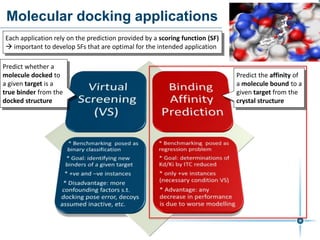
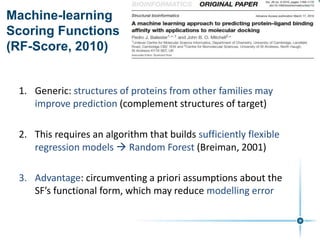
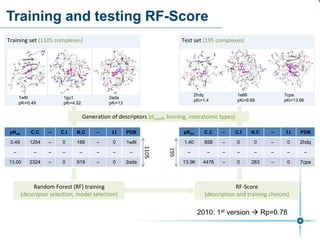
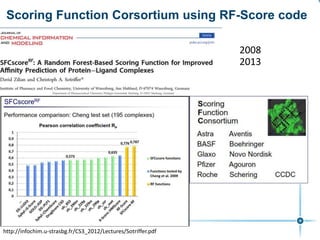
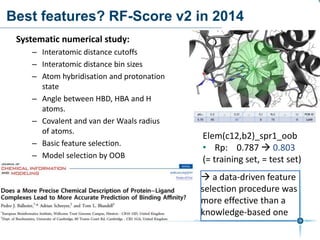
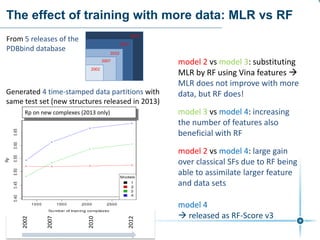
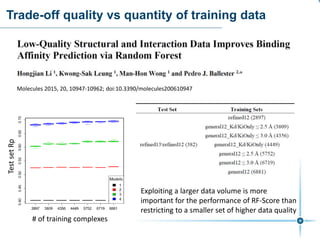
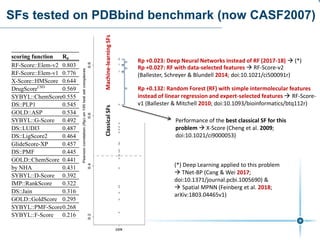
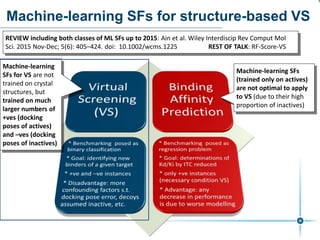
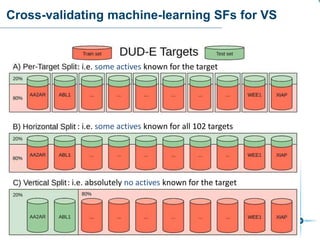
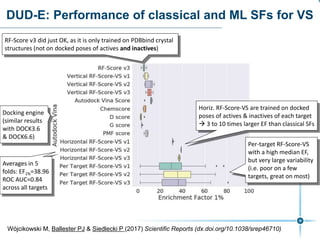
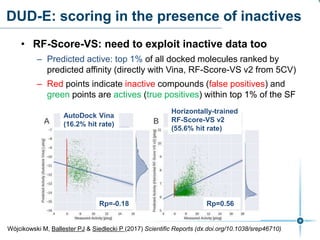
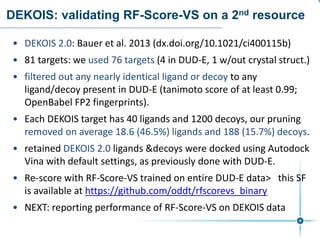
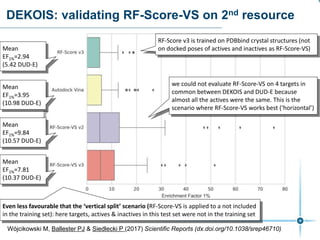
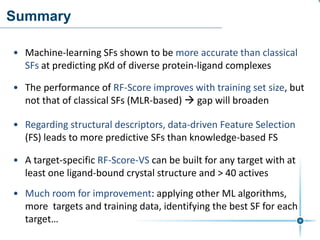
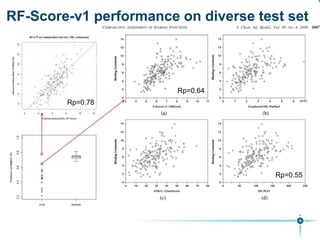
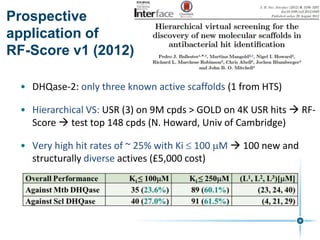
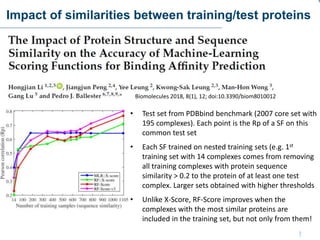
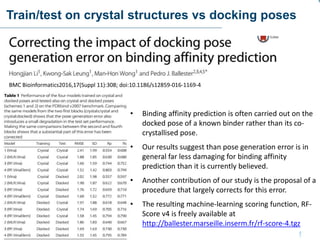
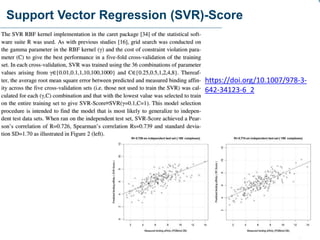
This document discusses the development and performance of machine-learning scoring functions (ML SFS) for predicting binding affinities in molecular docking, particularly focusing on the rf-score series. The findings highlight that ML SFS outperforms traditional scoring functions, especially with larger training sets and data-driven feature selection. It emphasizes the challenges and future directions in optimizing these scoring functions for diverse protein-ligand complexes.