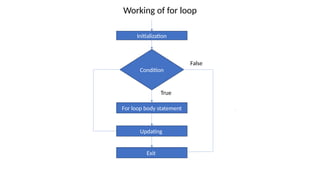
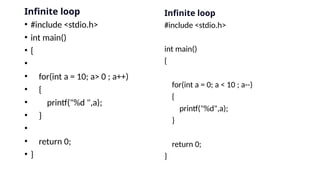
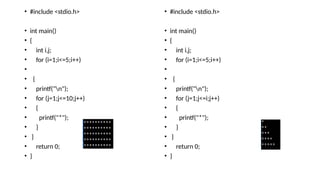
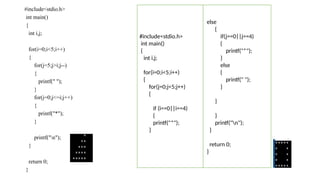
The document explains various looping statements in programming, including for, while, and do-while loops, detailing their syntax, behavior, and examples. It differentiates between entry-controlled and exit-controlled loops, illustrates the use of nested loops, and discusses jumping statements like break and continue. Additionally, code snippets demonstrate practical implementations such as calculating sums, checking for prime numbers, and generating Fibonacci series.