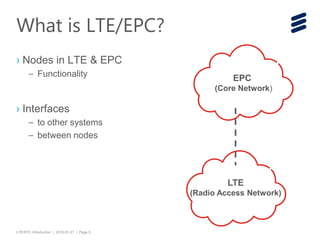
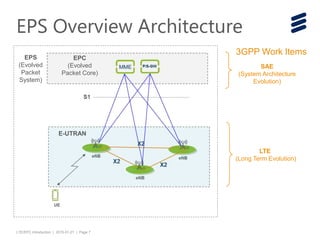
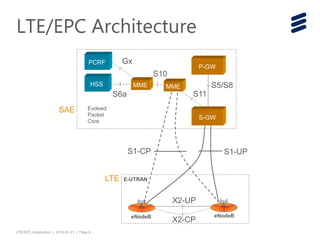
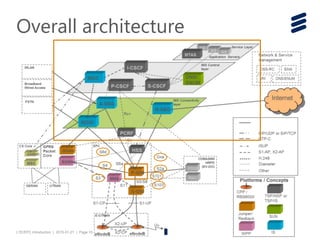
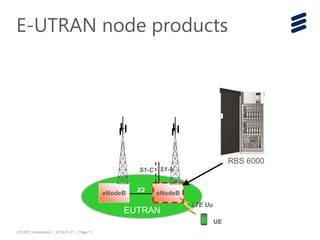
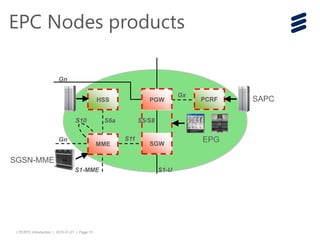
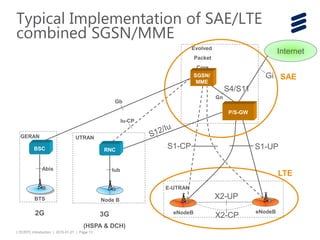
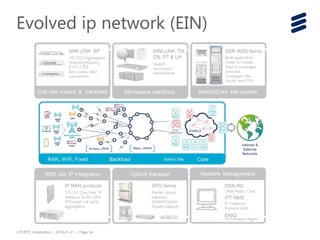
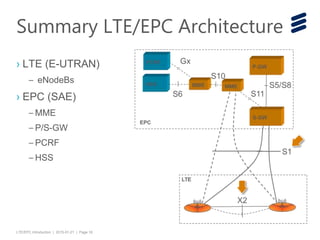
The document provides an introduction to LTE (Long Term Evolution) and EPC (Evolved Packet Core) architecture, covering essential components and functionalities of each node in the network. It outlines the learning objectives, including the description of LTE/EPC architecture, nodes, interfaces, and interconnections with other networks. Additional resources for in-depth training are mentioned for further exploration of the subject.







![LTE/EPC Introduction | 2015-01-21 | Page 19
› CPI store
› Product catalogue
For more in-depth instructor led
training, visit Academy Site
XX/MyLearning and search for
[course XXX, LZU 108 xxxx]
More
Information](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/lteepcintroduction-240725180810-207b71db/85/LTE_EPC_Introduction-ppt-19-320.jpg)
