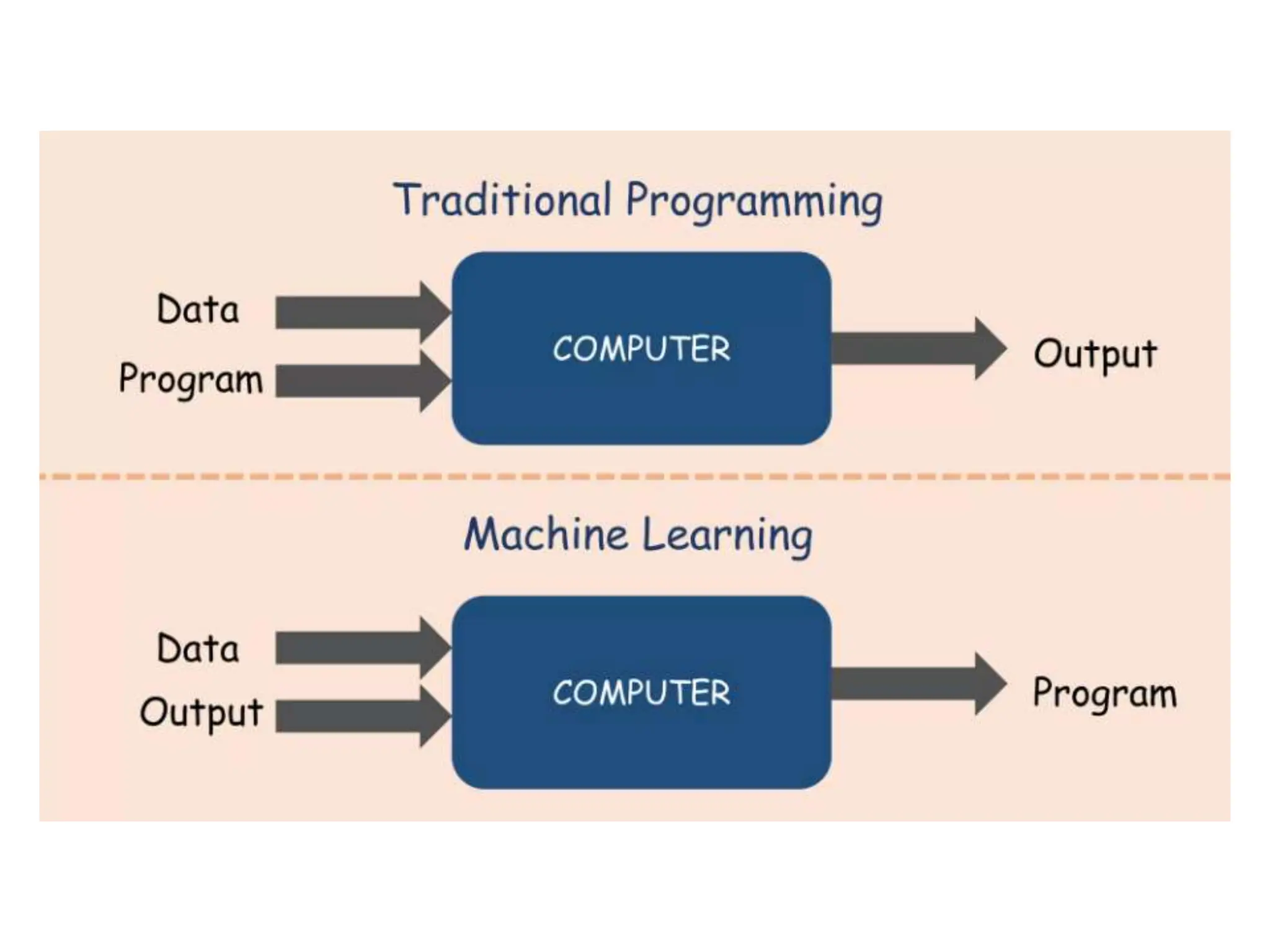
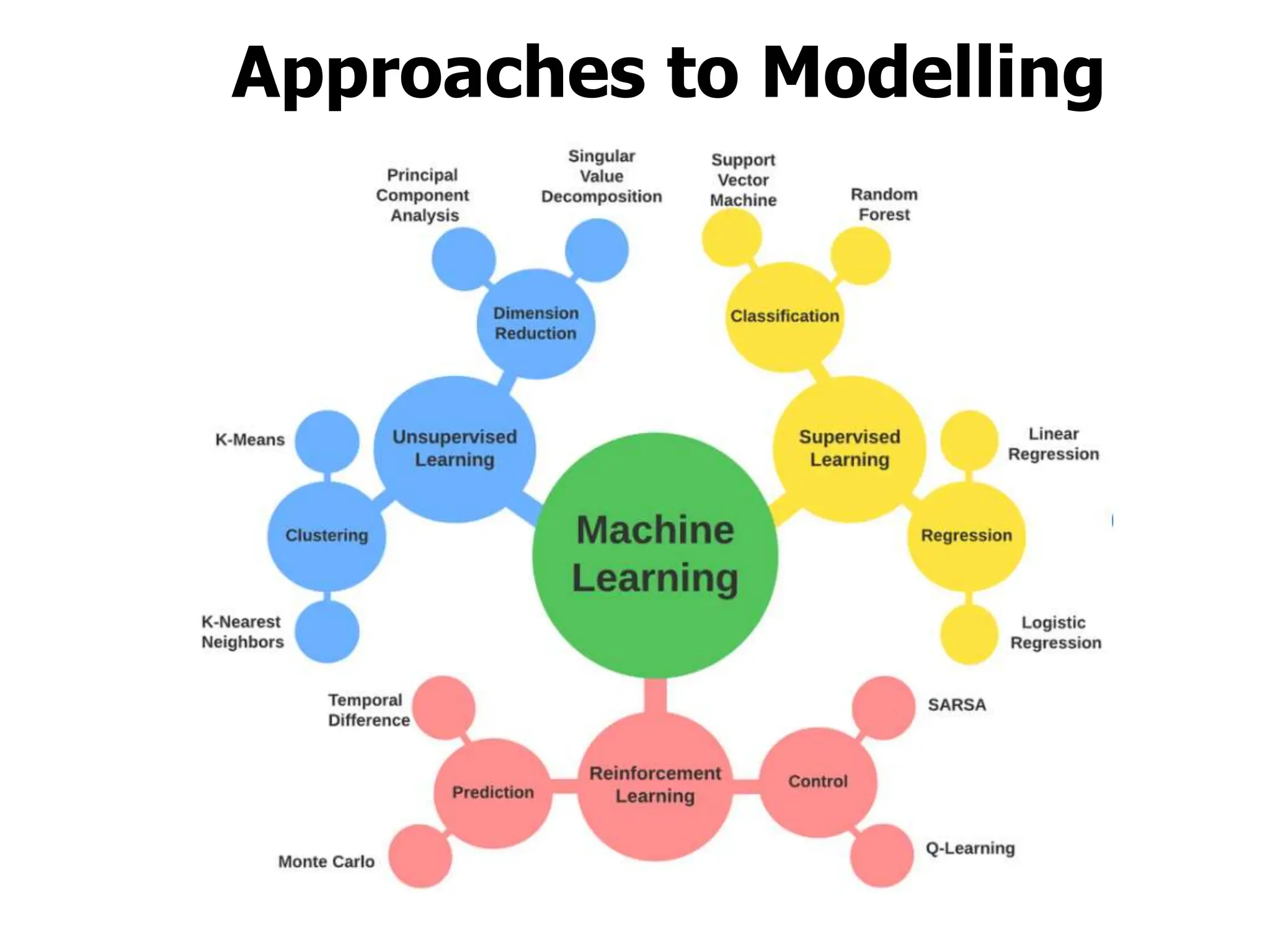
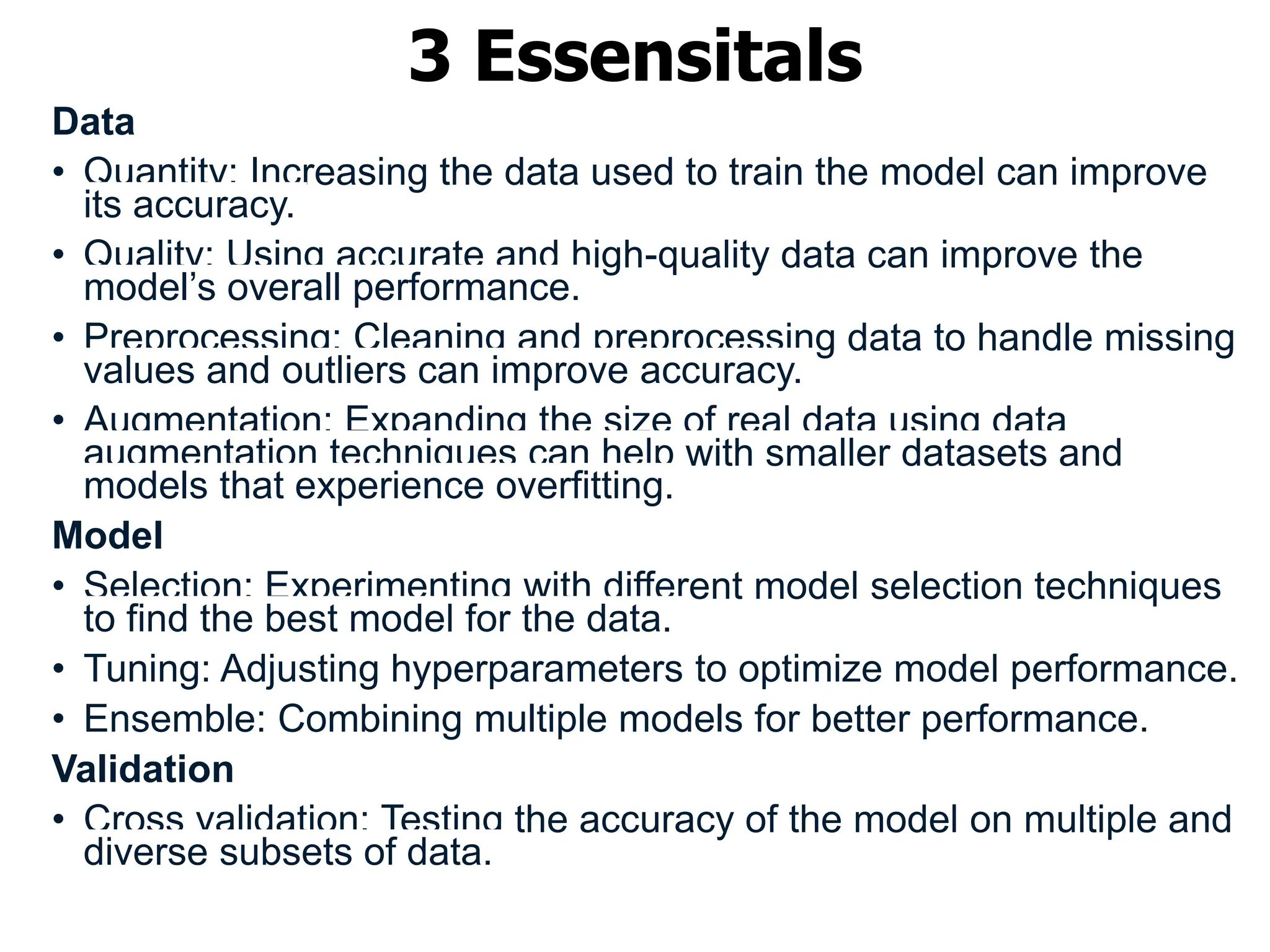
The document explains machine learning as the study of algorithms that enhance performance through experience, utilizing methods like supervised and unsupervised learning. Supervised learning uses labeled data to train models for tasks such as classification, while unsupervised learning identifies patterns in unlabeled data through techniques like clustering. Key elements for improving model performance include data quality and quantity, model selection and tuning, as well as validation techniques such as cross-validation.