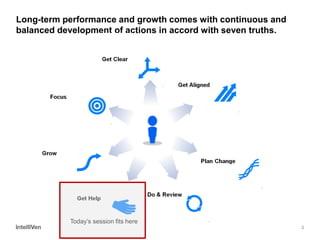
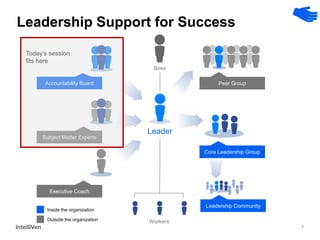
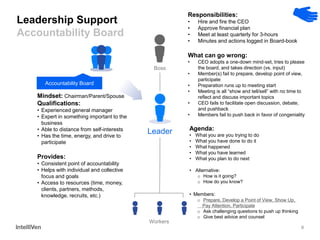
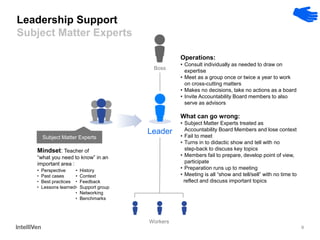
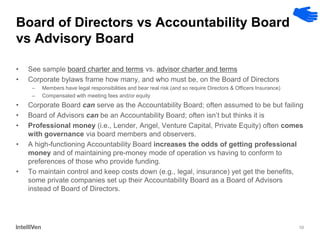
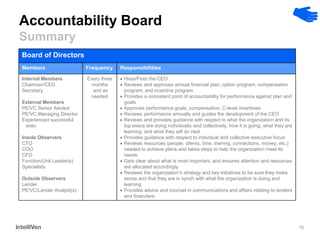
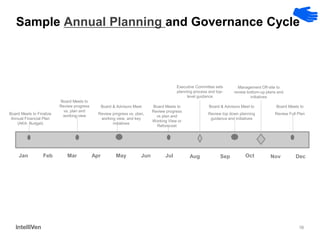
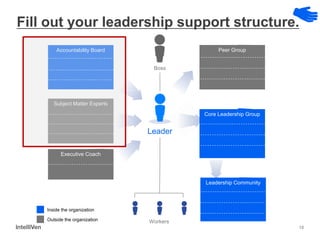
This document discusses how CEOs can use Accountability Boards and Subject Matter Experts to support organizational performance and growth. It recommends that CEOs establish an Accountability Board, comprised of experienced managers and experts, to provide consistent accountability and access to resources. The board should meet quarterly to review performance, plans, resources, and lessons learned. It also advises utilizing Subject Matter Experts as consultants to draw on their expertise and discuss cross-cutting issues. Regular meetings and clear roles help ensure these groups effectively support the organization's leadership.