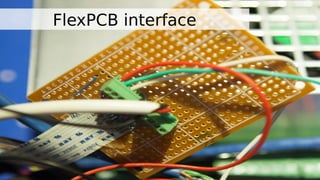
The document discusses the integration of LinuxCNC with laser engraving technologies, including issues and solutions related to hardware and software use. It covers the setup of motion control, calibration, and safety interlocks for laser operation, as well as personal experiences with equipment failures. The author also shares resources for purchasing related components and emphasizes the flexibility of LinuxCNC for managing various CNC machines.