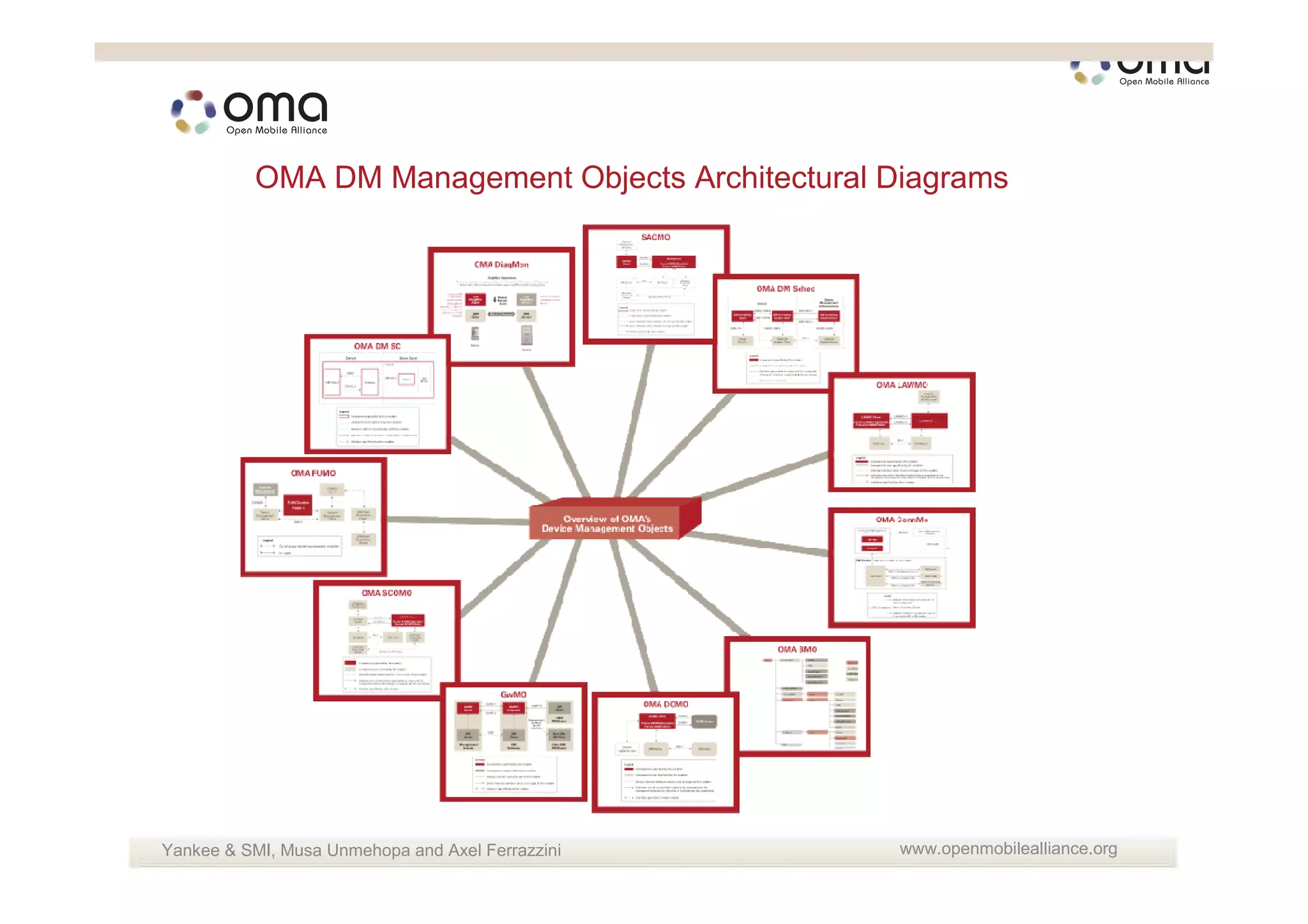
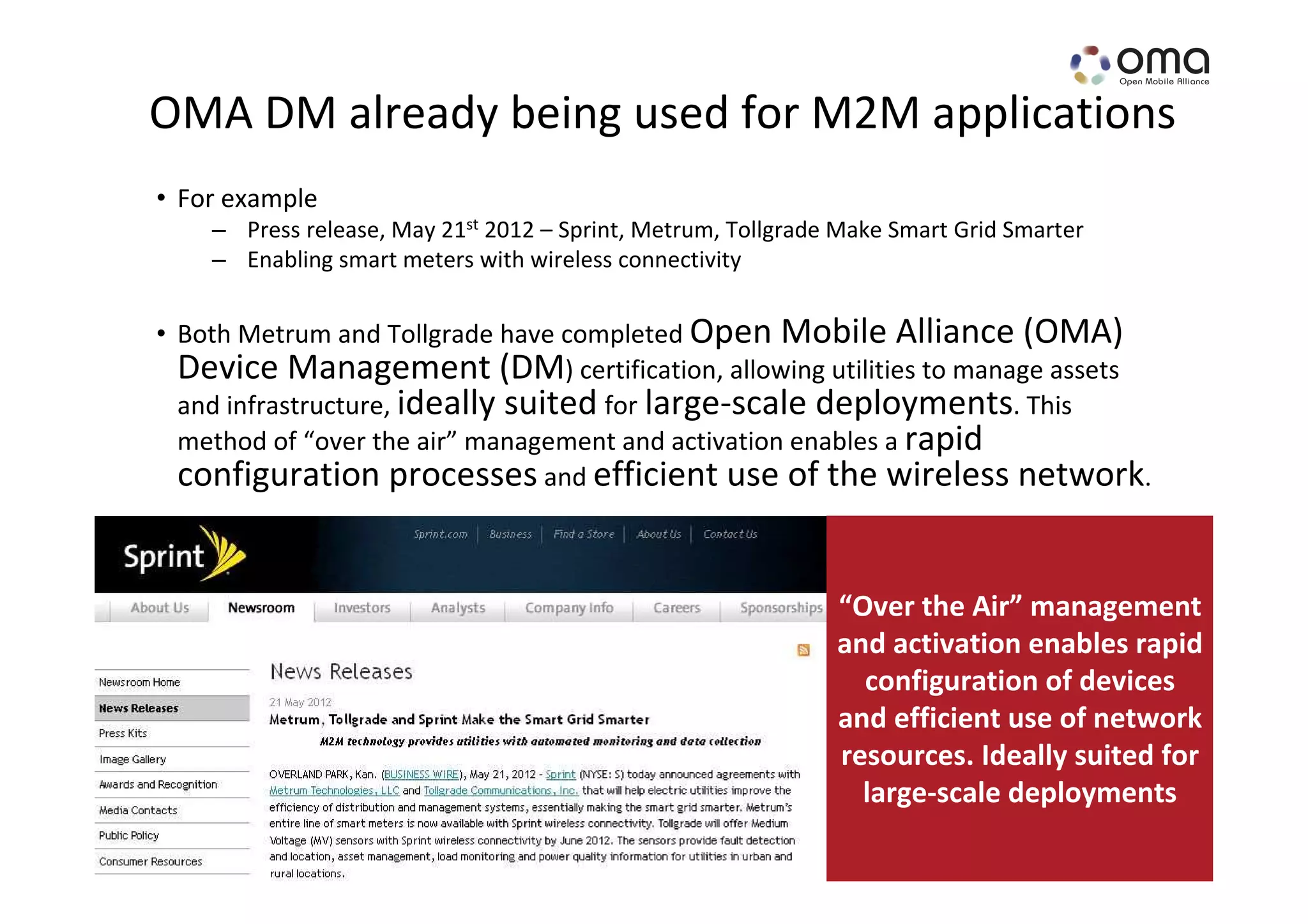
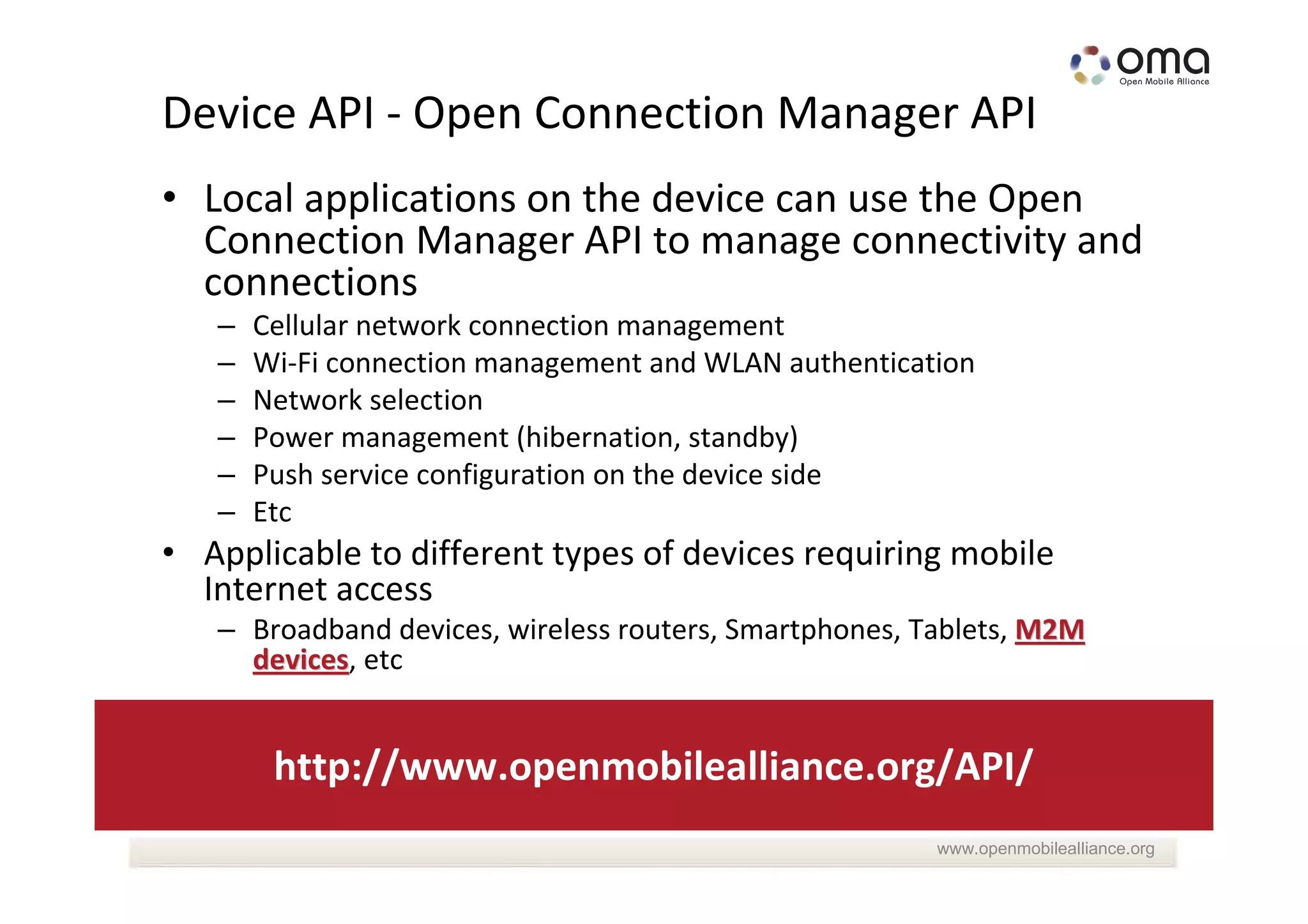
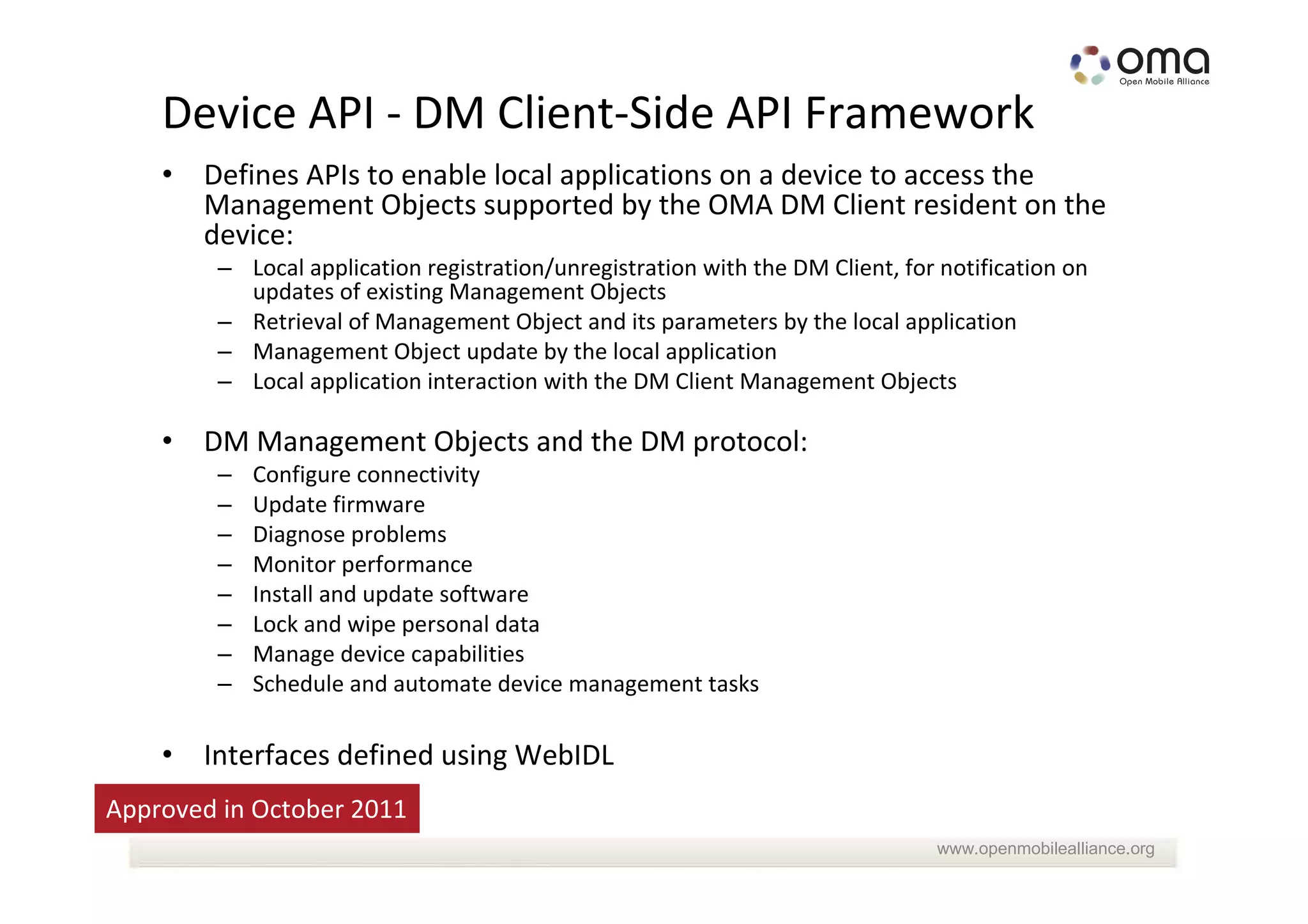
The document discusses the management and provisioning of machine-to-machine (M2M) devices, anticipating significant growth in connections, predicting up to 20 billion by 2020. It highlights the need for technological evolution in device management to accommodate diverse networks and M2M devices, including the introduction of various management protocols and frameworks. Additionally, it describes collaborative efforts within the industry, including partnerships with organizations like onem2m to enhance M2M capabilities and support service integration.

![M2M devices outnumber mobile devices by an
order of magnitude
• Analysys Mason: Forecasts that the number of M2M device connections
will grow to 2.1 billion devices in 2020 [1]
• Machina Research: Number of M2M connections will grow to 12 billion
in 2020 [2]
• GSMA: Estimates that there will be 20 billion devices connected to the
web by 2020 [3]
• Another way of looking at this:
There will be more M2M devices shipped each year than PCs,
cell phones, tablets, set-top boxes, and gaming platforms put together [4]
Remote device management and provisioning of all these M2M devices
will be a critical aspect to support this tremendous growth opportunity
www.openmobilealliance.org](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/openmobilealliancem2munmehopa-120619213313-phpapp01/75/Management-and-Provisioning-of-M2M-Devices-and-Applications-2-2048.jpg)




![Where does the revenue come from?
M2M may represent a good growth
opportunity overall for MNOs –
but not in terms of traffic revenue
M2M generated 1.2% of mobile data revenue in 2010,
falling to 0.8% in 2013, before rising to 1.4% in 2020
(Machina Research [2])
Connecting, provisioning and managing
all these billions of devices will unlock
tremendous potential to provide
innovative and exciting applications
www.openmobilealliance.org](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/openmobilealliancem2munmehopa-120619213313-phpapp01/75/Management-and-Provisioning-of-M2M-Devices-and-Applications-13-2048.jpg)




![References
• [1]
http://www.analysysmason.com/Research/Content/Reports/RRE02_M2M
_devices_forecast/
• [2] http://www.machinaresearch.com/
– M2M Global Forecast and Analysis 2010-20
• [3] http://www.gsm.org/index.htm
• [4] http://blogs.windriver.com/m2m/
Image credits:
• Jerry Maguire © 1996 TriStar Pictures, Inc. All Rights Reserved.
• http://www.sparlingkites.com
18 www.openmobilealliance.org](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/openmobilealliancem2munmehopa-120619213313-phpapp01/75/Management-and-Provisioning-of-M2M-Devices-and-Applications-20-2048.jpg)