Embed presentation
Download to read offline









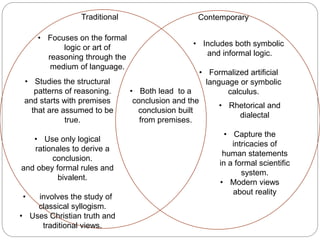

Traditional logic focuses on formal reasoning through language using symbolic calculus and studying structural reasoning patterns. It uses premises assumed to be true and only logical rationales to reach bivalent conclusions in accordance with formal rules. Contemporary logic aims to capture the intricacies of human statements scientifically while incorporating modern views of reality, with conclusions built from premises through both deductive and rhetorical means.











