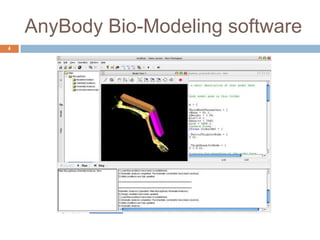
The document outlines a project aimed at constructing an application to analyze forces during leg-weight lifting exercises using MATLAB and Anybody bio-modeling software. It details the development of a leg model and an exo-skeleton model, along with a GUI for user interaction and analysis of various models. Future directions include incorporating additional exercises and improving methodologies for better validation of real-time muscle forces.