More Related Content
PPTX
PDF
02 - Conception D Aero Aerodynamisme.pdf PDF
aeronautical engineering AERODYNAMICS - Lecture 3.pdf PPTX
Me438 Aerodynamics (week 1-2-3) PDF
00 - ConceptionAeroAerodynamisme2015.pdf PPTX
Chapter 2_Aerodynamics Performance in aerospace vehicle design.pptx PPT
Unit 1 Basic Aerodynamics ATPP 200 PDF
Similar to Lift and Force in aircrafts ................
PDF
Lift-Forces-in-External-Flows-Lesson-3-Handout.pdf PDF
Drag-Force-in-External-Flows-Lesson-2-Handout.pdf PPTX
the forces of flight commonly as Lift and Drag.pptx PPT
PPT
AERODYNAMICS FORCES AND MOMENTS.ppt PPT
PPT
PPT
PPT
PDF
Chapter-1 Basic Aerodynamic Principles.pdf PPT
PPTX
EASA PART-66 MODULE 8.2 : AERODYNAMICS PPTX
Principles of Flight_FINAL.pptx PPTX
Principles of Flight_FINAL.pptx PPTX
Aerodynamics in Atomotive DOCX
The basic principles behind flight DOCX
The basic principles behind flight PPTX
PDF
Introduction to aeronautical engineering.pdf PPTX
Forces acting in an airplane edwin pitty s. Recently uploaded
PDF
HubbleRevealsComplexMultiscaleStructureintheEdge-onProtoplanetaryDisk IRAS230... PPT
Fractures_of_upper_extremity.ppt589874417 PPTX
Dengue infection by Krutika Gulvi.pptx microbiology department Maharashtra PDF
Directional Searching for Light Dark Matter with Quantum Sensors PPTX
Cancer Biology (Introduction, features of cancer cells, properties of tumor c... PDF
TheFirstTripleRadioActiveGalacticNucleus inanOngoingGalaxyMerger PDF
Minimal Ranks, Maximum Confidence: Parameter-efficient Uncertainty Quantifica... PPTX
CHROMOSOME MUTATION: CHROMOSOME REARRANGEMENT, ANEUPLOIDY AND POLYPLOIDY PDF
The First Star-by-star 𝑁-body/Hydrodynamics Simulation of Our Galaxy Coupling... PPTX
Year_7_Food_Digestion_Energy_UK_Science.pptx PPTX
Case presentation on liver abscess of cow.pptx PPTX
Polymerase Chain Reaction Principle Types Applications Limitations PDF
MolecularGasinMajorMergersHostingDualandSingleAGNsat<10kpcNuclear Separations PPTX
lecture 2. classification of reptiles pptx PDF
FormationoftheLittleRedDotsfromtheCoreCollapseofSelf-interactingDarkMatter Halos PPTX
Arthritis 2025 (1) (1) (1) (1) (1) (1) (1) (1) (1) (1) (1) (1) (1) (1) (1) (1... PPTX
NEUROBIOLOGY OF BEHAVIOUR: NEUROLOGICAL ASPECTS OF DRIVE, MOTIVATION, HUNGER,... PPTX
Case presentation on the macrocytic anaemia PPTX
Potts_Spine_With_Radiology_MRI_pptx.pptx PDF
Primordial Black Holes as Seeds for Extremely Overmassive AGN Observed by JWST Lift and Force in aircrafts ................
- 1.
- 2.
What Are Liftand Drag?
Aerodynamic forces in air
Lift: pushes up
Drag: pulls back
Act on moving objects
- 3.
Lift Force –Basic Concept
Acts
perpendicula
r to airflow
Supports
flight
Created by
pressure
difference
Depends on
wing shape
- 4.
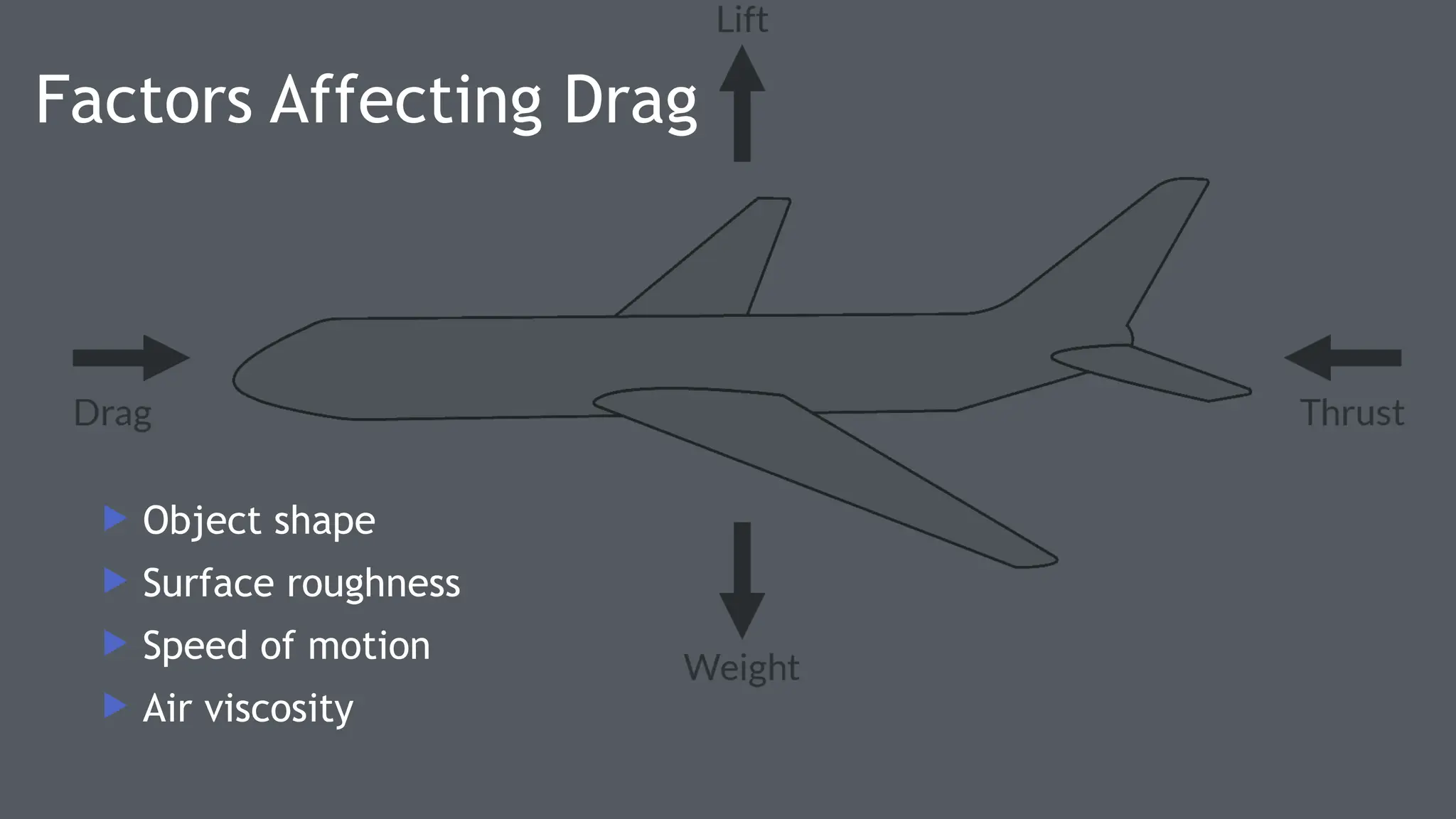
Drag Force –Basic Concept
Opposes
motion
Acts
parallel
to
airflow
Increase
s with
speed
Affected
by shape
and
surface
- 5.
Lift Equation
ρ= Air density
v = Velocity
S = Surface area
CL = Lift coefficient
- 6.
- 7.
- 8.
- 9.
Lift Example
Given:
- Airdensity (ρ) = 1.2 kg/m³
- Velocity (v) = 50 m/s
- Wing area (S) = 20 m²
- Lift coefficient (CL) = 0.5
Formula:
Solution:
L = 0.5 × 1.2 × (50)² × 20 × 0.5 = 0.5 × 1.2 × 2500 × 20 × 0.5
= 15,000 N
- 10.
Drag Example
Given:
- Airdensity (ρ) = 1.2 kg/m³
- Velocity (v) = 50 m/s
- Surface area (S) = 20 m²
- Drag coefficient (CD) = 0.05
Formula:
Solution:
D = 0.5 × 1.2 × (50)² × 20 × 0.05 = 0.5 × 1.2 × 2500 × 20 × 0.05
= 1,500 N
- 11.
- 12.
- 13.