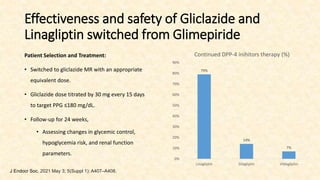
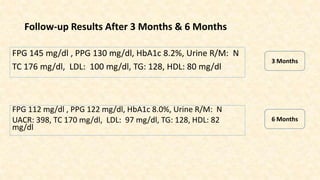
This document discusses a 63-year-old man with type 2 diabetes and chronic kidney disease who presents with increased fatigue and hypoglycemia. He has a history of diabetes for 11 years and hypertension for 6.5 years. Laboratory tests show uncontrolled diabetes with early declining renal function. His treatment is modified by substituting gliclazide for glimepiride and continuing linagliptin based on his estimated glomerular filtration rate. Studies show linagliptin improves glycemic control in patients with kidney disease without worsening renal function or increasing hypoglycemia risk. After treatment changes, his blood sugar, albuminuria, and kidney function show improvement at 3 and 6 month follow ups.







![Date of Download: 8/2/2023
1. Diabetes Care. 2020;43(11):2889-2893. doi:10.2337/dc20-0902
2. Diabetologia (2016) 59:2579–2587
Renal hemodynamic and tubular effects of linagliptin and glimepiride after 8 weeks of
treatment. Mean ± SEM (A–C and F), median [IQR] (D and E), and baseline-corrected mean
difference (95% CI). Multivariable linear regression models were used to examine baseline-
corrected linagliptin-induced effects compared with glimepiride. Paired t tests (A–C and F) or
Wilcoxon signed rank tests (D and E) were used for within-group comparisons. Significant
differences are indicated in boldface type. PAH, para-aminohippuric acid; Wk, week.
Compared to Glimepiride,
• Linagliptin had no significant impact on fasting GFR
and ERPF. 1
Compare to Glimepiride, Linagliptin tended to
• Reduce UACR by 26% from baseline
• No between-group differences were observed.1
This neutral effect of Linagliptin on
• GFR and ERPF is consistent with previous placebo-
controlled trials involving T2DM patients without
renal impairment. 2
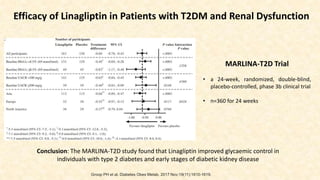
Effects of DPP-4 Inhibitor Linagliptin Versus Sulfonylurea Glimepiride as Add-on to
Metformin on Renal Physiology in Overweight Patients With Type 2 Diabetes (RENALIS):
A Randomized, Double-Blind Trial
GFR: Glomerular Filtration Rate
ERPF: Effective Renal Plasma Flow
UACR: urinary albumin-to-creatinine ratio](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/linagliptinendocrinologistprespective-case-231227040106-25f7e92c/85/Linagliptin-Endocrinologist-Prespective-Case-pptx-11-320.jpg)
![Effects of Linagliptin on Cardiovascular and Kidney
Outcomes in People With Normal and Reduced
Kidney Function: Secondary Analysis of the
CARMELINA Trial
Linagliptin vs. placebo effect on 3P-MACE (major
adverse cardiovascular events): No significant
difference (HR 1.02 [95% CI 0.89, 1.17])
Linagliptin vs. placebo effect on secondary
kidney outcome: No significant difference (HR
1.04 [95% CI 0.89, 1.22])
Albuminuria progression reduced with
linagliptin regardless of eGFR
HbA1c levels decreased with linagliptin without
increasing hypoglycemia risk
Adverse events (AEs) balanced among groups overall
and across eGFR categories
Diabetes Care 2020;43(8):1803–1812
Study population:
• 6,979 subjects, mean age 65.9 years
• eGFR 54.6 mL/min/1.73 m², 80.1% with albuminuria
• Follow-up duration: 2.2 years
Overall effects on eGFR (MDRD) slope from baseline to last value on treatment and by
eGFR category G ≤ 2 to ≥ G4 for linagliptin (Lina) vs. placebo (pbo)](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/linagliptinendocrinologistprespective-case-231227040106-25f7e92c/85/Linagliptin-Endocrinologist-Prespective-Case-pptx-12-320.jpg)