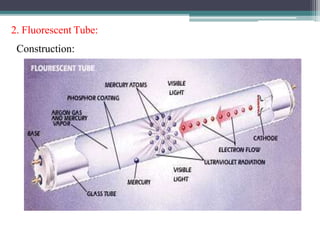
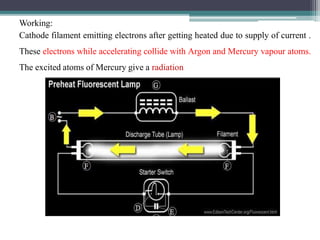
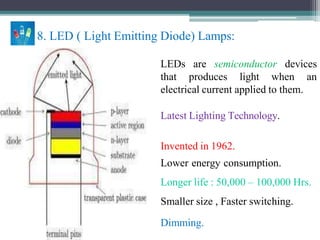
This document summarizes different types of lamps including incandescent, fluorescent, compact fluorescent (CFL), and LED lamps. It describes the construction, working principles, and applications of each type of lamp. Incandescent lamps work by heating a tungsten filament until it glows, but have a short lifespan. Fluorescent tubes use mercury vapor and phosphors to emit light. CFLs are more efficient than incandescent lamps and have a longer lifespan. LED lamps have the longest lifespan, highest efficiency, and ability to emit specific colors through RGB mixing. The document provides details on the materials, workings, and typical uses of each kind of lighting technology.