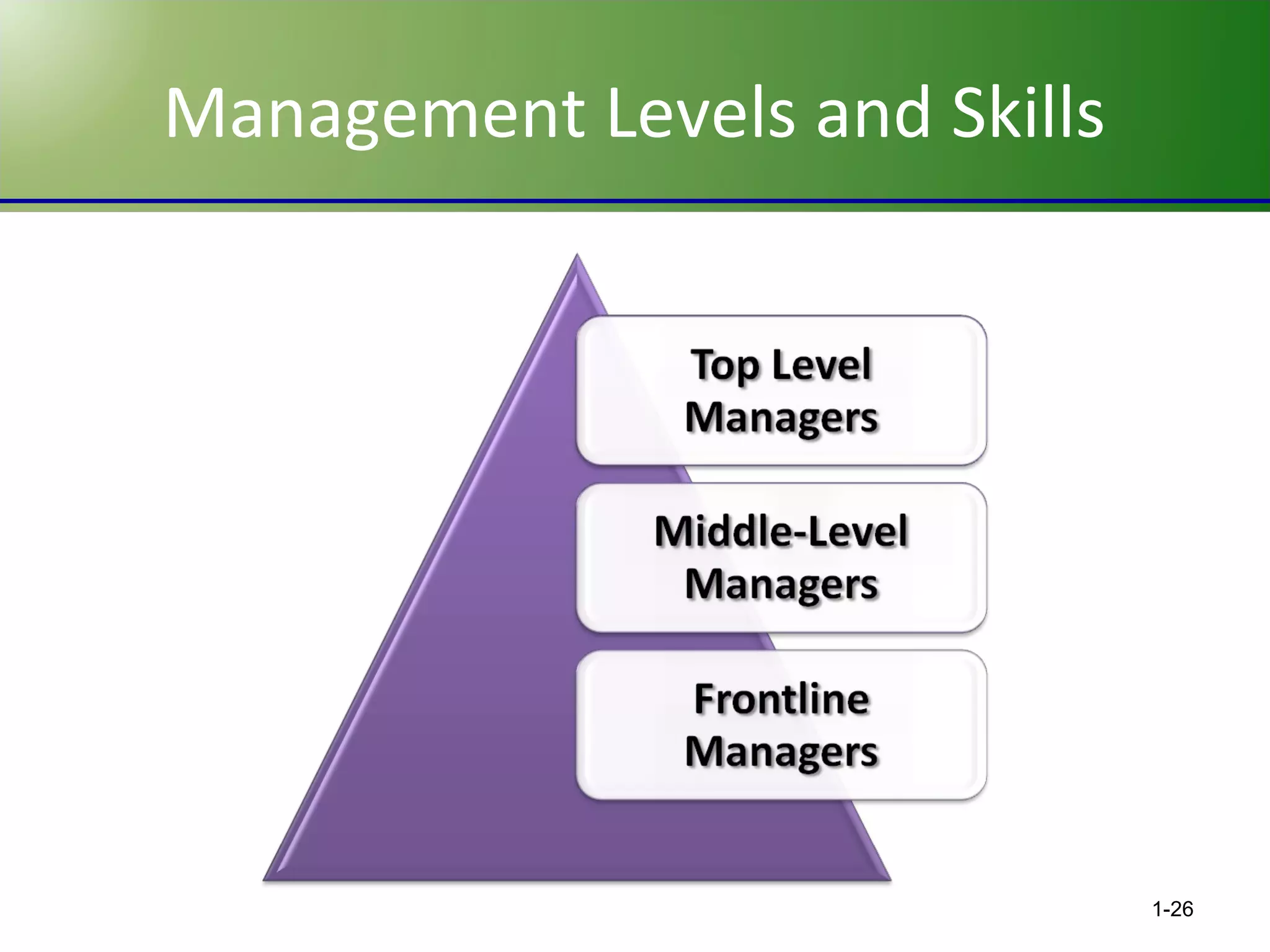
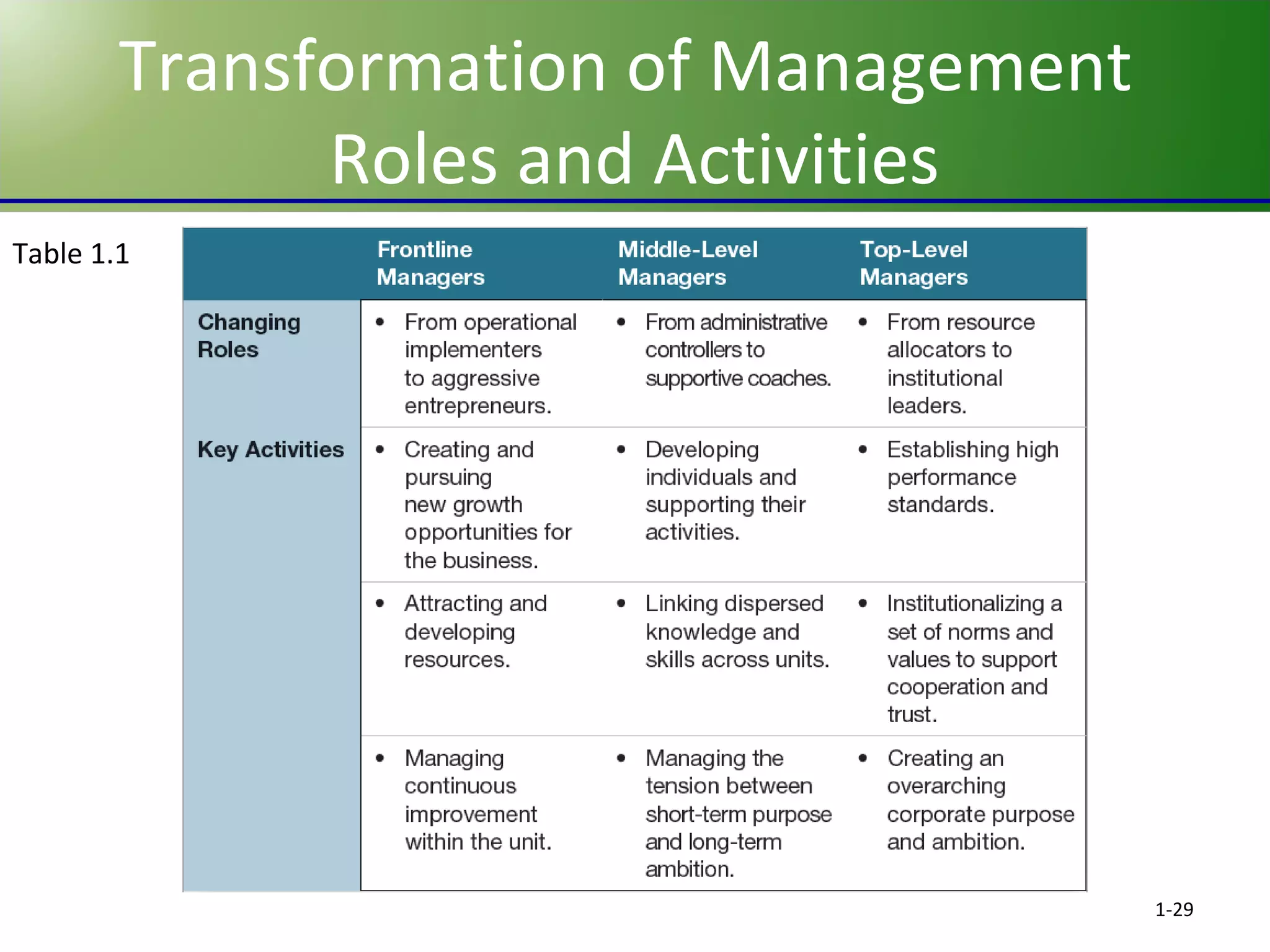
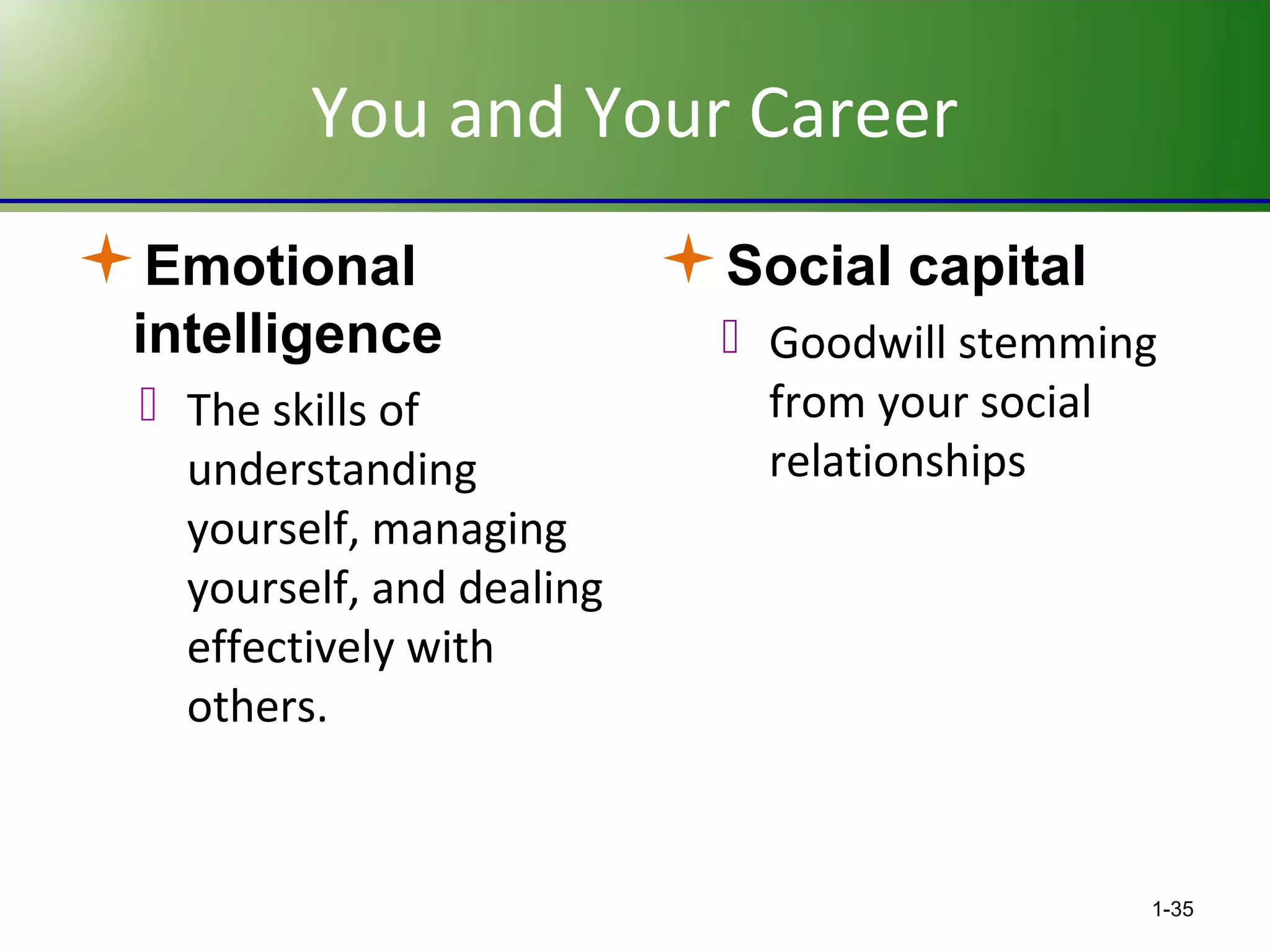
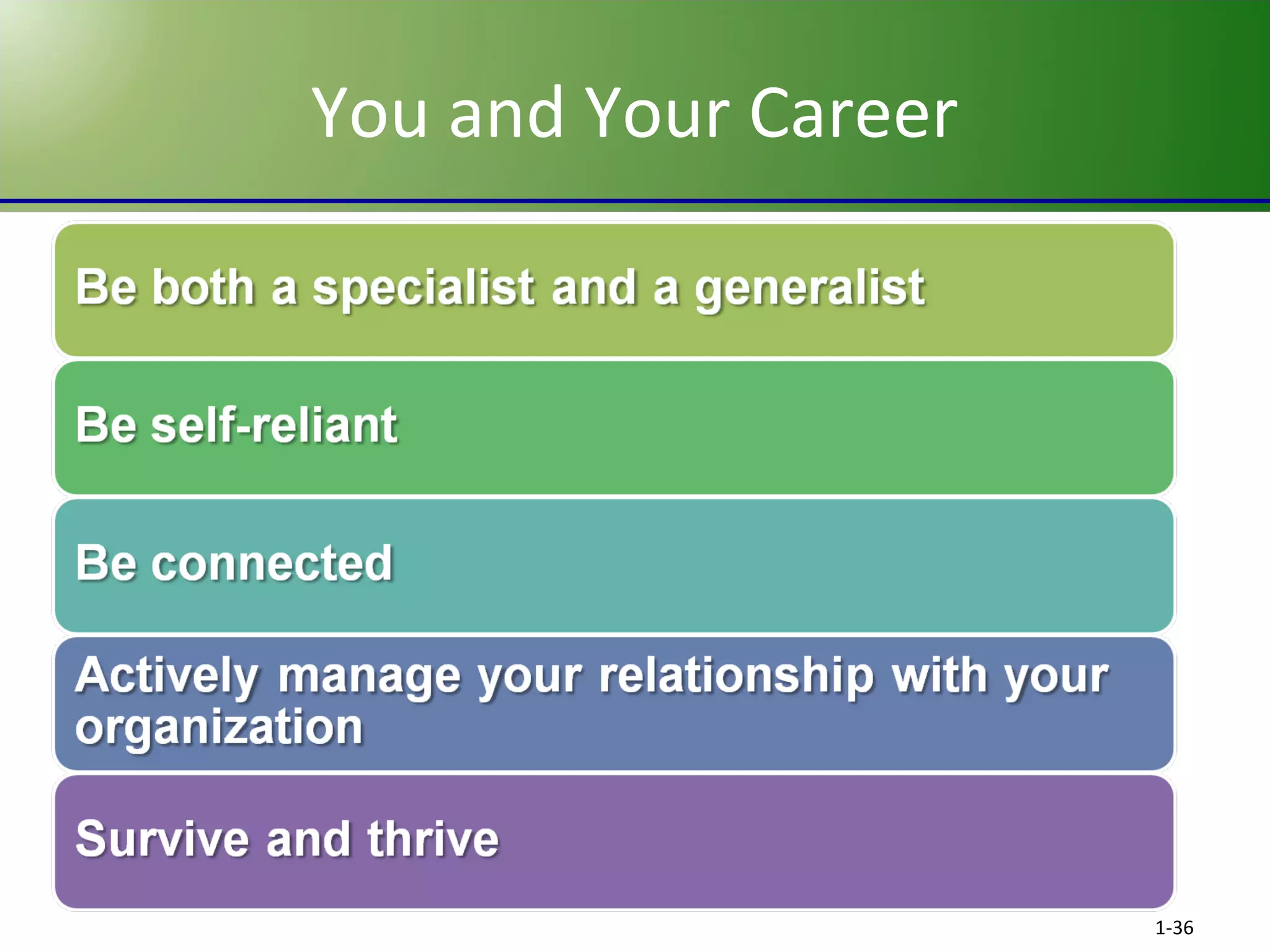
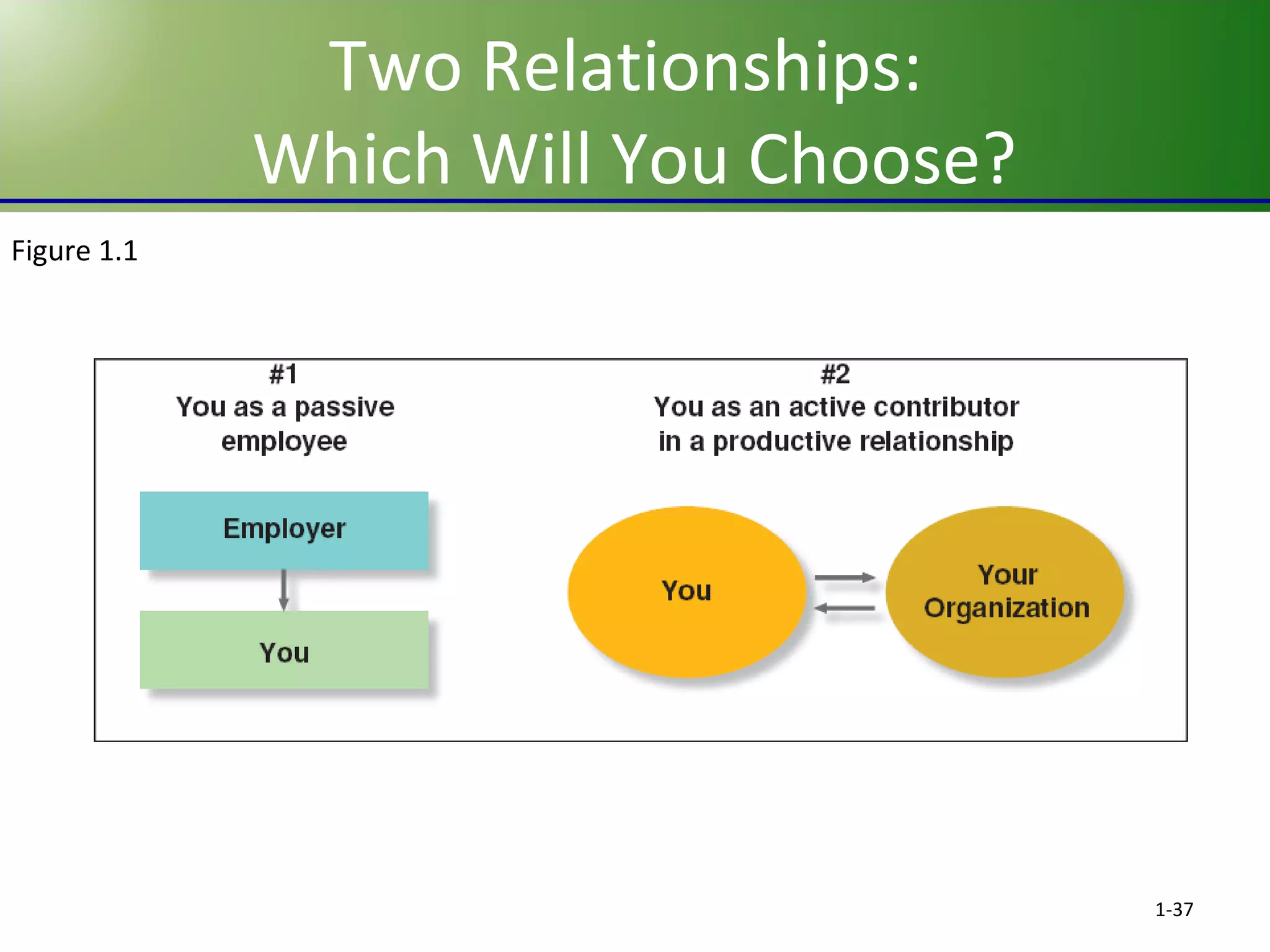
This chapter discusses the evolving challenges of management in today's globalized and technology-driven business environment. It outlines the key sources of competitive advantage such as innovation, quality, speed, service, and cost competitiveness. It also describes the core management functions of planning, organizing, leading and controlling. Additionally, it compares management skills needed at different organizational levels and emphasizes interpersonal skills for effective management. Finally, it stresses the importance of self-management and social relationships for career success.