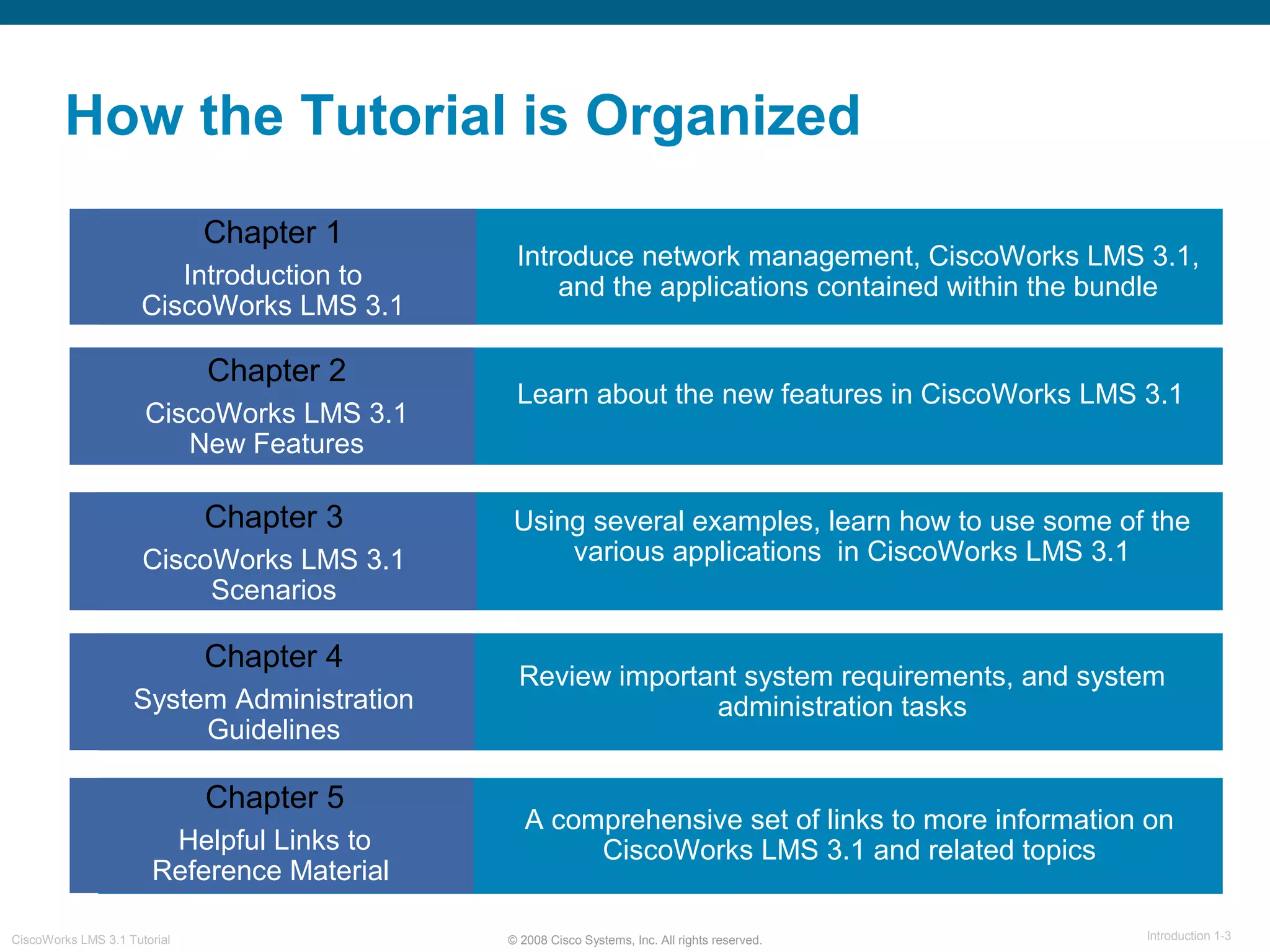
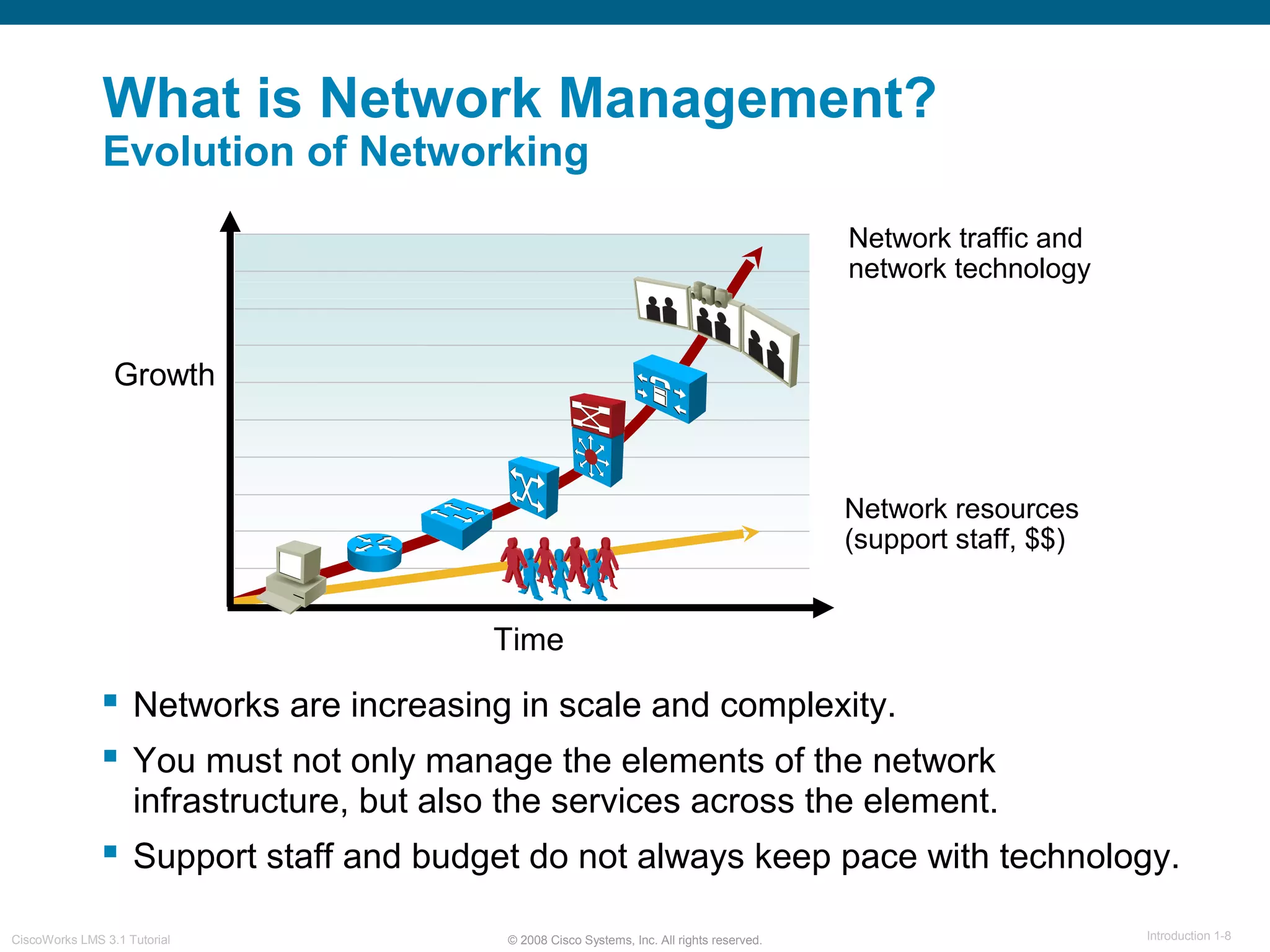
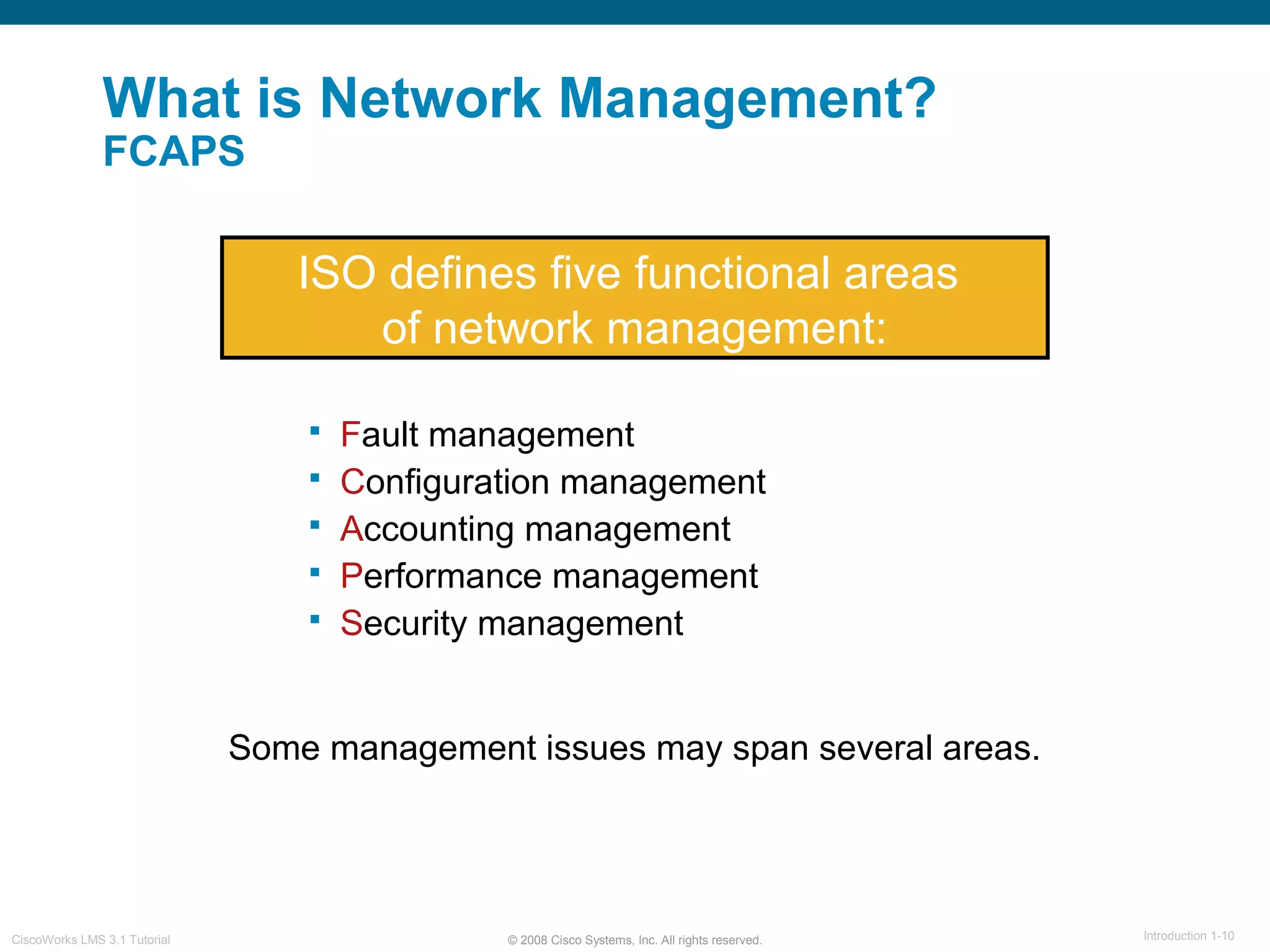
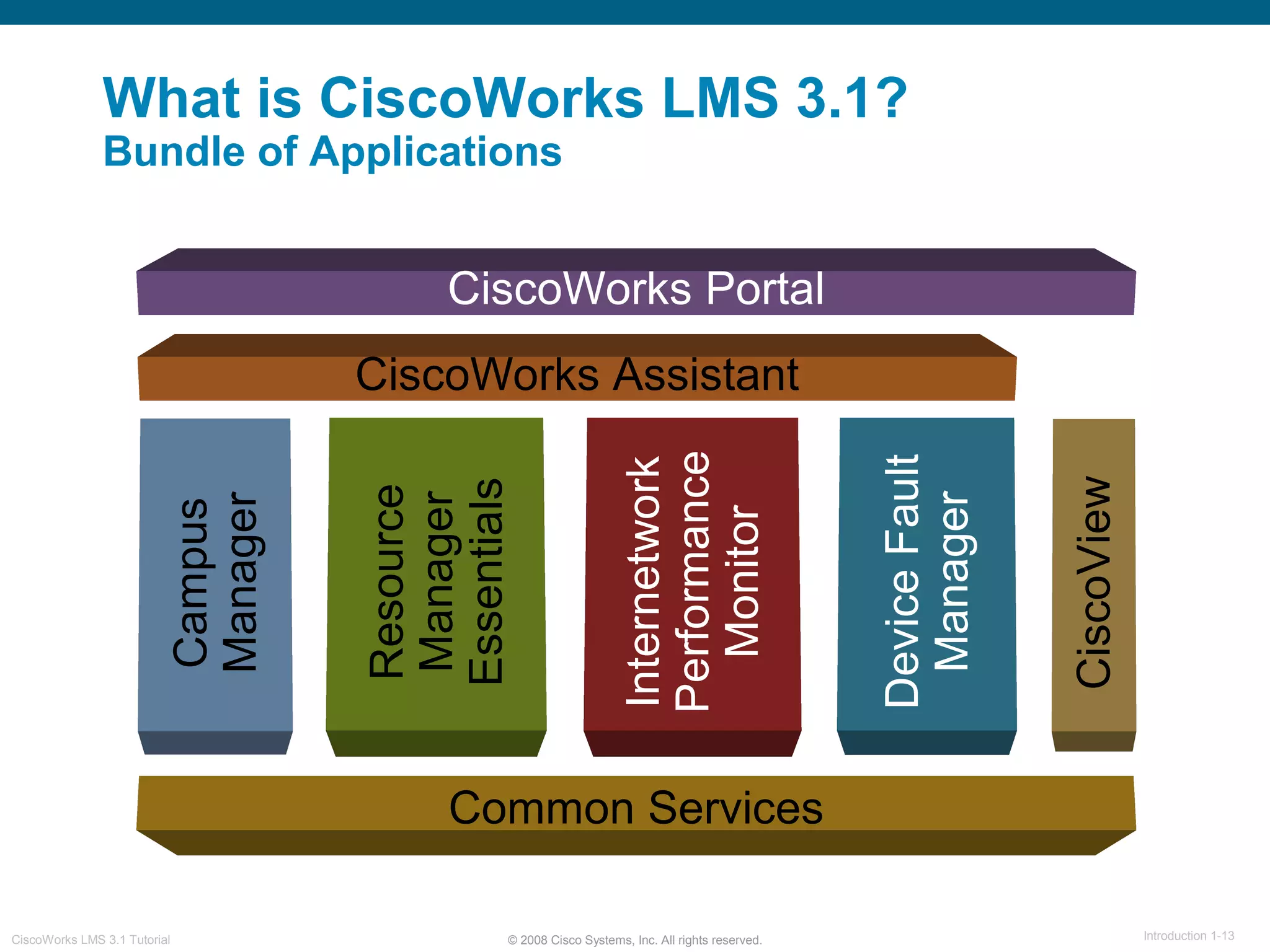
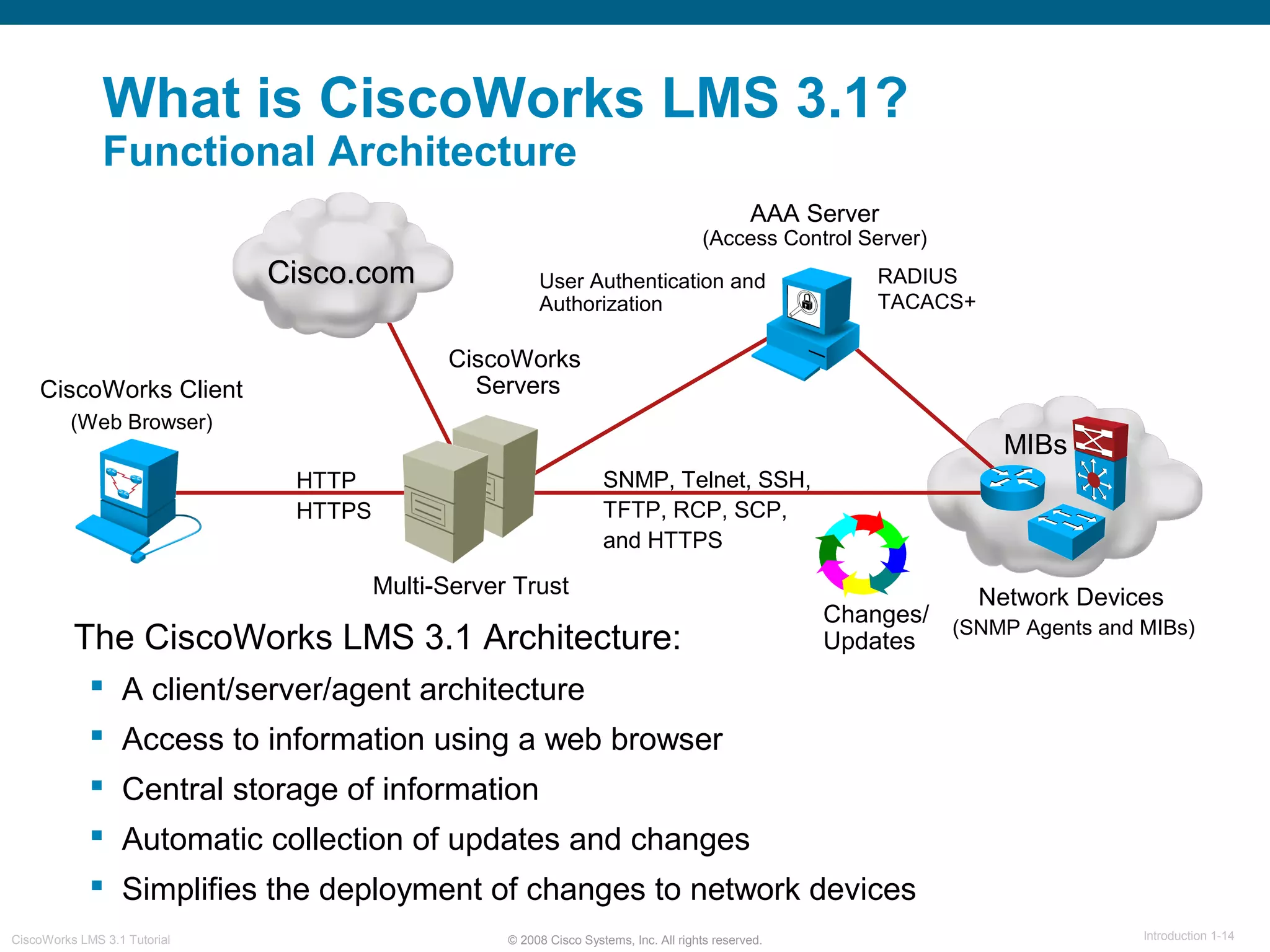
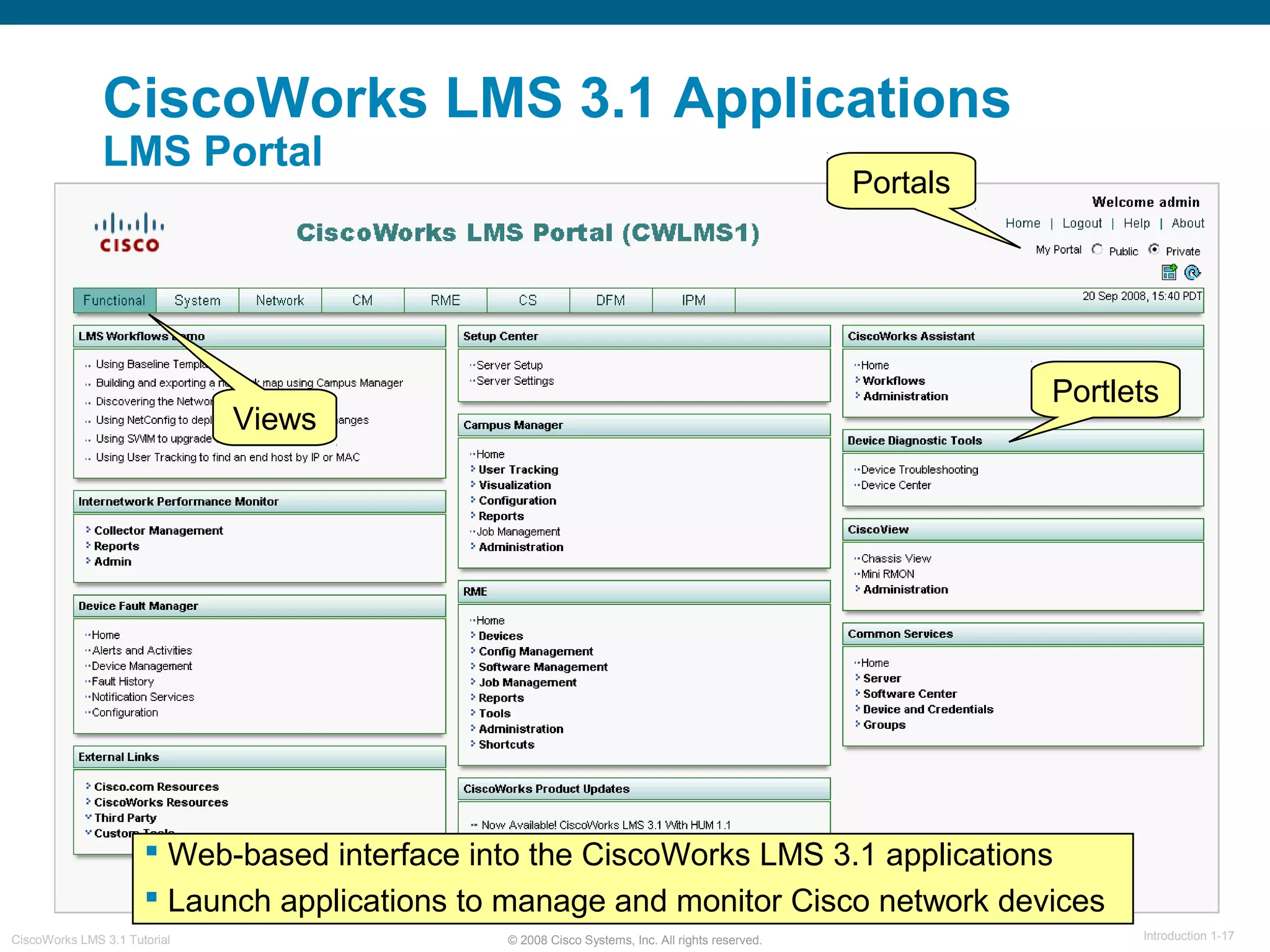
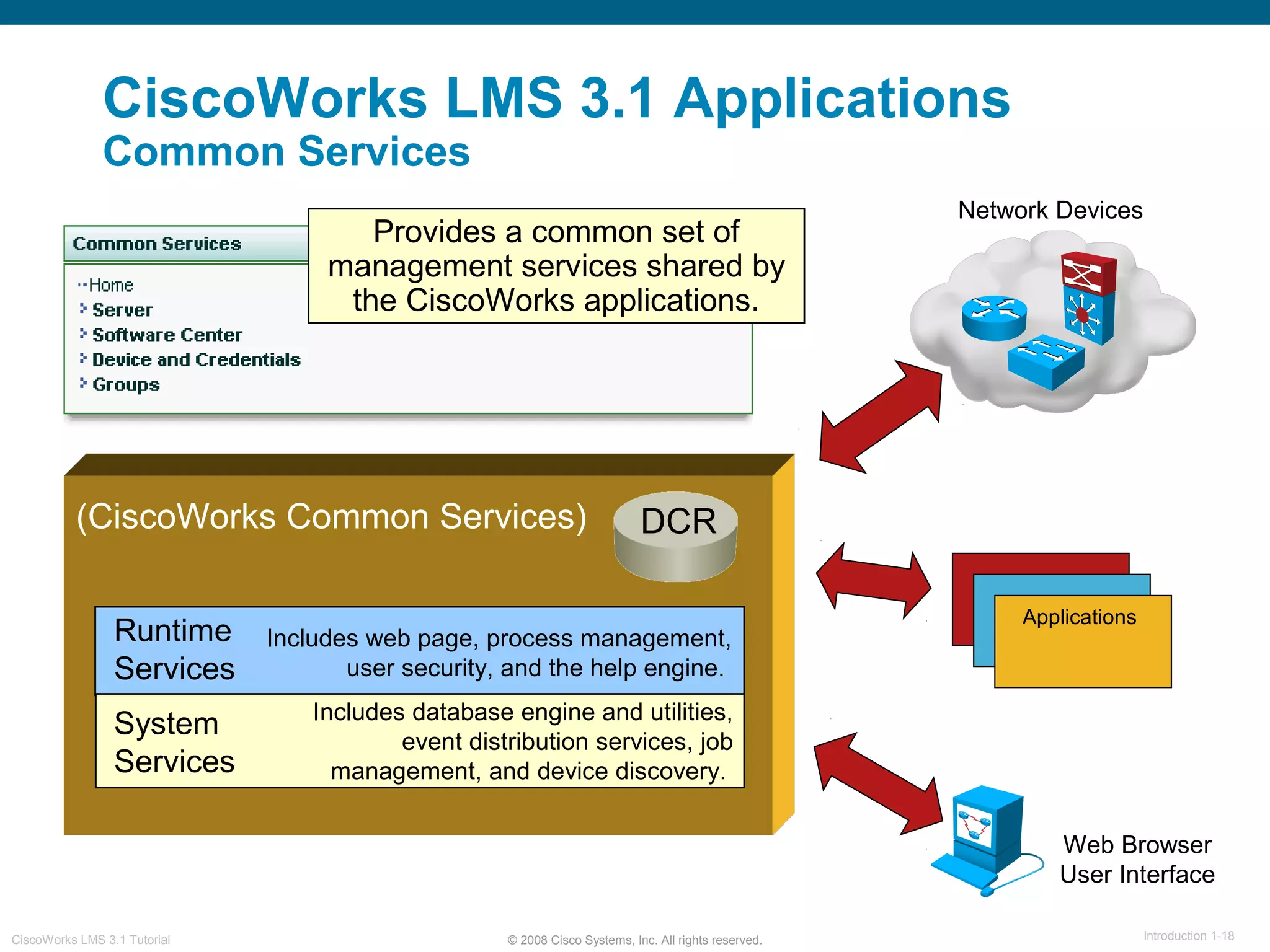
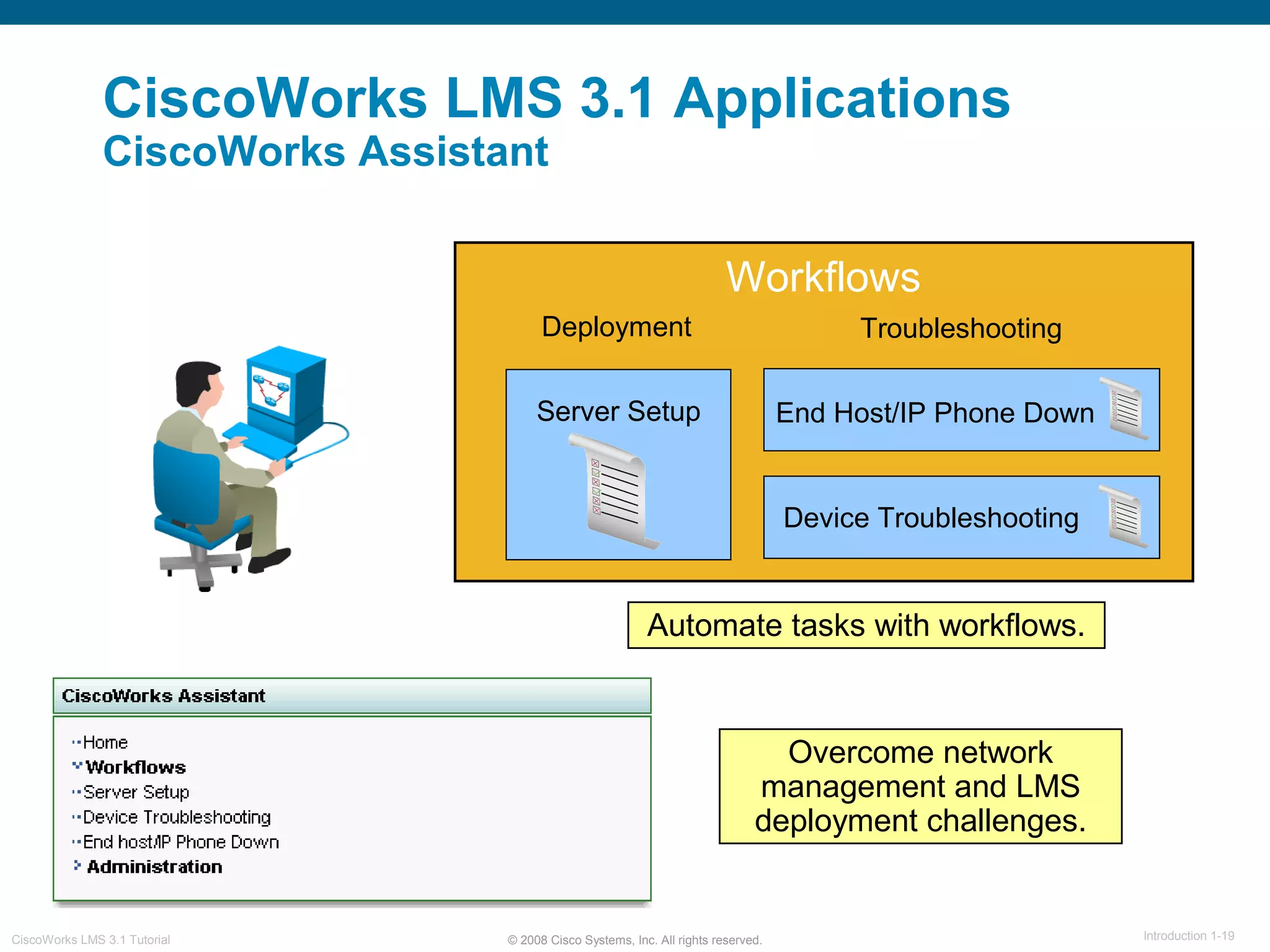
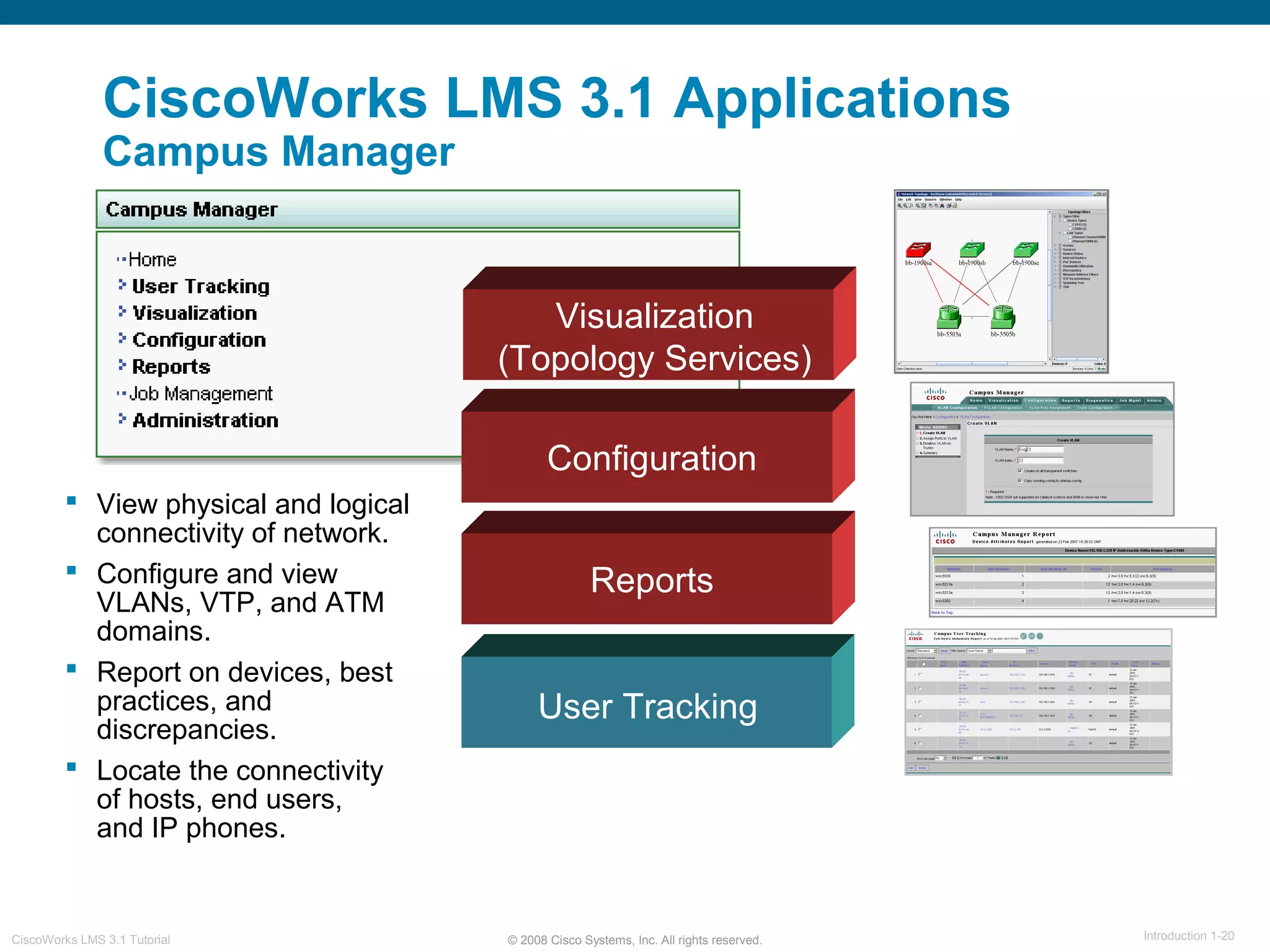
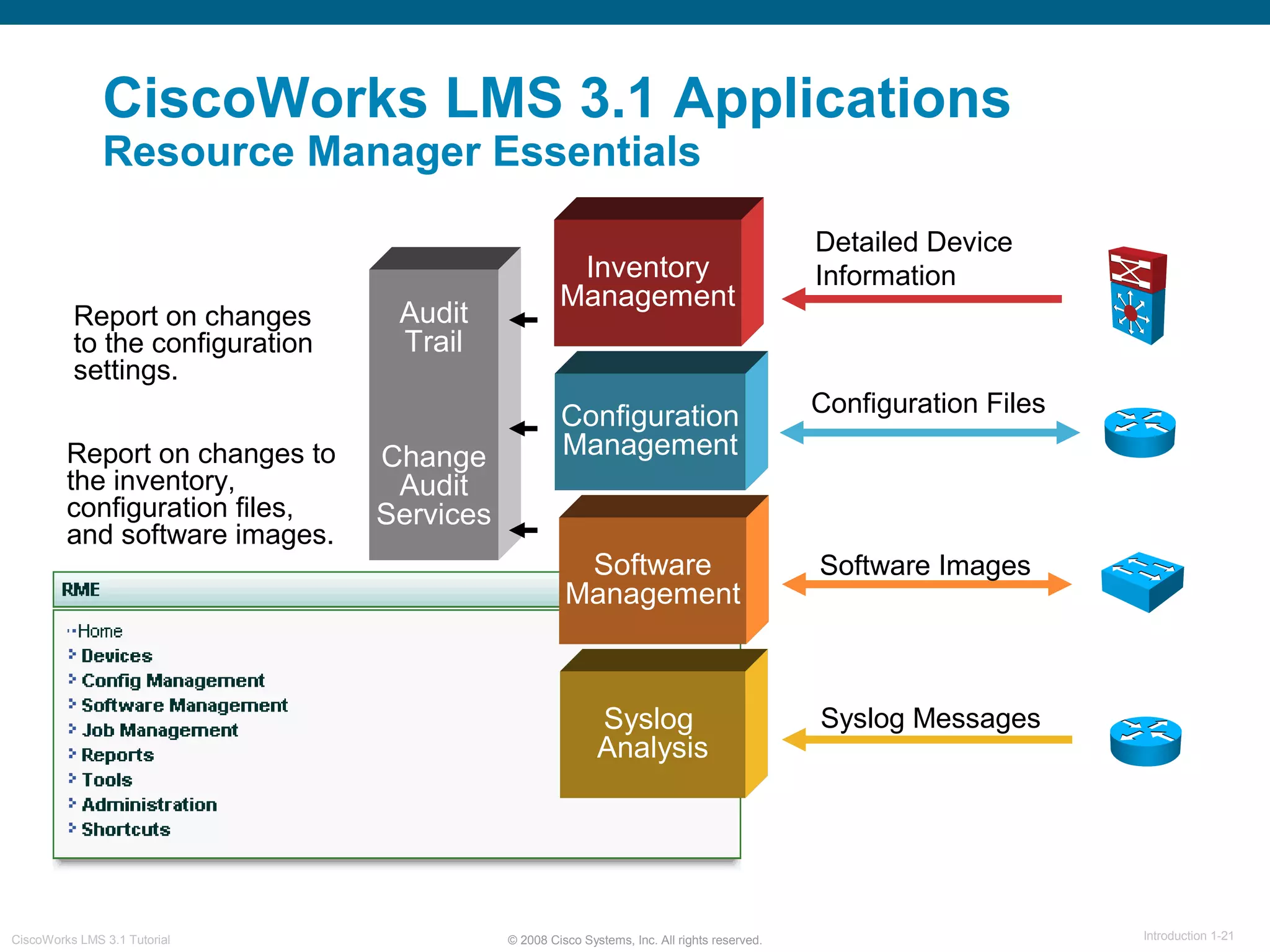
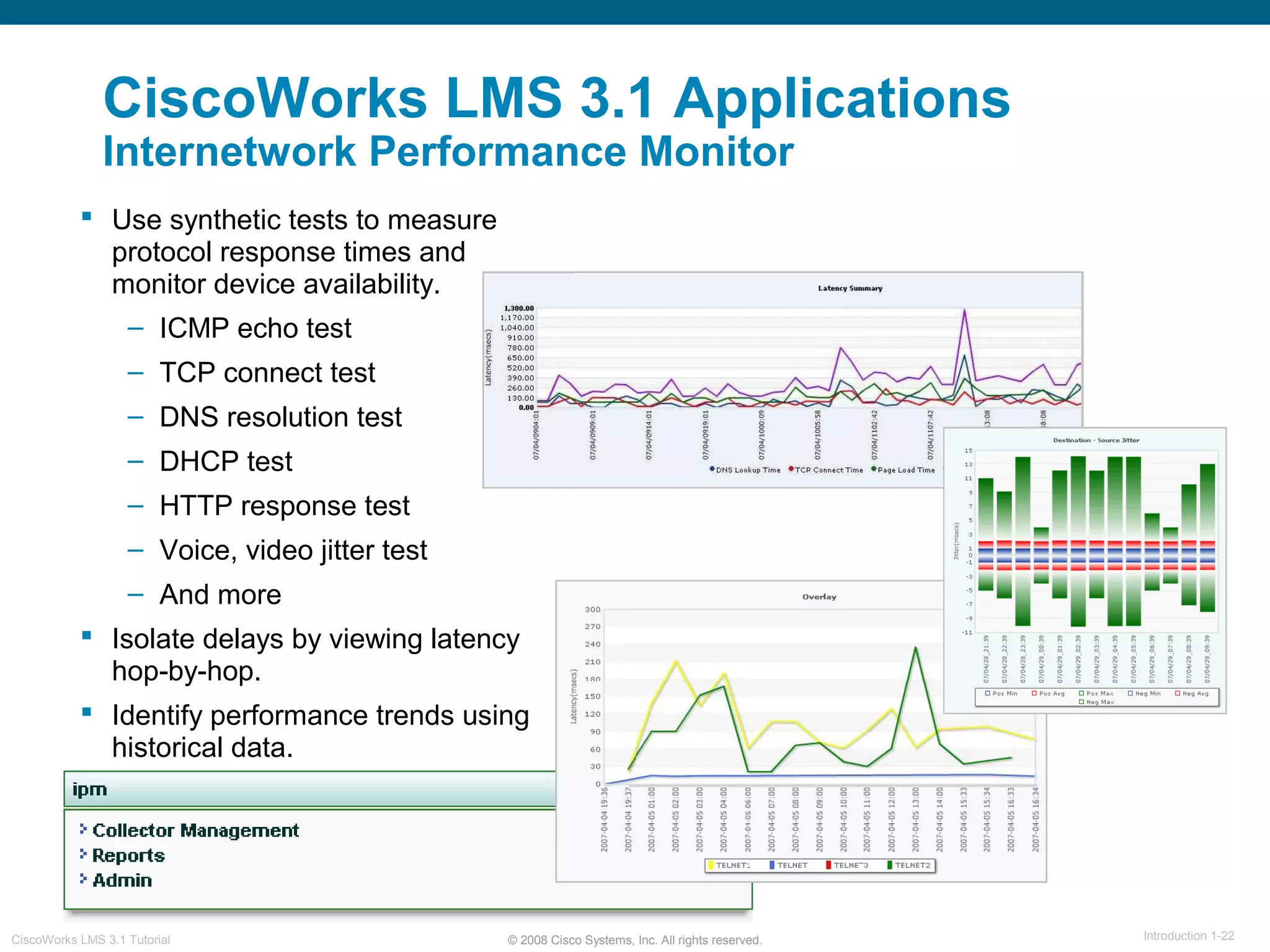
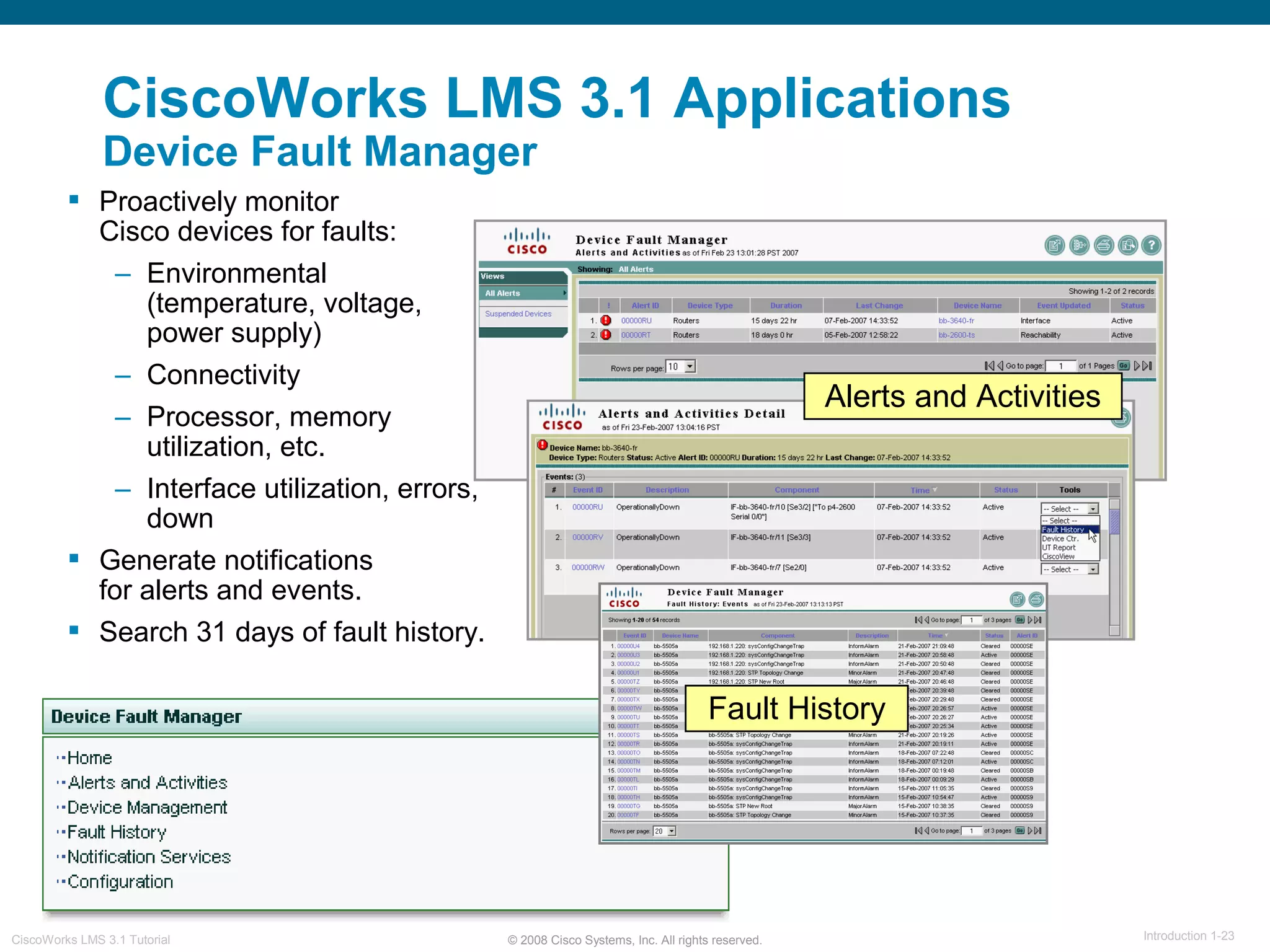
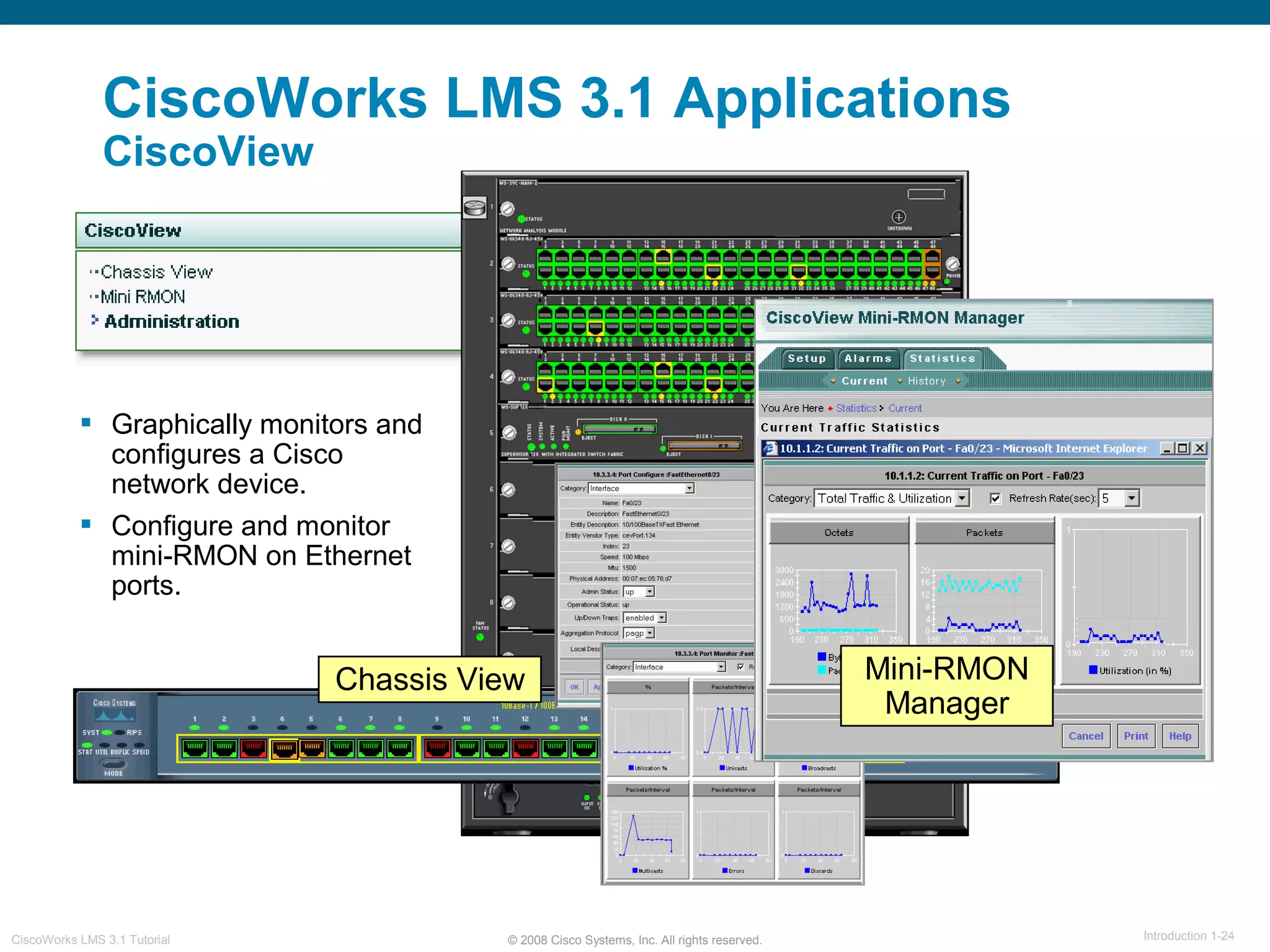
This document provides an overview of the CiscoWorks LMS 3.1 network management tutorial. The tutorial introduces CiscoWorks LMS 3.1 and its applications, highlights new features, provides usage scenarios, and offers administration guidelines. It is organized into chapters covering introduction, new features, scenarios, administration, and reference materials. The introduction defines network management and the CiscoWorks LMS 3.1 suite of applications for fault, configuration, accounting, performance, and security management of network devices.