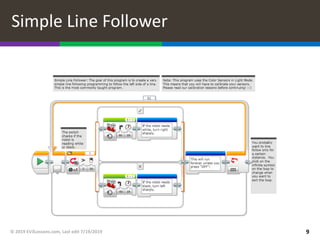
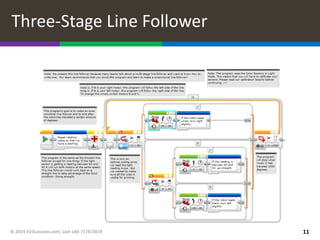
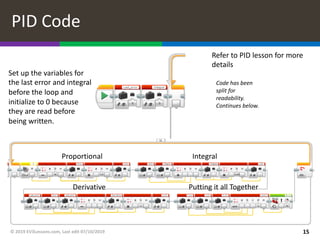
This document provides an overview of different types of line following programs for robots, including simple, smooth, proportional, and PID controllers. It discusses the strengths and weaknesses of each approach and which is best suited for different situations. Code examples are provided for proportional and PID line followers. The document also includes challenges for writing different line following programs and notes about calibrating sensors and setting up the code examples.