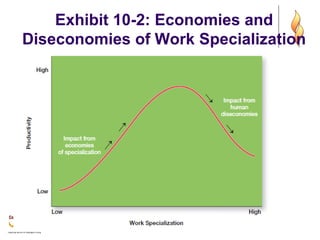
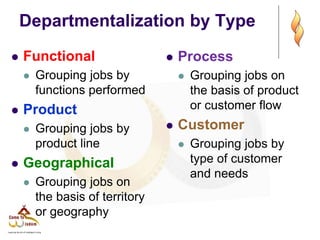
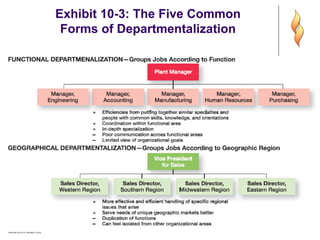
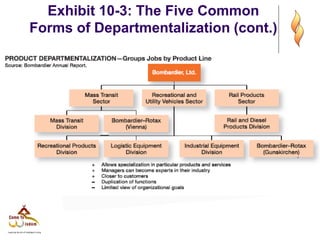
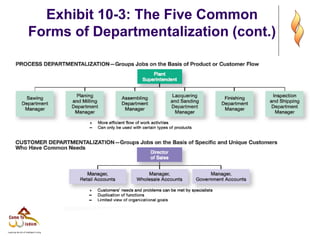
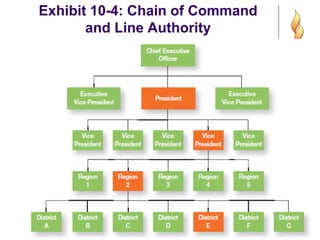
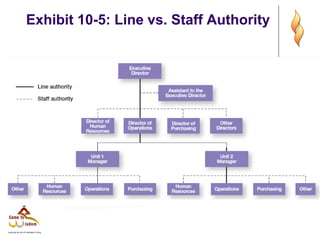
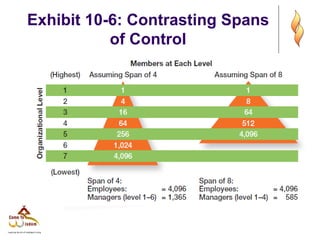
This document provides an overview of organizational structure and design. It discusses key elements of organizational structure, including work specialization, departmentalization, chain of command, span of control, and centralization vs. decentralization. The document also defines these various concepts and provides examples to illustrate different types of structures. It aims to explain how arranging jobs and dividing work accomplishes an organization's goals through formal structure.