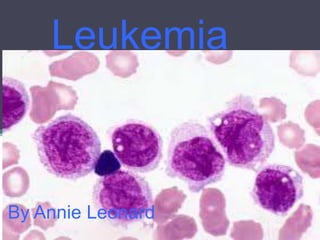
There are four main types of leukemia: acute myeloid leukemia, acute lymphocytic leukemia, chronic myeloid leukemia, and chronic lymphocytic leukemia. Leukemia occurs when cancerous white blood cells fill the bone marrow, preventing healthy blood cell production. Symptoms can include excessive bleeding, fatigue, fever, and swollen organs. Diagnosis involves blood and bone marrow tests. Treatment may include chemotherapy, radiation, stem cell transplants, and biological therapies to try and stop the abnormal cell growth.