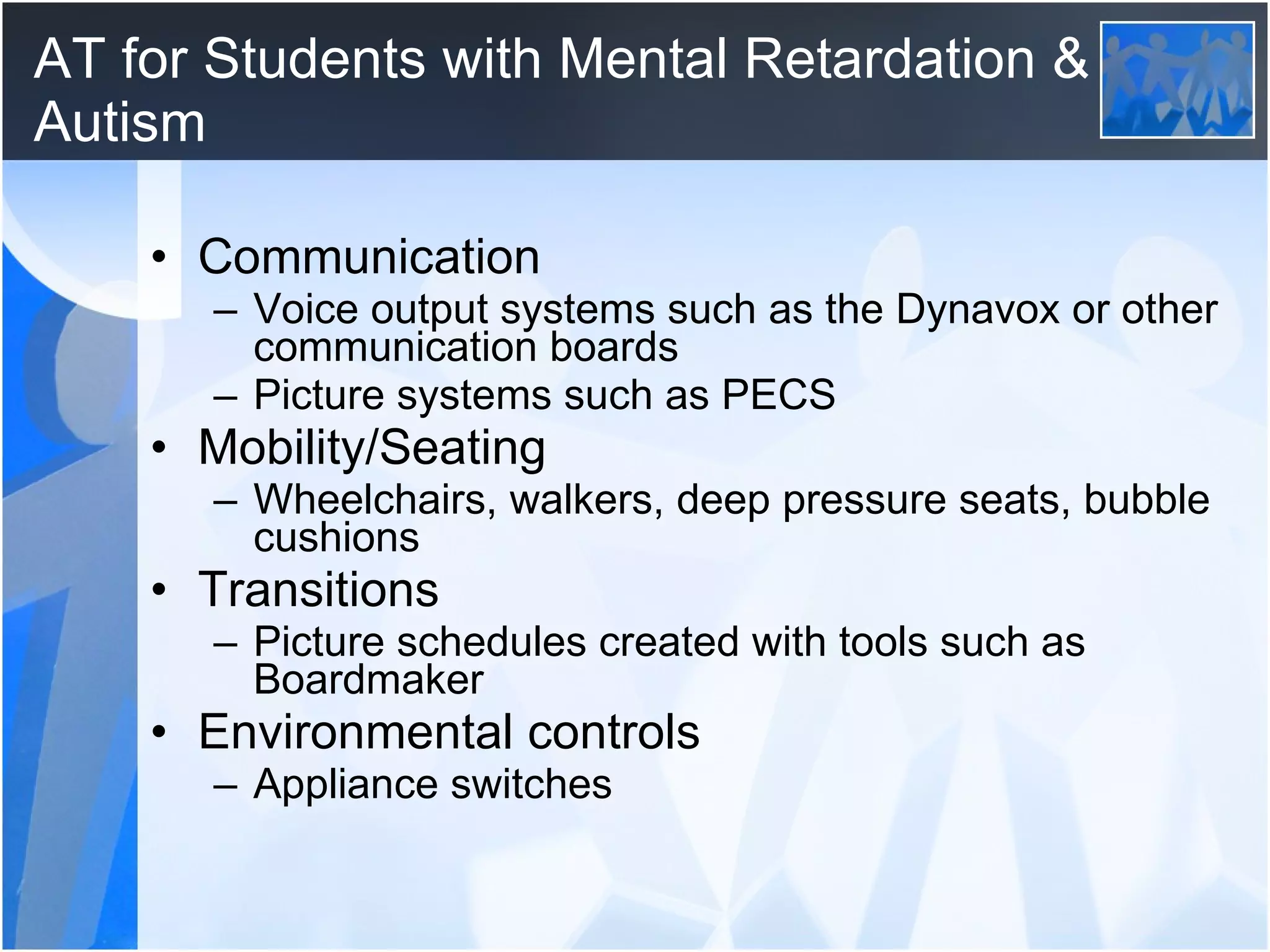
The document discusses assistive technology and instructional strategies that can aid students with disabilities. It provides an overview of different types of disabilities covered by IDEA and the components of an IEP. Examples of assistive technologies and instructional strategies are given for specific disabilities like ADHD, learning disabilities, auditory disabilities, and autism. Guidelines are outlined for selecting appropriate assistive technologies for students.