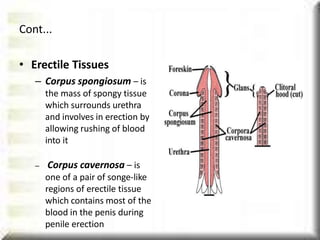
The document summarizes the male reproductive system. It identifies the main organs - the external genital organs of penis and scrotum, and internal genital organs of testes, epididymis, vas deferens, and accessory glands. It describes the functions of each organ and traces the pathway of sperm cells from production in the testes through storage in the epididymis and transport via the vas deferens during ejaculation through the urethra. The document also explains spermatogenesis, the process of sperm cell formation, and ejaculation, which involves muscular contractions that expel semen from the penis.