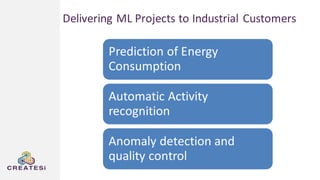
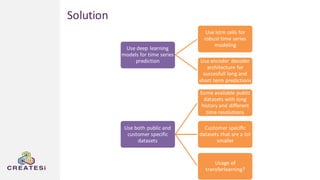
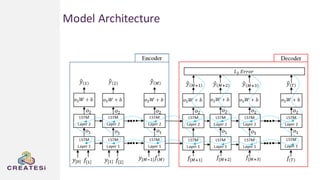
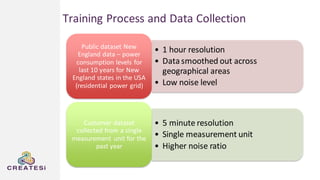
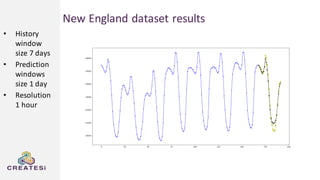
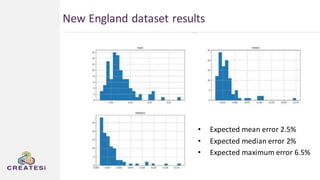
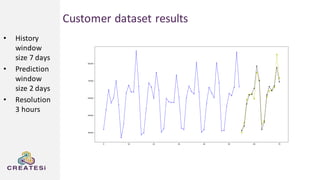
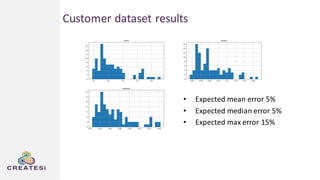
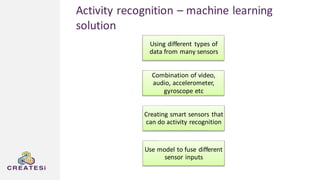
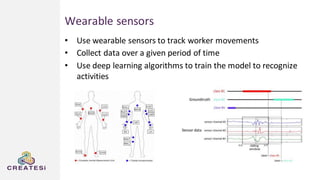
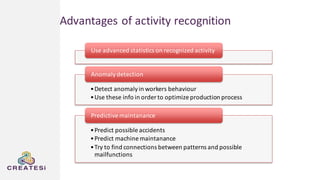
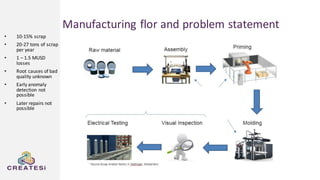
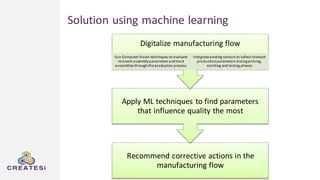
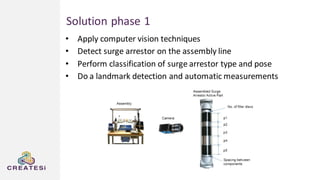
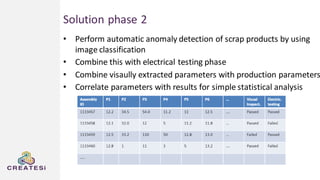
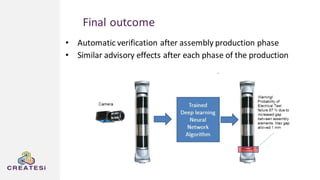
Createsi, founded in 2014 and headquartered in Switzerland, specializes in applying advanced machine learning techniques to solve operational problems in manufacturing. Their work includes projects on energy consumption prediction, activity recognition, anomaly detection, and quality control, utilizing diverse data sources and sensor technologies. Key challenges in the application of machine learning in industrial settings include integration costs, data acquisition challenges, and managing customer expectations regarding accuracy and performance.