The document discusses search engine optimization (SEO) and pay-per-click (PPC) advertising. It provides definitions and overviews of key concepts such as on-page and off-page SEO, content networks for PPC advertising, and how search engine results pages are organized. The document also examines factors that influence search engine rankings and click-through rates, such as keyword use, link popularity, and ad relevance to content.












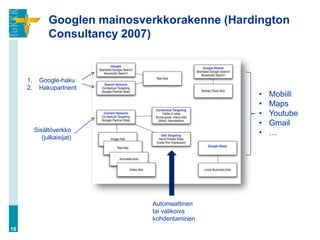



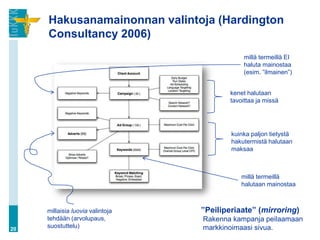






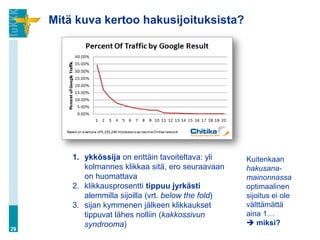
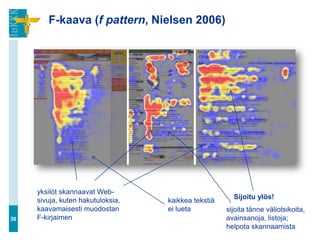




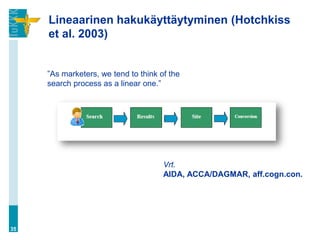
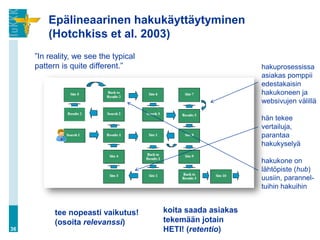


![Hakukoneiden valta (…jatkuu)
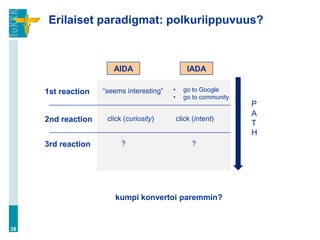
“So, why should non-search sites improve if the search engines
collect all the gains? There are two reasons:
1. Do nothing and you’ll disappear when your competitors improve
enough to easily outbid you and therefore consume all the space on
the first search engine results page. ([…] more than 90% of users
never go beyond the initial SERP.)
2. While search engines will take all the profits from users who arrive
from search ads, you get to keep the increased earnings from all
other users. Thus, non-search users become the true source of
added value from website improvements.
In addition to paid search listings, websites also often receive search
traffic from free, so-called organic listings. These visitors are
obviously no problem, except that you can‟t count on them as a
sustainable strategy, since organic listings can change without
notice.” (Nielsen 2006)
40](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/ma8hakukonemarkkinointiluento2-120315160521-phpapp02/85/MA8-Digitaalinen-markkinointi-luento-2-40-320.jpg)
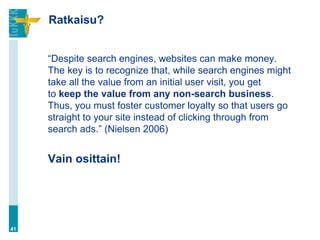

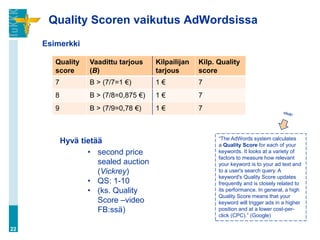
![Klikkihinnan ROI-paradoksi
Koska konversiosuhde vaihtelee, voit maksaa klikeistä
eri määrän (enemmän tai vähemmän), mutta
myynneistä saman verran.
– “Hence, if you bid $1 per click for an ad group about
digital cameras, Bob‟s blog could cost $0.05 per click.
If you received 1000 clicks from Bob‟s blog, [with low
conversion] the actual cost per conversion is $50.
However, on CNET‟s review site, you may pay $1 for
each click, however, the conversion rate maybe 1 in
50 which would make the traffic from CNET also have
a $50 cost per conversion.” (Geddes 2007)
Vaihtelu pätee paitsi sijoituksen kohdalla, myös eri
avainsanojen välillä.
Palataan tähän konversio-optimoinnin yhteydessä…
45](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/ma8hakukonemarkkinointiluento2-120315160521-phpapp02/85/MA8-Digitaalinen-markkinointi-luento-2-45-320.jpg)