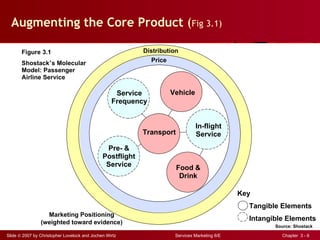
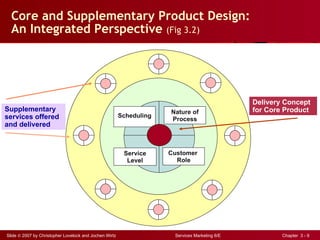
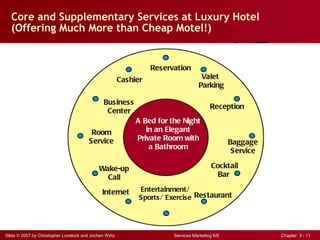
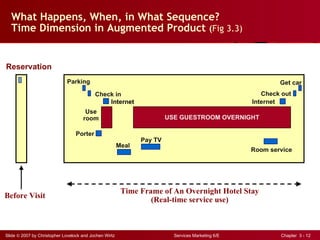
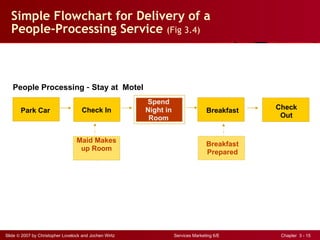
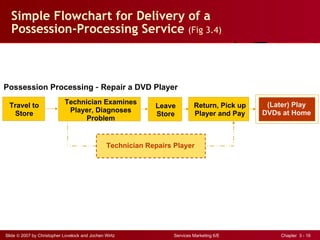
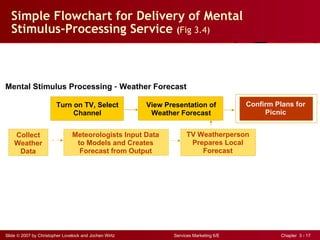
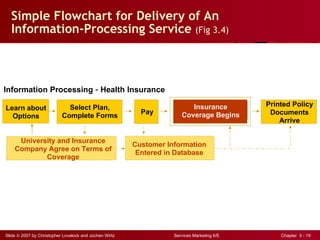
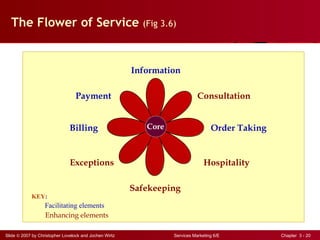
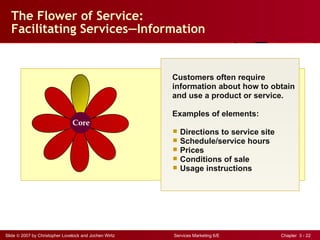
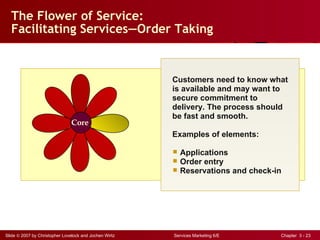
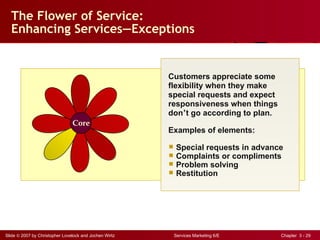
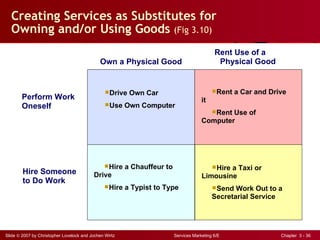
The document discusses planning and developing service concepts, including core and supplementary elements. It defines core products as the central component that supplies the principal benefits customers seek. Supplementary services augment the core product by facilitating its use and enhancing its value and appeal. The document provides examples of core products and supplementary services for different types of services and industries. It also discusses developing new service categories and reengineering service processes.