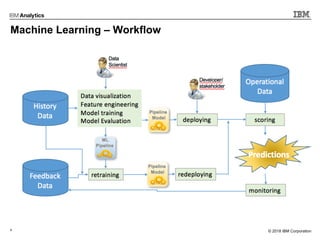
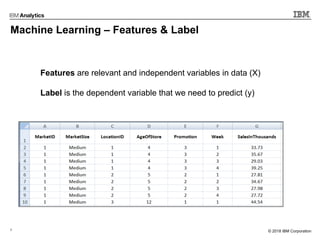
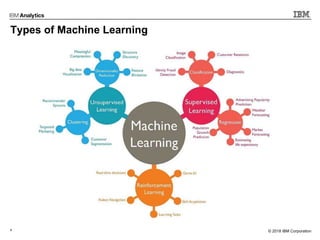
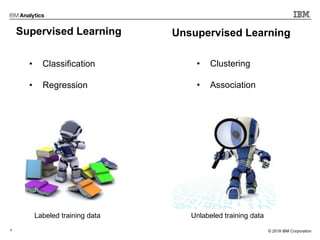
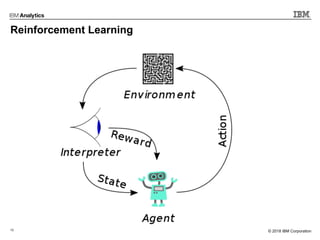
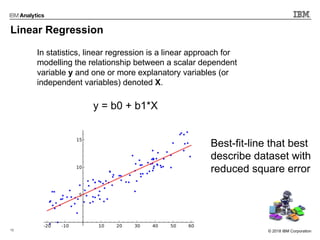
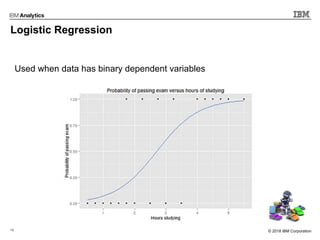
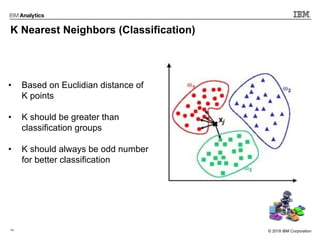
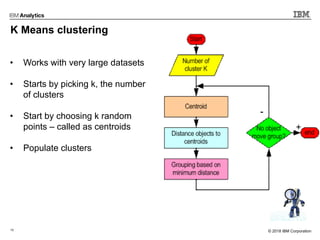
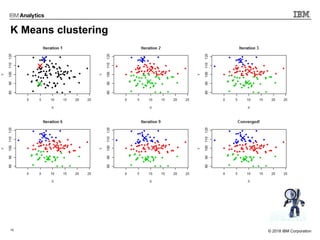
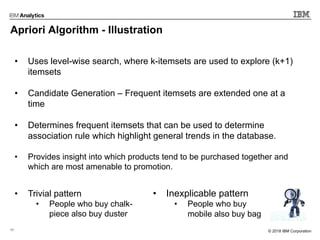
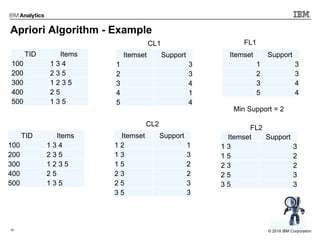
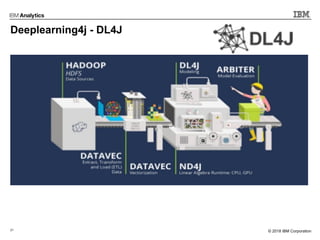
This document outlines an agenda for a machine learning workshop for Java developers. The agenda includes introductions to machine learning algorithms like linear regression, logistic regression, K-nearest neighbors, and K-means clustering. It also discusses machine learning frameworks for Java like Weka, Deeplearning4j, and how to use Jupyter notebooks with Java. The workshop will demonstrate examples using these tools and frameworks.