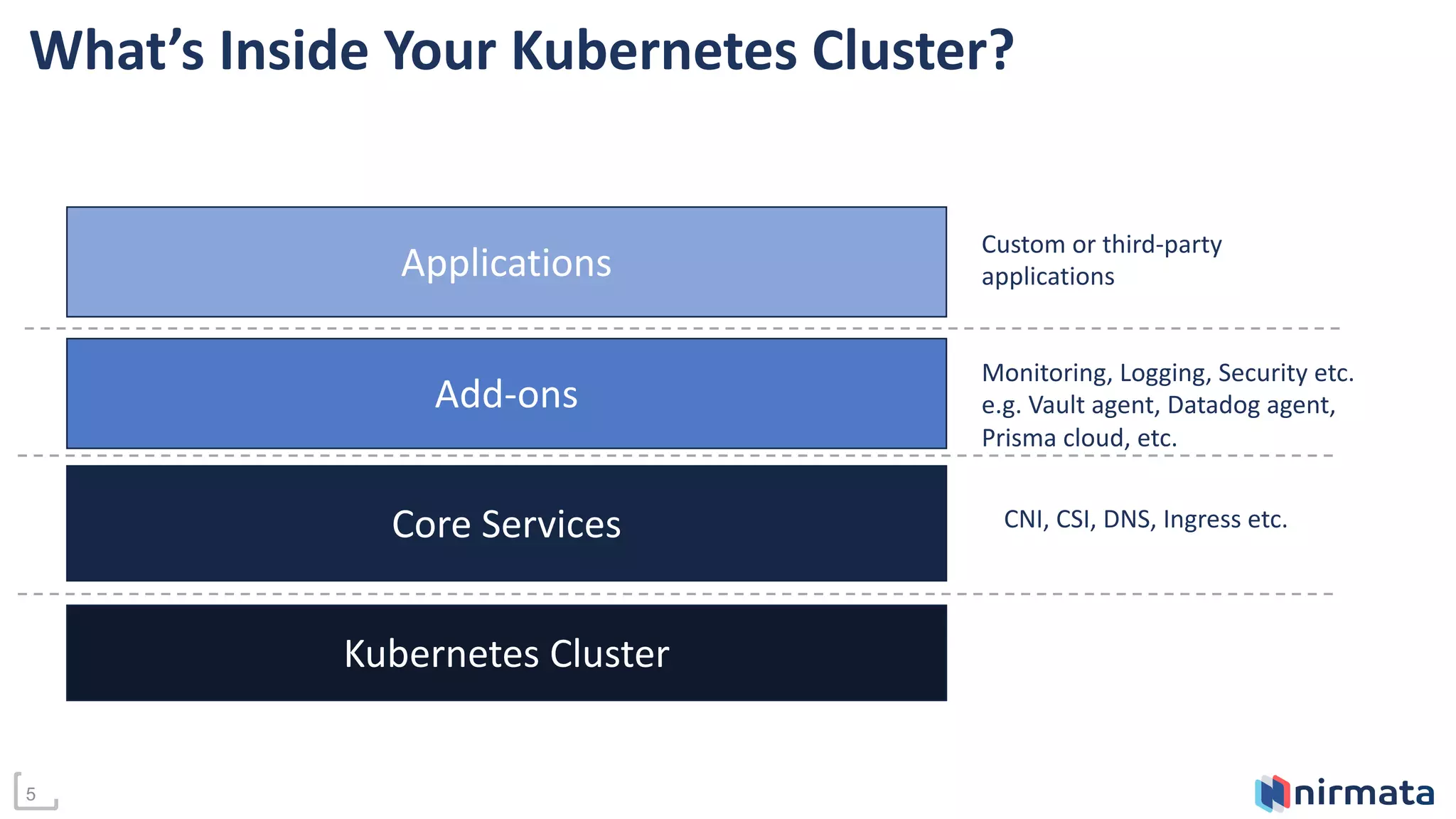
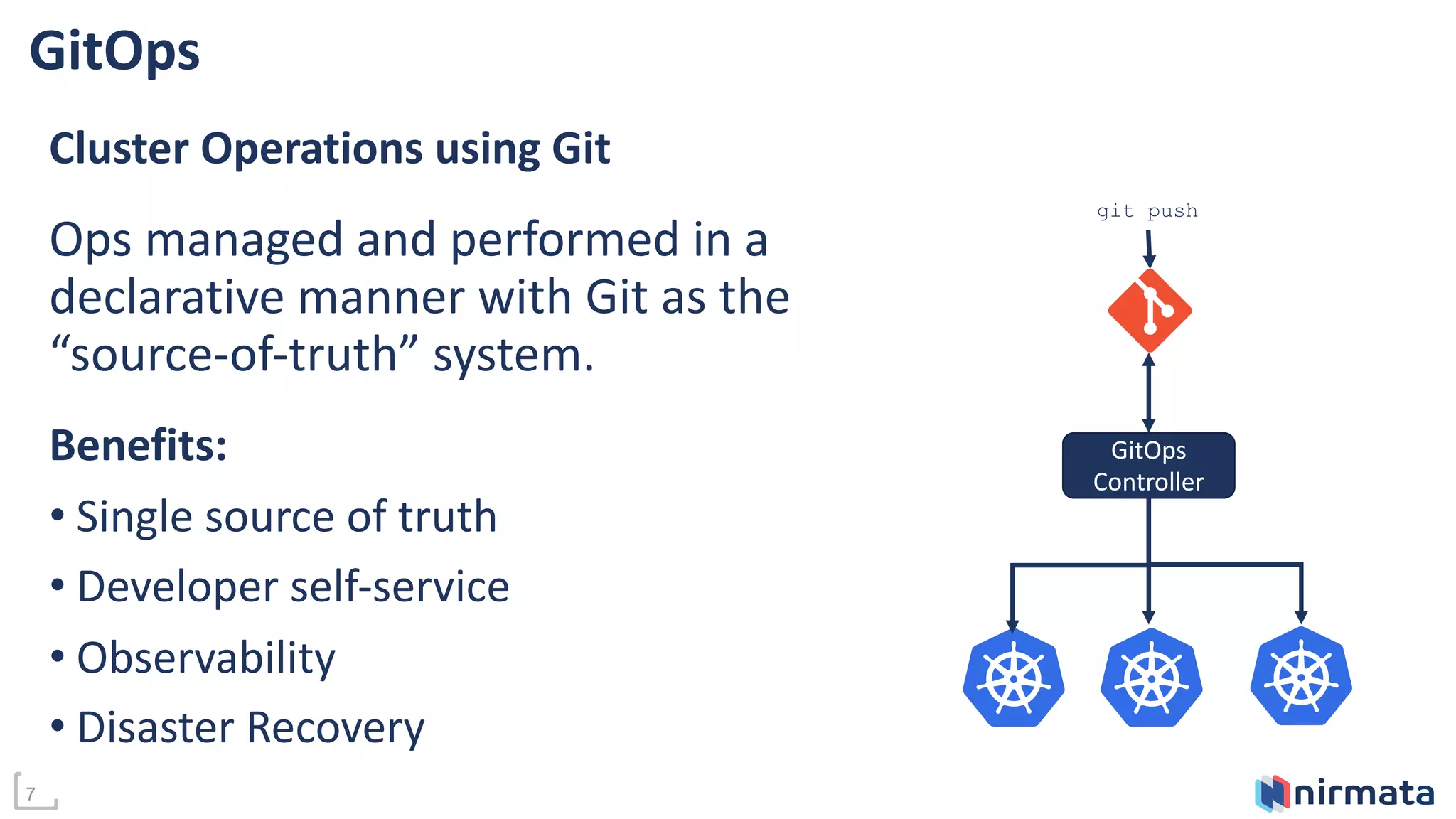
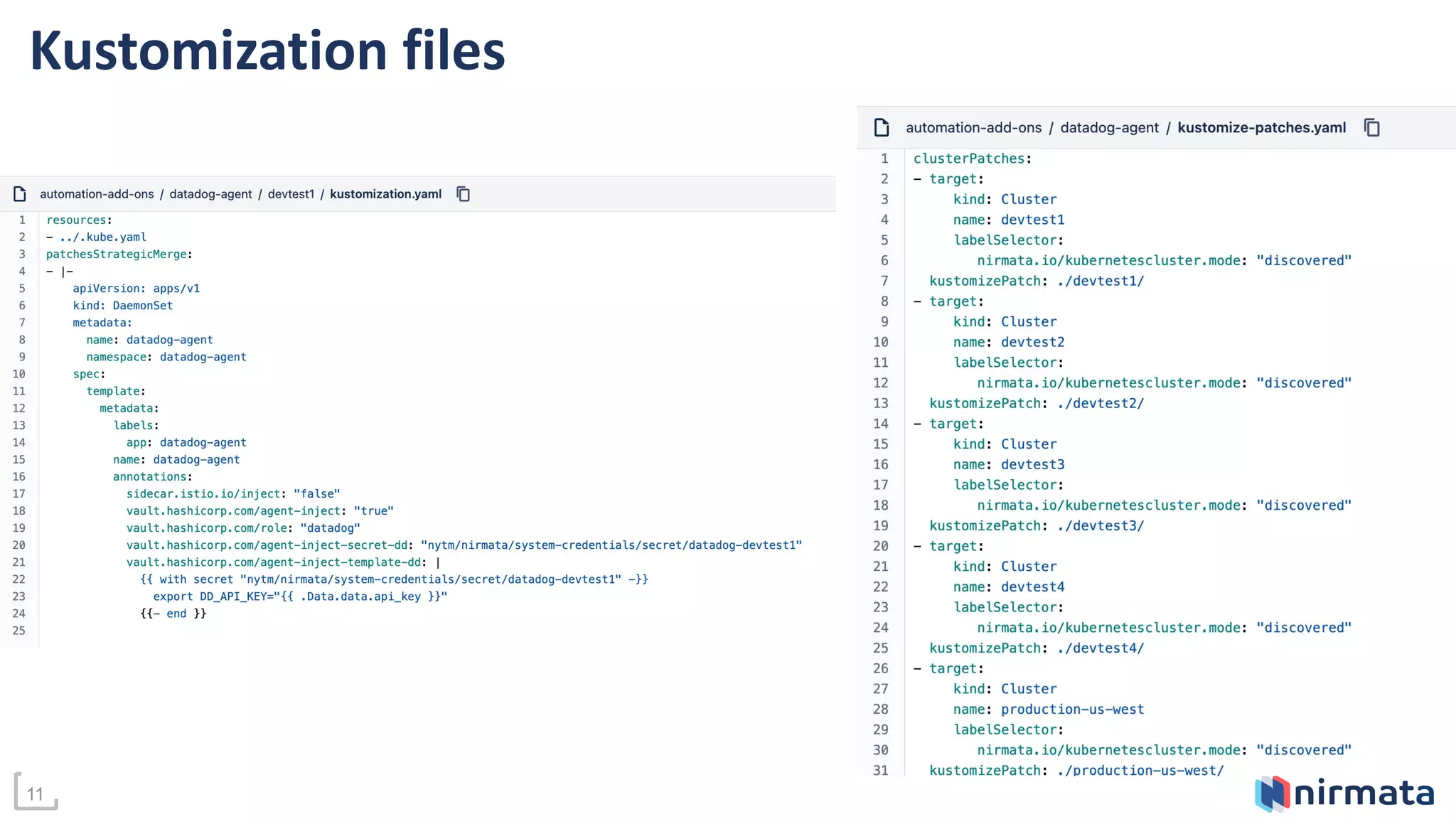
This document discusses managing add-ons across Kubernetes clusters. It defines add-ons as standardized services like monitoring, logging, and security that need to be available in every cluster. While GitOps is useful for cluster operations, it has limitations for add-on management across multiple clusters. The document proposes using Kustomize along with a central secrets store like Vault to fully automate add-on deployment and updates. It suggests GitOps controllers can further streamline add-on management by applying configurations per target cluster. A demo is provided to illustrate how Kustomization files can be used to reproduce YAML configurations for add-on deployment on any cluster.